
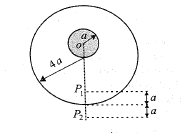
Find the gravitational field intensity at point ${P_1}$ .
A.$\dfrac{{GM}}{{16{a^2}}}$
B.$\dfrac{{GM}}{{8{a^2}}}$
C.$\dfrac{{GM}}{{2{a^2}}}$
D.$\dfrac{{GM}}{{4{a^2}}}$

Answer
597k+ views
Hint: To solve this type of problem firstly we should understand about Gravitational Field, Gravitational field intensity and the concept behind these terms. We will study all the related information as well. And by using this information we can easily approach our answer.
Complete answer:
Gravitational Field: It is the region of space which surrounds a body in which another body incident a force of gravitational attraction.
Gravitational Field Intensity: It is defined as gravitational force per unit mass. Gravitational field intensity at any point is defined as negative of the gradient of gravitational potential at a point.
${E_g} = F/m$
Or, ${E_g} = - \left[ {GMm/{r^2}} \right]\,/m\,\mathop r\limits^ \wedge $
$ \Rightarrow $ Gravitational field Intensity$\left( {Eg} \right) = - GM/{r^2}\mathop r\limits^ \wedge $
Where $\mathop r\limits^ \wedge $ represent the unit vector along the radial direction,$\mathop r\limits^ \to = x\mathop i\limits^ \wedge + y\mathop j\limits^ \wedge + z\mathop k\limits^ \wedge $ represents the position vector of the test mass from the source mass. The gravitational field intensity depends only upon the source mass and the distance of unit test mass from the source mass. The gravitational field intensity is having unit $N/kg$ . The dimensional formula is given by$\left[ {{M^0}{L^1}{T^{ - 2}}} \right]$ .The dimensional formula of gravitational field intensity is similar to the acceleration (preferably we call it as acceleration due to gravity from the view of gravitation.)
Field at point ${P_1}$ due to the superposition of inner and outer spheres,
Gravitational field intensity of a point mass
${E_g} = - GM/{r^2}\,\mathop r\limits^ \wedge $
Gravitational Field Intensity due to Ring
$dE = Gdm/{r^2}$
So,${g_1} = \dfrac{{GM}}{{{{\left( {4a} \right)}^2}}} = \dfrac{{GM}}{{16{a^2}}}$
The field inside a shell is constant.
So, the correct answer is option A - $\dfrac{{GM}}{{16{a^2}}}$
Note: Gravitational field intensity states that, if we bring a unit test mass from intensity to a gravitational field, then the gravitational force acted on that unit test mass due to a comparable bigger mass for which the gravitational field is created is called gravitational field intensity.
Complete answer:
Gravitational Field: It is the region of space which surrounds a body in which another body incident a force of gravitational attraction.
Gravitational Field Intensity: It is defined as gravitational force per unit mass. Gravitational field intensity at any point is defined as negative of the gradient of gravitational potential at a point.
${E_g} = F/m$
Or, ${E_g} = - \left[ {GMm/{r^2}} \right]\,/m\,\mathop r\limits^ \wedge $
$ \Rightarrow $ Gravitational field Intensity$\left( {Eg} \right) = - GM/{r^2}\mathop r\limits^ \wedge $
Where $\mathop r\limits^ \wedge $ represent the unit vector along the radial direction,$\mathop r\limits^ \to = x\mathop i\limits^ \wedge + y\mathop j\limits^ \wedge + z\mathop k\limits^ \wedge $ represents the position vector of the test mass from the source mass. The gravitational field intensity depends only upon the source mass and the distance of unit test mass from the source mass. The gravitational field intensity is having unit $N/kg$ . The dimensional formula is given by$\left[ {{M^0}{L^1}{T^{ - 2}}} \right]$ .The dimensional formula of gravitational field intensity is similar to the acceleration (preferably we call it as acceleration due to gravity from the view of gravitation.)
Field at point ${P_1}$ due to the superposition of inner and outer spheres,
Gravitational field intensity of a point mass
${E_g} = - GM/{r^2}\,\mathop r\limits^ \wedge $
Gravitational Field Intensity due to Ring
$dE = Gdm/{r^2}$
So,${g_1} = \dfrac{{GM}}{{{{\left( {4a} \right)}^2}}} = \dfrac{{GM}}{{16{a^2}}}$
The field inside a shell is constant.
So, the correct answer is option A - $\dfrac{{GM}}{{16{a^2}}}$
Note: Gravitational field intensity states that, if we bring a unit test mass from intensity to a gravitational field, then the gravitational force acted on that unit test mass due to a comparable bigger mass for which the gravitational field is created is called gravitational field intensity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




