
Find the capacity in liters of the conical vessel with
A) Radius 7 cm, slant height 25 cm
B) Height 12 cm, slant height 13 cm
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: Capacity of objects implies the volume of that object.
The given question can be directly solved by using the formula of the given object.
For reference, the volume of a cone \[ = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \mathop r\nolimits^2 h{\text{ }}cubic{\text{ }}units\] .
Here, r is the base radius of the cone; h is the perpendicular height of the cone.
Assume $\pi = \dfrac{{22}}{7}$ , unless stated otherwise.
Unit conversion can easily be done by the unitary method.
The unitary method is a technique for solving a problem by first finding the value of a single unit, and then finding the necessary value by multiplying the single unit value.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step 1: Relation between base radius, slant height, and height of the cone
Let base radius of cone is denoted by r
The slant height of cone is denoted by l
And height of cone is denoted by h
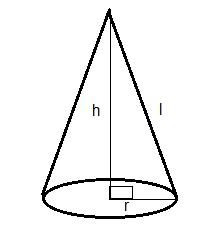
Base radius and height fall perpendicular to each other, i.e., the angle between them is ${90^ \circ }$.
Thus, a radius of length r cm, a height of length h cm, and a slant height of length l cm of the cone form a right-angled triangle.
Therefore, by applying Pythagoras theorem:
Pythagoras theorem: square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the square of base and square of perpendicular.
In a right-angled triangle, the base and perpendicular are at the angle of $90^\circ $ each other and hypotenuse is the longest side.
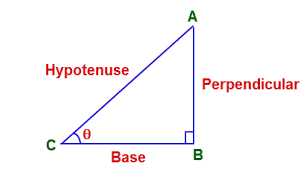
$\mathop {{\text{Hypotenuse}}}\nolimits^{\text{2}} {\text{ = }}\mathop {{\text{ Base}}}\nolimits^{{\text{2 }}} {\text{ + }}\mathop {{\text{ Perpendicular}}}\nolimits^{\text{2}} $
$\because \mathop {{\text{ slant height}}}\nolimits^2 = \mathop {{\text{radius}}}\nolimits^2 + \mathop {{\text{height}}}\nolimits^2 $
$ \Rightarrow {\text{ }}\mathop l\nolimits^2 = \mathop r\nolimits^2 + \mathop h\nolimits^2 $
This relationship can be directly use if one of the parameter among $l,{\text{ }}r,{\text{ and }}h$ is unknown.
Step 2: Volume calculations
Given that:
Radius, r = 7 cm
Slant height, l = 25 cm
For calculation of volume of cone base radius and height of cone should be known.
We know, ${\text{ }}\mathop l\nolimits^2 = \mathop r\nolimits^2 + \mathop h\nolimits^2 $
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{ }}\mathop {25}\nolimits^2 = \mathop 7\nolimits^2 + \mathop h\nolimits^2 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ 625}} = 49 + \mathop h\nolimits^2 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }}\mathop h\nolimits^2 = 625 - 49 = 576 \\
\Rightarrow h = \sqrt {576} \\
\]
Hence, height, $h = 24{\text{ cm}}$
Volume of cone \[ = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \mathop r\nolimits^2 h{\text{ }}cubic{\text{ }}units\]
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times \mathop 7\nolimits^2 \times {\text{24}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{1232 }}\mathop {{\text{cm}}}\nolimits^3 \\
\]
Given that:
Height, h = 12 cm
Slant height, l = 13 cm
For calculation of volume of cone base radius and height of cone should be known.
We know, ${\text{ }}\mathop l\nolimits^2 = \mathop r\nolimits^2 + \mathop h\nolimits^2 $
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{ }}\mathop {13}\nolimits^2 = \mathop r\nolimits^2 + \mathop {12}\nolimits^2 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ 169}} = \mathop r\nolimits^2 + 144 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }}\mathop r\nolimits^2 = 169 - 144 = 25 \\
\Rightarrow r = \sqrt {25} \\
\]
Hence, radius, $r = 5{\text{ cm}}$
Volume of cone \[ = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \mathop r\nolimits^2 h{\text{ }}cubic{\text{ }}units\]
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times \mathop 5\nolimits^2 \times 12 \\
\Rightarrow 314.28{\text{ }}\mathop {{\text{cm}}}\nolimits^3 \\
\]
Step 3: Convert the cubic centimeters into liters.
We know, 1 cubic meter = 1000 liters
Also, 1 cubic meter $ = {10^6}$ cubic centimeters
Hence, ${10^6}$cubic centimeters = 1000 litres
So, 1 cubic centimeter $ = \dfrac{{1000}}{{{{10}^6}}}$ liters
$ = \dfrac{1}{{1000}}$ or 0.001 liters
Therefore, \[{\text{1232 c}}{{\text{m}}^3} = 1232 \times 0.001{\text{ liters}}\]
$ \Rightarrow 1.232{\text{ liters}}$
Therefore, \[{\text{314}}{\text{.28 c}}{{\text{m}}^3} = 314.28 \times 0.001{\text{ liters}}\]
$ \Rightarrow 0.314{\text{ liters}}$
Final answer: The capacity of conical vessels in (i) is $1.232{\text{ liters}}$ and in (ii) is $0.314{\text{ liters}}$.
Note: The mensuration formulae for 3-dimensional objects are only for right circular objects i.e. its axis is perpendicular to the center of the base.
Volumes of other important objects:
The volume of the right circular cylinder \[ = \pi \mathop r\nolimits^2 h{\text{ }}cubic{\text{ }}units\]
where r is the base radius and h is the height of the cylinder.
Volume of sphere $ = \dfrac{4}{3}\pi \mathop r\nolimits^3 {\text{ cubic units}}$
where r is the radius of the sphere.
The given question can be directly solved by using the formula of the given object.
For reference, the volume of a cone \[ = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \mathop r\nolimits^2 h{\text{ }}cubic{\text{ }}units\] .
Here, r is the base radius of the cone; h is the perpendicular height of the cone.
Assume $\pi = \dfrac{{22}}{7}$ , unless stated otherwise.
Unit conversion can easily be done by the unitary method.
The unitary method is a technique for solving a problem by first finding the value of a single unit, and then finding the necessary value by multiplying the single unit value.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step 1: Relation between base radius, slant height, and height of the cone
Let base radius of cone is denoted by r
The slant height of cone is denoted by l
And height of cone is denoted by h

