
Find the equation and the length of the common chord of the following circles:
\[{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} + 2{\text{x + 2y + 1 = 0}}\] & \[{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} + 4{\text{x + 3y + 2 = 0}}\]
Answer
619.5k+ views
Hint: Here we will be using the equation of common chord which is ${\text{S - }}{{\text{S}}_1}{\text{ = 0}}$ along with the concept of how to find the perpendicular distance from a single point to a straight line.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that
The equation of the common chord is given by ${\text{S - }}{{\text{S}}_1}{\text{ = 0}}$, Where are two circles.
\[{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} + 2{\text{x + 2y + 1 = 0}}\] & \[{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} + 4{\text{x + 3y + 2 = 0}}\] respectively.
Here we are just representing the equation of circle \[{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} + 2{\text{x + 2y + 1 = 0}}\] by S and \[{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} + 4{\text{x + 3y + 2 = 0}}\] by ${{\text{S}}_1}$
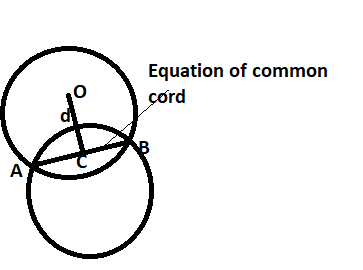
⟹ on applying the result S−S1=0
⟹\[\left( {{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} + 2{\text{x + 2y + 1}}} \right){\text{ - }}\left( {{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} + 4{\text{x + 3y + 2}}} \right) = 0\]
i.e., 2x+y+1=0
On subtracting the equation of circle S and ${{\text{S}}_1}$ we get the equation of the common chord which is 2x+y+1=0
Equation of 1st circle S= \[{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} + 2{\text{x + 2y + 1 = 0}}\]
General equation of circle is \[{\text{a}}{{\text{x}}^2} + {\text{b}}{{\text{y}}^2} + 2g{\text{x + 2hy + c = 0}}\]
Center of S=0 is (−g, −f)
So on comparing General equation of circle with equation of 1st circle
Center of S=0 is (−1, −1) which is coordinate of Point O
We know the formula of Radius of circle which is $\sqrt {{{\text{g}}^2} + {{\text{f}}^2} - {\text{c}}} $
Radius OB =\[\sqrt {{{( - 1)}^2} + {{( - 1)}^2} - 1} \]
Radius OB (r) = 1cm
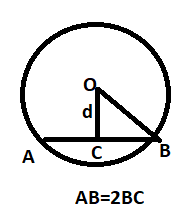
Length of the perpendicular OC represented by d in shown figure from the center is given by,
${\text{d = }}\left| {\dfrac{{{\text{ax + by + c}}}}{{\sqrt {{{\text{a}}^2} + {{\text{b}}^2}} }}} \right|$
∴ If O (−1, −1) is the center, so to find the length of the perpendicular to the chord,
In the above formula, put coordinates of O which is the center of the circle, in place of x & y. From the equation of the common chord which is 2x+y+1=0 so, a=2, b=1 and c=1
On putting all values in above formula
${\text{d = }}\left| {\dfrac{{{\text{2( - 1) + 1( - 1) + 1}}}}{{\sqrt {{2^2} + {1^2}} }}} \right|$
${\text{d = }}\left| {\dfrac{{\text{2}}}{{\sqrt 5 }}} \right|$
${\text{d = }}\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 5 }}$
Length of the Chord AB is $2\sqrt {{{\text{r}}^2} - {{\text{d}}^2}} $. Which we can also find by Pythagoras theorem.
=$2\sqrt {{1^2} - {{\left( {\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 5 }}} \right)}^2}} $
= $2\sqrt {1 - \dfrac{4}{5}} $
= $2\sqrt {\dfrac{1}{5}} $
So length of the common chord = $\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 5 }}$
Note: Whenever we came up with this type of problem where we are given the equation of circles or straight line, first make clear diagram then apply the available results like here we used equation of common chord and use different basic concept like perpendicular distance from a single point and Pythagoras theorem to find distance.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that
The equation of the common chord is given by ${\text{S - }}{{\text{S}}_1}{\text{ = 0}}$, Where are two circles.
\[{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} + 2{\text{x + 2y + 1 = 0}}\] & \[{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} + 4{\text{x + 3y + 2 = 0}}\] respectively.
Here we are just representing the equation of circle \[{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} + 2{\text{x + 2y + 1 = 0}}\] by S and \[{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} + 4{\text{x + 3y + 2 = 0}}\] by ${{\text{S}}_1}$

⟹ on applying the result S−S1=0
⟹\[\left( {{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} + 2{\text{x + 2y + 1}}} \right){\text{ - }}\left( {{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} + 4{\text{x + 3y + 2}}} \right) = 0\]
i.e., 2x+y+1=0
On subtracting the equation of circle S and ${{\text{S}}_1}$ we get the equation of the common chord which is 2x+y+1=0
Equation of 1st circle S= \[{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} + 2{\text{x + 2y + 1 = 0}}\]

General equation of circle is \[{\text{a}}{{\text{x}}^2} + {\text{b}}{{\text{y}}^2} + 2g{\text{x + 2hy + c = 0}}\]
Center of S=0 is (−g, −f)
So on comparing General equation of circle with equation of 1st circle
Center of S=0 is (−1, −1) which is coordinate of Point O
We know the formula of Radius of circle which is $\sqrt {{{\text{g}}^2} + {{\text{f}}^2} - {\text{c}}} $
Radius OB =\[\sqrt {{{( - 1)}^2} + {{( - 1)}^2} - 1} \]
Radius OB (r) = 1cm
Length of the perpendicular OC represented by d in shown figure from the center is given by,
${\text{d = }}\left| {\dfrac{{{\text{ax + by + c}}}}{{\sqrt {{{\text{a}}^2} + {{\text{b}}^2}} }}} \right|$
∴ If O (−1, −1) is the center, so to find the length of the perpendicular to the chord,
In the above formula, put coordinates of O which is the center of the circle, in place of x & y. From the equation of the common chord which is 2x+y+1=0 so, a=2, b=1 and c=1
On putting all values in above formula
${\text{d = }}\left| {\dfrac{{{\text{2( - 1) + 1( - 1) + 1}}}}{{\sqrt {{2^2} + {1^2}} }}} \right|$
${\text{d = }}\left| {\dfrac{{\text{2}}}{{\sqrt 5 }}} \right|$
${\text{d = }}\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 5 }}$
Length of the Chord AB is $2\sqrt {{{\text{r}}^2} - {{\text{d}}^2}} $. Which we can also find by Pythagoras theorem.
=$2\sqrt {{1^2} - {{\left( {\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 5 }}} \right)}^2}} $
= $2\sqrt {1 - \dfrac{4}{5}} $
= $2\sqrt {\dfrac{1}{5}} $
So length of the common chord = $\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 5 }}$
Note: Whenever we came up with this type of problem where we are given the equation of circles or straight line, first make clear diagram then apply the available results like here we used equation of common chord and use different basic concept like perpendicular distance from a single point and Pythagoras theorem to find distance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




