
How can I find the chiral centers in the ring structure?
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint Ring structures are those in which there is no straight chain, there is a closed system, and this closed system can have single bonds and multiple bonds. Chiral center means the carbon atom in the system that has all the different substituents.
Complete step by step answer:
Ring structures are those in which there is no straight chain, there is a closed system, and this closed system can have single bonds and multiple bonds. So, cyclohexane is a ring structure and it has only single bonds.
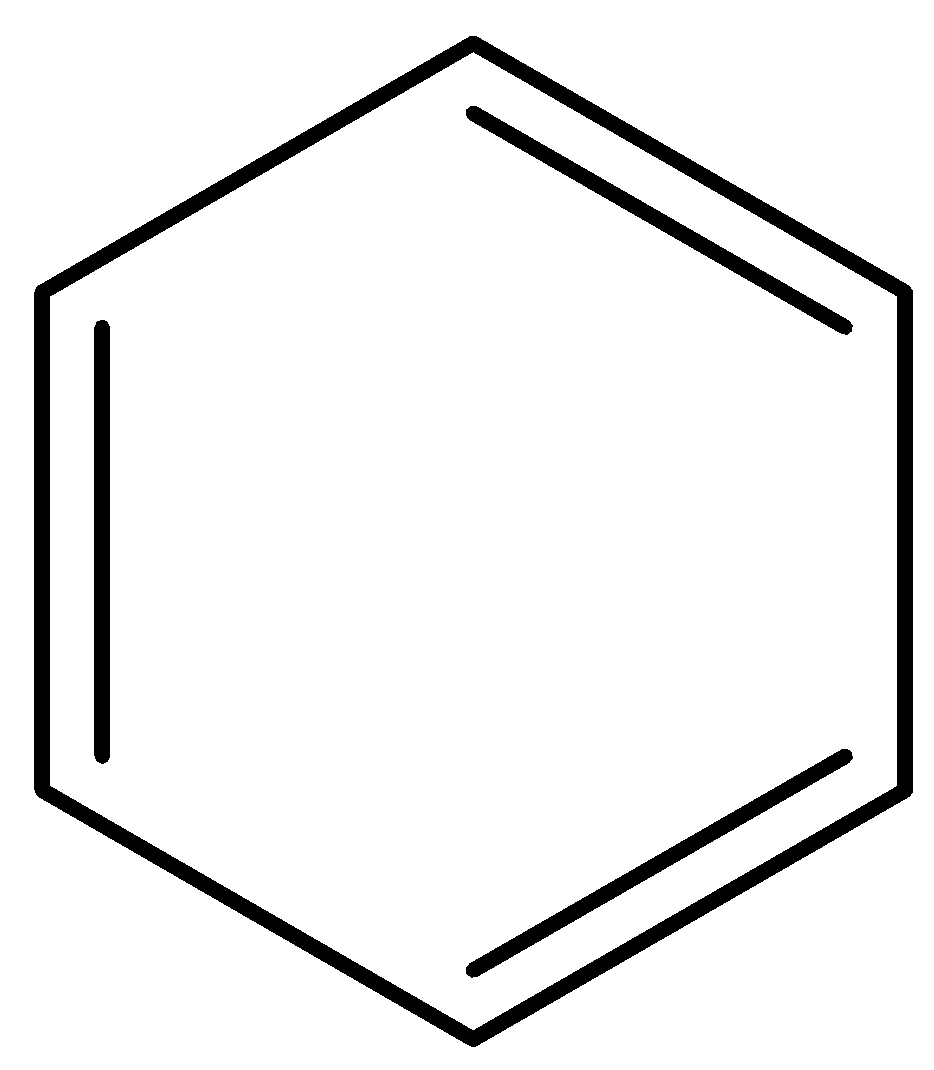
Benzene is also a ring structure having a multiple bond system i.e., double bonds. It is given below:
Chiral center means the carbon atom in the system that has all the different substituents. So, in the ring structure, we have to find which carbon atom is attached to four different compounds or elements.
This can be explained with an example. Let us take 2-aminocyclohexanol, in this structure, there is a ring of 6 carbon atoms, the first carbon atom has a hydroxyl group and the second carbon atom has an amine group. This is given below:
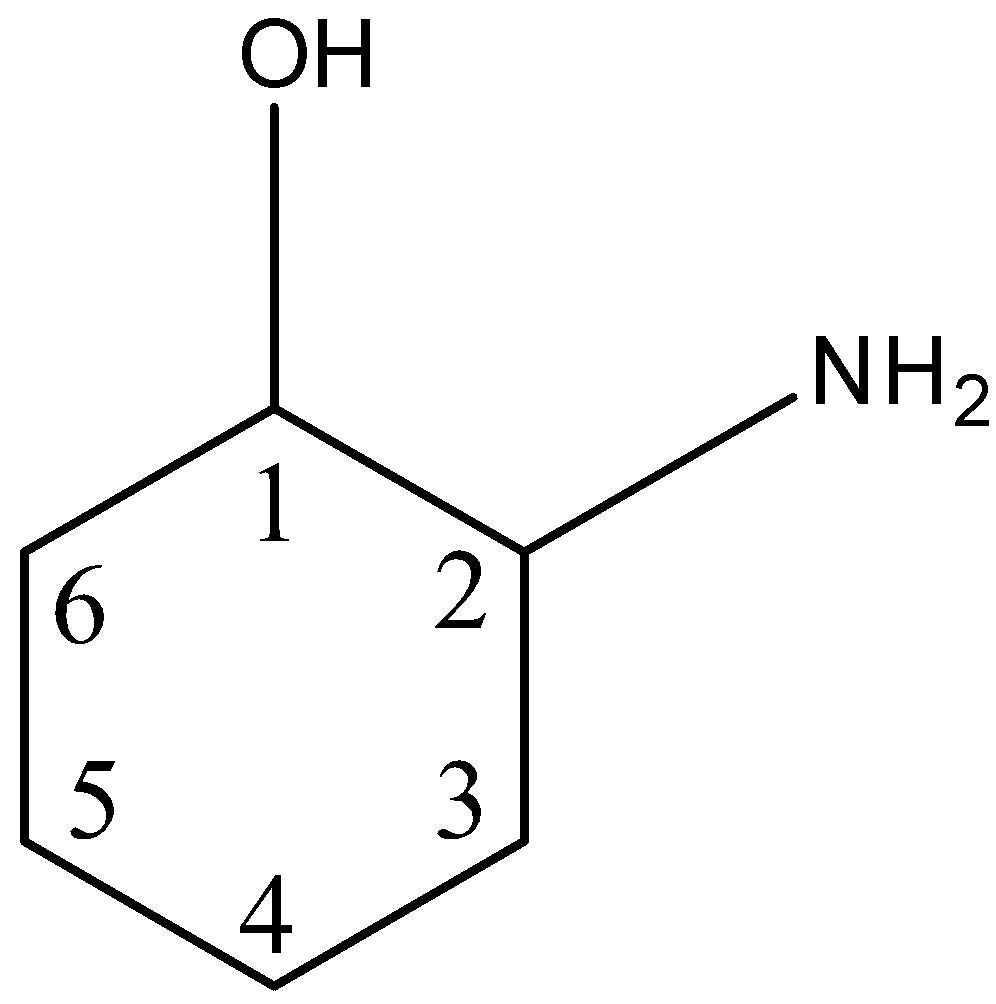
So, in this structure, there are two chiral centers i.e., the 1st carbon atom and the 2nd carbon atom. The first carbon atom has four different substituents: a hydrogen atom, hydroxyl group, carbon atom of the ring having no substituent (${{C}_{6}}$), and the carbon atom of the ring having ammine as a substituent (${{C}_{2}}$).
The second atom has four different substituents: a hydrogen atom, amine group, carbon atom of the ring having no substituent (${{C}_{3}}$), and the carbon atom of the ring having hydroxyl as a substituent (${{C}_{1}}$).
In this way, we can find the chiral centers in the ring system.