Base radius and height fall perpendicular to each other, i.e., the angle between them is ${90^ \circ }$.
Thus, a radius of length r cm, a height of length h cm, and a slant height of length l cm of the cone form a right-angled triangle.
Therefore, by applying Pythagoras theorem:
Pythagoras theorem: square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the square of base and square of perpendicular.
In a right-angled triangle, the base and perpendicular are at the angle of $90^\circ $ each other and hypotenuse is the longest side.

$\mathop {{\text{Hypotenuse}}}\nolimits^{\text{2}} {\text{ = }}\mathop {{\text{ Base}}}\nolimits^{{\text{2 }}} {\text{ + }}\mathop {{\text{ Perpendicular}}}\nolimits^{\text{2}} $
$\because \mathop {{\text{ slant height}}}\nolimits^2 = \mathop {{\text{radius}}}\nolimits^2 + \mathop {{\text{height}}}\nolimits^2 $
$ \Rightarrow {\text{ }}\mathop l\nolimits^2 = \mathop r\nolimits^2 + \mathop h\nolimits^2 $
This relationship can be directly use if one of the parameter among $l,{\text{ }}r,{\text{ and }}h$ is unknown.
Step 2: Volume calculations
Given that:
Radius, r = 7 cm
Slant height, l = 25 cm
For calculation of volume of cone base radius and height of cone should be known.
We know, ${\text{ }}\mathop l\nolimits^2 = \mathop r\nolimits^2 + \mathop h\nolimits^2 $
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{ }}\mathop {25}\nolimits^2 = \mathop 7\nolimits^2 + \mathop h\nolimits^2 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ 625}} = 49 + \mathop h\nolimits^2 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }}\mathop h\nolimits^2 = 625 - 49 = 576 \\
\Rightarrow h = \sqrt {576} \\
\]
Hence, height, $h = 24{\text{ cm}}$
Volume of cone \[ = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \mathop r\nolimits^2 h{\text{ }}cubic{\text{ }}units\]
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times \mathop 7\nolimits^2 \times {\text{24}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{1232 }}\mathop {{\text{cm}}}\nolimits^3 \\
\]
Given that:
Height, h = 12 cm
Slant height, l = 13 cm
For calculation of volume of cone base radius and height of cone should be known.
We know, ${\text{ }}\mathop l\nolimits^2 = \mathop r\nolimits^2 + \mathop h\nolimits^2 $
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{ }}\mathop {13}\nolimits^2 = \mathop r\nolimits^2 + \mathop {12}\nolimits^2 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ 169}} = \mathop r\nolimits^2 + 144 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }}\mathop r\nolimits^2 = 169 - 144 = 25 \\
\Rightarrow r = \sqrt {25} \\
\]
Hence, radius, $r = 5{\text{ cm}}$
Volume of cone \[ = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \mathop r\nolimits^2 h{\text{ }}cubic{\text{ }}units\]
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times \mathop 5\nolimits^2 \times 12 \\
\Rightarrow 314.28{\text{ }}\mathop {{\text{cm}}}\nolimits^3 \\
\]
Step 3: Convert the cubic centimeters into liters.
We know, 1 cubic meter = 1000 liters
Also, 1 cubic meter $ = {10^6}$ cubic centimeters
Hence, ${10^6}$cubic centimeters = 1000 litres
So, 1 cubic centimeter $ = \dfrac{{1000}}{{{{10}^6}}}$ liters
$ = \dfrac{1}{{1000}}$ or 0.001 liters
Therefore, \[{\text{1232 c}}{{\text{m}}^3} = 1232 \times 0.001{\text{ liters}}\]
$ \Rightarrow 1.232{\text{ liters}}$
Therefore, \[{\text{314}}{\text{.28 c}}{{\text{m}}^3} = 314.28 \times 0.001{\text{ liters}}\]
$ \Rightarrow 0.314{\text{ liters}}$
Final answer: The capacity of conical vessels in (i) is $1.232{\text{ liters}}$ and in (ii) is $0.314{\text{ liters}}$.
Note: The mensuration formulae for 3-dimensional objects are only for right circular objects i.e. its axis is perpendicular to the center of the base.
Volumes of other important objects:
The volume of the right circular cylinder \[ = \pi \mathop r\nolimits^2 h{\text{ }}cubic{\text{ }}units\]
where r is the base radius and h is the height of the cylinder.

Volume of sphere $ = \dfrac{4}{3}\pi \mathop r\nolimits^3 {\text{ cubic units}}$
where r is the radius of the sphere.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




