
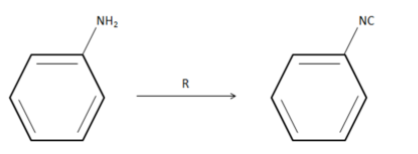
Find the reactant R in the following reaction
(1) ${N_2}$
(2) $CHC{l_3}/KOH(alcoholic)$
(3) $N{H_3}$
(4) $KCN$

Answer
570.3k+ views
Hint:An extra Carbon atom is being substituted so check of options that have a carbon atom in them. Clearly there are no other reagents so the $ - NC$ molecule that is substituted in the place of $ - N{H_2}$ must be from the reaction between aniline and the reactant R.
Complete answer:
Given to us, aniline has to be converted to phenyl isocyanide. When we treat aniline with chloroform in presence of a strong base such as alcoholic $KOH$ in this case, phenyl isocyanide is formed. This reaction is known as carbylamine reaction. In this reaction, first we need to attach a carbon to the Nitrogen of amine group in aniline. So when chloroform reacts with aniline, nitrogen atom is attached to the carbon atom eliminating $HCl$ molecule. When this reaction takes place in the presence of alcoholic $KOH$ we get phenyl isocyanide.
Hence, the reagent R is $CHC{l_3}/KOH(alcoholic)$ i.e. option 2.
Additional information:
Carbylamine reaction is also known as Hofmann isocyanide synthesis. This process involves the formation of isocyanide by the reaction between an aliphatic or an aromatic primary amide, chloroform and a base. Secondary and tertiary amines do not give this reaction.
Note:
In the reaction given to us, a primary amide is being converted to an isocyanide in the presence of a reagent R. This reaction can be explained by carbylamine reaction or Hoffmann isocyanide synthesis. In this reaction a primary amide is treated with chloroform and a strong base to form an isocyanide.
Complete answer:
Given to us, aniline has to be converted to phenyl isocyanide. When we treat aniline with chloroform in presence of a strong base such as alcoholic $KOH$ in this case, phenyl isocyanide is formed. This reaction is known as carbylamine reaction. In this reaction, first we need to attach a carbon to the Nitrogen of amine group in aniline. So when chloroform reacts with aniline, nitrogen atom is attached to the carbon atom eliminating $HCl$ molecule. When this reaction takes place in the presence of alcoholic $KOH$ we get phenyl isocyanide.
Hence, the reagent R is $CHC{l_3}/KOH(alcoholic)$ i.e. option 2.
Additional information:
Carbylamine reaction is also known as Hofmann isocyanide synthesis. This process involves the formation of isocyanide by the reaction between an aliphatic or an aromatic primary amide, chloroform and a base. Secondary and tertiary amines do not give this reaction.
Note:
In the reaction given to us, a primary amide is being converted to an isocyanide in the presence of a reagent R. This reaction can be explained by carbylamine reaction or Hoffmann isocyanide synthesis. In this reaction a primary amide is treated with chloroform and a strong base to form an isocyanide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