Note: Due to this chiral center, the compound can rotate the plane-polarized light and shows optical activity. The carbon atoms having double and triple bonds cannot be chiral centers in any compound.
Complete step by step answer:
Ring structures are those in which there is no straight chain, there is a closed system, and this closed system can have single bonds and multiple bonds. So, cyclohexane is a ring structure and it has only single bonds.

Benzene is also a ring structure having a multiple bond system i.e., double bonds. It is given below:

Chiral center means the carbon atom in the system that has all the different substituents. So, in the ring structure, we have to find which carbon atom is attached to four different compounds or elements.
This can be explained with an example. Let us take 2-aminocyclohexanol, in this structure, there is a ring of 6 carbon atoms, the first carbon atom has a hydroxyl group and the second carbon atom has an amine group. This is given below:

So, in this structure, there are two chiral centers i.e., the 1st carbon atom and the 2nd carbon atom. The first carbon atom has four different substituents: a hydrogen atom, hydroxyl group, carbon atom of the ring having no substituent (${{C}_{6}}$), and the carbon atom of the ring having ammine as a substituent (${{C}_{2}}$).
The second atom has four different substituents: a hydrogen atom, amine group, carbon atom of the ring having no substituent (${{C}_{3}}$), and the carbon atom of the ring having hydroxyl as a substituent (${{C}_{1}}$).
In this way, we can find the chiral centers in the ring system.
Note: Due to this chiral center, the compound can rotate the plane-polarized light and shows optical activity. The carbon atoms having double and triple bonds cannot be chiral centers in any compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




