
Find the range of function f(x) where f(x) = ${{e}^{x}}$ in [0, 1].
Answer
621.3k+ views
Hint: We have to first check the continuity of the function in the given interval. Then we have to find the limits of the function at its extreme intervals.
Complete step-by-step answer:
So here we are given a function ${{e}^{x}}$ in [0, 1] and we have to find its range.
First we need to find if this function is continuous in [0, 1].
f (x) = ${{e}^{x}}$
f (0) = ${{e}^{0}}$
= 1
f (1) =${{e}^{1}}$
= e
As the limits exist in the interval and there are no corner points where the function becomes discontinuous, we can say that the function is continuous in the interval [0, 1].
Here the function f(x) = ${{e}^{x}}$ is increasing in nature, which means f(x+1)>f(x).
So f(1) > f(0)
f (0) = ${{e}^{0}}$
= 1
f (1) =${{e}^{1}}$
= e
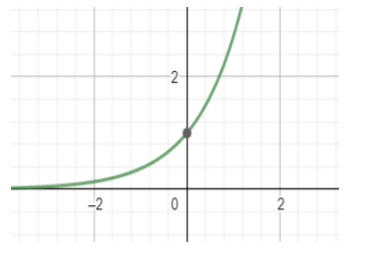
This is the graph of ${{e}^{x}}$. We can see that the function tends to 0 when x tends to -∞. And when x tends to ∞ then the function ${{e}^{x}}$ also tends to infinity. It intersects the y axis at the point (0,1) which means when the value of x = 0 , then the value of the function is 1.
We can see this is an increasing function and it is continuous in the interval [0, 1].
Therefore the range of the function f(x) = ${{e}^{x}}$ is [0, 1]
Note: We must remember the graphs of ${{e}^{x}}$ and ${{e}^{-x}}$ as they are very much important for boards as well as competitive exams. Where ${{e}^{x}}$ is always increasing in nature and on the other hand ${{e}^{-x}}$ is always decreasing in nature. They are also called exponential graphs, which are used to model populations.
Complete step-by-step answer:
So here we are given a function ${{e}^{x}}$ in [0, 1] and we have to find its range.
First we need to find if this function is continuous in [0, 1].
f (x) = ${{e}^{x}}$
f (0) = ${{e}^{0}}$
= 1
f (1) =${{e}^{1}}$
= e
As the limits exist in the interval and there are no corner points where the function becomes discontinuous, we can say that the function is continuous in the interval [0, 1].
Here the function f(x) = ${{e}^{x}}$ is increasing in nature, which means f(x+1)>f(x).
So f(1) > f(0)
f (0) = ${{e}^{0}}$
= 1
f (1) =${{e}^{1}}$
= e

This is the graph of ${{e}^{x}}$. We can see that the function tends to 0 when x tends to -∞. And when x tends to ∞ then the function ${{e}^{x}}$ also tends to infinity. It intersects the y axis at the point (0,1) which means when the value of x = 0 , then the value of the function is 1.
We can see this is an increasing function and it is continuous in the interval [0, 1].
Therefore the range of the function f(x) = ${{e}^{x}}$ is [0, 1]
Note: We must remember the graphs of ${{e}^{x}}$ and ${{e}^{-x}}$ as they are very much important for boards as well as competitive exams. Where ${{e}^{x}}$ is always increasing in nature and on the other hand ${{e}^{-x}}$ is always decreasing in nature. They are also called exponential graphs, which are used to model populations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




