
Find the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs of lengths 5 and 12 ?
Answer
552.9k+ views
Hint: Pythagoras theorem: For a right angled triangle the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
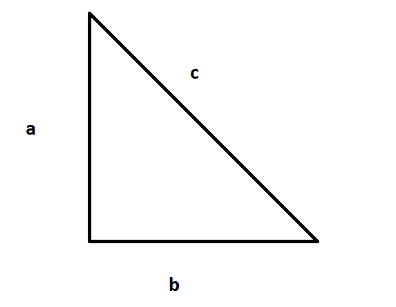
So on applying Pythagoras theorem to the above triangle we can write:
\[
{a^2} + {b^2} = {c^2} \\
\Rightarrow {c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} \\
\]
Also we can find the hypotenuse of the triangle by the equation:
\[c = \sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} \]
So by using the above equation and substituting the values $a\;{\text{and}}\;b$ we can find the value of the hypotenuse.
Complete step by step solution:
Given
Legs of lengths 5 and 12
\[ \Rightarrow a = 5\;{\text{and}}\;b = 12..........................\left( i \right)\]
Now using this value we can draw a right angled triangle as below:
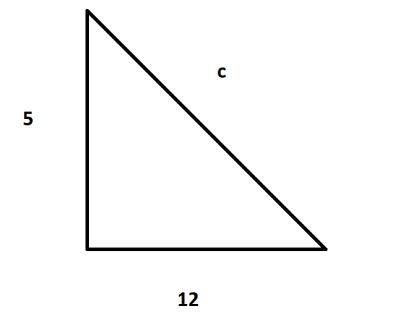
Now we need to find the hypotenuse such that we need to find the value of $c$:
So on applying Pythagoras theorem to the above triangle we can write:
\[
{a^2} + {b^2} = {c^2} \\
\Rightarrow {c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} \\
\]
Now in order to find the value of$c$we need to take root of the LHS:
\[c = \sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} .............................\left( {ii} \right)\]
Now we have the values: \[a = 5\;{\text{and}}\;b = 12\]
Substituting the above values in (ii) we can write:
\[
c = \sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} \\
\Rightarrow c = \sqrt {{{\left( 5 \right)}^2} + {{\left( {12} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow c = \sqrt {25 + 144} \\
\Rightarrow c = \sqrt {169} \\
\Rightarrow c = 13 \\
\]
Therefore length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs of lengths \[5\;{\text{and}}\;{\text{1}}2\;{\text{is}}\;13\].
Additional Information:
There are two types of Right angled triangle:
1. Isosceles Right angled triangle.
2. Scalene Right angled triangle.
Also in a right angled triangle the sum of the three angles is ${180^ \circ }$.
Note: Here care must be taken while taking the roots of different numbers. One of the most useful and widely used shapes in mathematics is the right angled triangle. It’s not only used in the Pythagoras theorem but also has a large area of development in the field of trigonometry consisting of sine, cosine, tangent etc.

So on applying Pythagoras theorem to the above triangle we can write:
\[
{a^2} + {b^2} = {c^2} \\
\Rightarrow {c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} \\
\]
Also we can find the hypotenuse of the triangle by the equation:
\[c = \sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} \]
So by using the above equation and substituting the values $a\;{\text{and}}\;b$ we can find the value of the hypotenuse.
Complete step by step solution:
Given
Legs of lengths 5 and 12
\[ \Rightarrow a = 5\;{\text{and}}\;b = 12..........................\left( i \right)\]
Now using this value we can draw a right angled triangle as below:

Now we need to find the hypotenuse such that we need to find the value of $c$:
So on applying Pythagoras theorem to the above triangle we can write:
\[
{a^2} + {b^2} = {c^2} \\
\Rightarrow {c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} \\
\]
Now in order to find the value of$c$we need to take root of the LHS:
\[c = \sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} .............................\left( {ii} \right)\]
Now we have the values: \[a = 5\;{\text{and}}\;b = 12\]
Substituting the above values in (ii) we can write:
\[
c = \sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} \\
\Rightarrow c = \sqrt {{{\left( 5 \right)}^2} + {{\left( {12} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow c = \sqrt {25 + 144} \\
\Rightarrow c = \sqrt {169} \\
\Rightarrow c = 13 \\
\]
Therefore length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs of lengths \[5\;{\text{and}}\;{\text{1}}2\;{\text{is}}\;13\].
Additional Information:
There are two types of Right angled triangle:
1. Isosceles Right angled triangle.
2. Scalene Right angled triangle.
Also in a right angled triangle the sum of the three angles is ${180^ \circ }$.
Note: Here care must be taken while taking the roots of different numbers. One of the most useful and widely used shapes in mathematics is the right angled triangle. It’s not only used in the Pythagoras theorem but also has a large area of development in the field of trigonometry consisting of sine, cosine, tangent etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




