
Find the number of geometrical isomers in $[Co(en)(pn){(N{O_2})_2}]$ .
(a) $5$
(b) $3$
(c) $6$
(d) $4$
Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint: First we have to know what are the different types of geometrical isomers of any coordination compound. Then draw the structure, by viewing the structure we can easily know about the structure that will help to find the geometrical isomers.
Complete answer:
Starting from the definition of Geometrical isomerism:
Geometrical isomerism: The isomerism in which the coordination compounds have the same molecular formula, same functional groups but the spatial arrangement of some compounds are different given in the figure below.
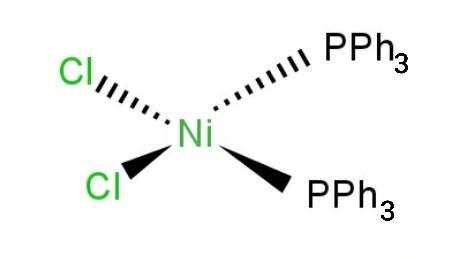
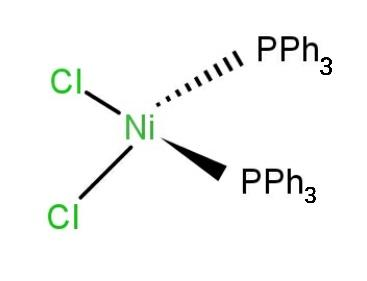
$ \rightleftharpoons $
There are the types of geometrical isomers:
(a) cis and trans isomers.
(b) facial and meridional isomers.
This compound has four geometrical isomers.
Two cis- and trans- , two mer- and fac- and one coordination isomer. But, there are only four geometrical isomers.
Hence, the correct option is (d) $4$ .
Additional information:
There are different types of isomers in the coordination compounds:
(a) Stereoisomers: The molecules having the same chemical formulas and bonds but their spatial arrangement of the atoms are different are called stereoisomers.
(b) Structural isomers: The molecules which have the same chemical formula but the structure is not same, i.e, the arrangement of atoms are not same are called Structural isomers.
(a) Stereoisomers
Types of stereoisomers are:
(a) Geometrical isomers
(b) Optical isomers
(b) Structural isomers
Types of Structural isomers are:
(a) Linkage Isomerism
(b) Coordination Isomerism
(c) Ionization Isomerism
(d) Solvate Isomerism
Note:
Enantiomers and Diastereomers are the types of the stereoisomers, where the enantiomers are the stereoisomers having non-superimposable mirror image of each other whereas the diastereomers are the stereoisomers having non-superimposable mirror image of each other with two or more stereo centres.
Complete answer:
Starting from the definition of Geometrical isomerism:
Geometrical isomerism: The isomerism in which the coordination compounds have the same molecular formula, same functional groups but the spatial arrangement of some compounds are different given in the figure below.


$ \rightleftharpoons $
There are the types of geometrical isomers:
(a) cis and trans isomers.
(b) facial and meridional isomers.
This compound has four geometrical isomers.
Two cis- and trans- , two mer- and fac- and one coordination isomer. But, there are only four geometrical isomers.
Hence, the correct option is (d) $4$ .
Additional information:
There are different types of isomers in the coordination compounds:
(a) Stereoisomers: The molecules having the same chemical formulas and bonds but their spatial arrangement of the atoms are different are called stereoisomers.
(b) Structural isomers: The molecules which have the same chemical formula but the structure is not same, i.e, the arrangement of atoms are not same are called Structural isomers.
(a) Stereoisomers
Types of stereoisomers are:
(a) Geometrical isomers
(b) Optical isomers
(b) Structural isomers
Types of Structural isomers are:
(a) Linkage Isomerism
(b) Coordination Isomerism
(c) Ionization Isomerism
(d) Solvate Isomerism
Note:
Enantiomers and Diastereomers are the types of the stereoisomers, where the enantiomers are the stereoisomers having non-superimposable mirror image of each other whereas the diastereomers are the stereoisomers having non-superimposable mirror image of each other with two or more stereo centres.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




