
Find the product B
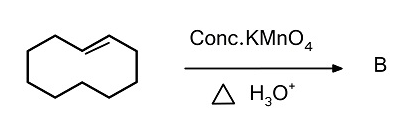
(A)
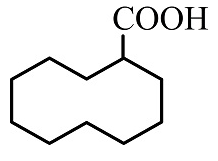
(B)
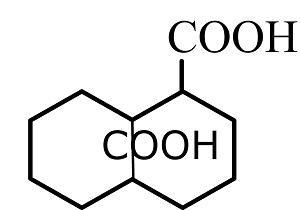
(C)
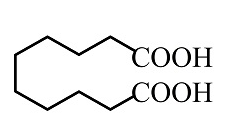
(D)
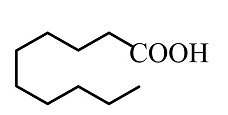





Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: The potassium permanganate is used as an oxidizing agent, which is able to oxidize the carbon atom when a weak bond is present like carbon atoms containing bonds as in alkenes and alkynes.
Complete step by step answer:
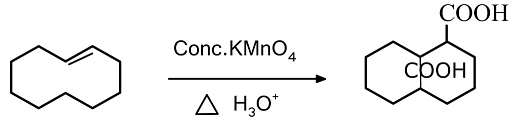
In alkenes under mild condition, potassium permanganate converts alkenes into glycol. It further oxidizes the glycol by breaking the carbon-carbon bond. The cyclic manganese diester is the intermediate product formed in the oxidation of aromatic alkene which results in the formation of glycol which is formed by the syn addition.
By further heating the solution and adding more concentrated potassium permanganate, the glycol can be further oxidized by breaking the carbon-carbon bond.
In this reaction, the oxidation of cyclooctene takes place with the help of potassium permanganate. The reaction is preceded by the attack of lone pairs present in one of the oxygen atoms of $MnO_4^ -$ to the double bond present in the ring. After the attack it forms an intermediate as the $MnO_4^ -$ gets attached to the ring. After that shifting of electrons takes place with the removal of $MnO_2^ -$ and attacking an alcoholic group. Further cleavage of carbon- carbon bond takes place which results in formation of carboxylic groups.
The product formed in this reaction is shown below.
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: The substitution olefins will end up after the formation of ketone. The breaking of carbon – carbon bonds of alkenes to form ketone and carboxylic acid can be used to know the positioning of double bonds in the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
In alkenes under mild condition, potassium permanganate converts alkenes into glycol. It further oxidizes the glycol by breaking the carbon-carbon bond. The cyclic manganese diester is the intermediate product formed in the oxidation of aromatic alkene which results in the formation of glycol which is formed by the syn addition.
By further heating the solution and adding more concentrated potassium permanganate, the glycol can be further oxidized by breaking the carbon-carbon bond.
In this reaction, the oxidation of cyclooctene takes place with the help of potassium permanganate. The reaction is preceded by the attack of lone pairs present in one of the oxygen atoms of $MnO_4^ -$ to the double bond present in the ring. After the attack it forms an intermediate as the $MnO_4^ -$ gets attached to the ring. After that shifting of electrons takes place with the removal of $MnO_2^ -$ and attacking an alcoholic group. Further cleavage of carbon- carbon bond takes place which results in formation of carboxylic groups.
The product formed in this reaction is shown below.

So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: The substitution olefins will end up after the formation of ketone. The breaking of carbon – carbon bonds of alkenes to form ketone and carboxylic acid can be used to know the positioning of double bonds in the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




