
Find the equation of the bisector of the angle $A$ of the triangle whose vertices are $A\left( {4,3} \right)$, $B\left( {0,0} \right)$ and \[C\left( {2,3} \right)\].
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: We will first draw the diagram for the corresponding conditions. Let $AM$ be the angle bisector angle $A$. Then, find the coordinates of $M$ using the property of angle bisector and section formula. Then, find the equation of line $AM$ from the coordinates of $A$ and $M$.
Complete step by step solution: We are given that the coordinates of vertices of a triangle are $A\left( {4,3} \right)$, $B\left( {0,0} \right)$ and \[C\left( {2,3} \right)\]
Let $AM$ be the angle bisector of angle $A$
We will first draw the corresponding figure.
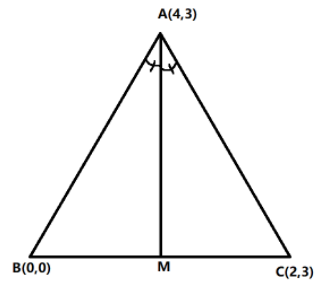
Since $AM$ is an angle bisector, then $AM$ divides the opposite sides of the triangle into two segments which are proportional to the distance of the other two sides.
That is, $AM$ divides $BC$ in the ratio of $AB: AC$
Hence, $AB:AC = AM:MC$
Now, let us find the distance $AB$ and the distance $AC$ using the distance formula,
If \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] are coordinates of two points, then distance between them is calculated as \[\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} \]
$
AB = \sqrt {{{\left( {4 - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {3 - 0} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow AB = \sqrt {16 + 9} \\
\Rightarrow AB = \sqrt {25} \\
\Rightarrow AB = 5 \\
$
Similarly the distance of $AC$ is,
$
AC = \sqrt {{{\left( {4 - 2} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {3 - 3} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow AC = \sqrt {4 + 0} \\
\Rightarrow AC = \sqrt 4 \\
\Rightarrow AC = 2 \\
$
Thus, the ratio of $AB: AC$ is 5:2 which is also equal to $AM: MC$.
We shall now find the coordinates of $M$ using section formula,
Section formula states that, if \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] are coordinates of two points and they are divided by the point $\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)$ in $m:n$,
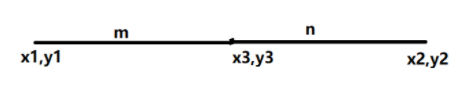
then the coordinates of $\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)$ are $\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{m{x_2} + n{x_1}}}{{m + n}},\dfrac{{m{y_2} + n{y_1}}}{{m + n}}} \right)$
Therefore, the coordinates of $M$ can be calculated as,
$
M = \left( {\dfrac{{\left( 5 \right)2 + \left( 2 \right)0}}{{5 + 2}},\dfrac{{\left( 5 \right)3 + \left( 2 \right)0}}{{5 + 2}}} \right) \\
M = \left( {\dfrac{{10}}{7},\dfrac{{15}}{7}} \right) \\
$
Next, we will find the equation of line $AM$ using the points $A\left( {4,3} \right)$ and $\left( {\dfrac{{10}}{7},\dfrac{{15}}{7}} \right)$
If \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] are coordinates of two points, then the equation of line is given as,
\[y - {y_1} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)\]
Therefore, equation of $AM$is
$
y - \dfrac{{15}}{7} = \dfrac{{3 - \dfrac{{15}}{7}}}{{4 - \dfrac{{10}}{7}}}\left( {x - \dfrac{{10}}{7}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow y - \dfrac{{15}}{7} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{6}{7}}}{{\dfrac{{18}}{7}}}\left( {x - \dfrac{{10}}{7}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow y - \dfrac{{15}}{7} = \dfrac{1}{3}\left( {x - \dfrac{{10}}{7}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow 3y - \dfrac{{45}}{7} = x - \dfrac{{10}}{7} \\
\Rightarrow 3y - x - \dfrac{{45}}{7} + \dfrac{{10}}{7} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 3y - x - \dfrac{{35}}{7} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 3y - x - 5 = 0 \\
$
Hence, the equation of the bisector of the angle $A$ of the triangle whose vertices are $A\left( {4,3} \right)$, $B\left( {0,0} \right)$ and \[C\left( {2,3} \right)\] is \[3y - x - 5 = 0\].
Note: Section formula is used to find the coordinates of the point when the point divides the line joined by two points in a certain ratio. If the point $\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)$ divides the line internally joined by the points, \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\], then the coordinates of the point is given as $\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{m{x_2} + n{x_1}}}{{m + n}},\dfrac{{m{y_2} + n{y_1}}}{{m + n}}} \right)$. But, if the point $\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)$ divides the line externally, then the coordinates of the point is given as $\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{m{x_2} - n{x_1}}}{{m - n}},\dfrac{{m{y_2} - n{y_1}}}{{m - n}}} \right)$
Complete step by step solution: We are given that the coordinates of vertices of a triangle are $A\left( {4,3} \right)$, $B\left( {0,0} \right)$ and \[C\left( {2,3} \right)\]
Let $AM$ be the angle bisector of angle $A$
We will first draw the corresponding figure.

Since $AM$ is an angle bisector, then $AM$ divides the opposite sides of the triangle into two segments which are proportional to the distance of the other two sides.
That is, $AM$ divides $BC$ in the ratio of $AB: AC$
Hence, $AB:AC = AM:MC$
Now, let us find the distance $AB$ and the distance $AC$ using the distance formula,
If \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] are coordinates of two points, then distance between them is calculated as \[\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} \]
$
AB = \sqrt {{{\left( {4 - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {3 - 0} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow AB = \sqrt {16 + 9} \\
\Rightarrow AB = \sqrt {25} \\
\Rightarrow AB = 5 \\
$
Similarly the distance of $AC$ is,
$
AC = \sqrt {{{\left( {4 - 2} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {3 - 3} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow AC = \sqrt {4 + 0} \\
\Rightarrow AC = \sqrt 4 \\
\Rightarrow AC = 2 \\
$
Thus, the ratio of $AB: AC$ is 5:2 which is also equal to $AM: MC$.
We shall now find the coordinates of $M$ using section formula,
Section formula states that, if \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] are coordinates of two points and they are divided by the point $\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)$ in $m:n$,

then the coordinates of $\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)$ are $\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{m{x_2} + n{x_1}}}{{m + n}},\dfrac{{m{y_2} + n{y_1}}}{{m + n}}} \right)$
Therefore, the coordinates of $M$ can be calculated as,
$
M = \left( {\dfrac{{\left( 5 \right)2 + \left( 2 \right)0}}{{5 + 2}},\dfrac{{\left( 5 \right)3 + \left( 2 \right)0}}{{5 + 2}}} \right) \\
M = \left( {\dfrac{{10}}{7},\dfrac{{15}}{7}} \right) \\
$
Next, we will find the equation of line $AM$ using the points $A\left( {4,3} \right)$ and $\left( {\dfrac{{10}}{7},\dfrac{{15}}{7}} \right)$
If \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] are coordinates of two points, then the equation of line is given as,
\[y - {y_1} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)\]
Therefore, equation of $AM$is
$
y - \dfrac{{15}}{7} = \dfrac{{3 - \dfrac{{15}}{7}}}{{4 - \dfrac{{10}}{7}}}\left( {x - \dfrac{{10}}{7}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow y - \dfrac{{15}}{7} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{6}{7}}}{{\dfrac{{18}}{7}}}\left( {x - \dfrac{{10}}{7}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow y - \dfrac{{15}}{7} = \dfrac{1}{3}\left( {x - \dfrac{{10}}{7}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow 3y - \dfrac{{45}}{7} = x - \dfrac{{10}}{7} \\
\Rightarrow 3y - x - \dfrac{{45}}{7} + \dfrac{{10}}{7} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 3y - x - \dfrac{{35}}{7} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 3y - x - 5 = 0 \\
$
Hence, the equation of the bisector of the angle $A$ of the triangle whose vertices are $A\left( {4,3} \right)$, $B\left( {0,0} \right)$ and \[C\left( {2,3} \right)\] is \[3y - x - 5 = 0\].
Note: Section formula is used to find the coordinates of the point when the point divides the line joined by two points in a certain ratio. If the point $\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)$ divides the line internally joined by the points, \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\], then the coordinates of the point is given as $\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{m{x_2} + n{x_1}}}{{m + n}},\dfrac{{m{y_2} + n{y_1}}}{{m + n}}} \right)$. But, if the point $\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)$ divides the line externally, then the coordinates of the point is given as $\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{m{x_2} - n{x_1}}}{{m - n}},\dfrac{{m{y_2} - n{y_1}}}{{m - n}}} \right)$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




