
How do you find the area bounded by\[{{y}^{2}}=4x\] and the line\[y=2x-4\]?
Answer
555k+ views
Hint: This question belongs to the topic of calculus. In this question, we have to find the area bounded between the curve and a line. For solving this question, we will first find the point of intersections by substituting both the equations. After substituting the equations, we will get the values of x and y. After that, we will find the bounded area between the curve and the line.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us solve this question.
In this question, we have to find the area bounded by the curve \[{{y}^{2}}=4x\]and the line\[y=2x-4\].
We will simplify both the equation to check where the curve and the line meet.
By putting the value of y from the equation\[y=2x-4\] in the equation\[{{y}^{2}}=4x\], we get
\[{{\left( 2x-4 \right)}^{2}}=4x\]
Using the formula \[{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab\] in the above equation, we can write
\[\Rightarrow 4{{x}^{2}}+16-16x=4x\]
The above equation can also be written as
\[\Rightarrow 4{{x}^{2}}+16-16x-4x=0\]
The above equation can also be written as
\[\Rightarrow 4{{x}^{2}}+16-20x=0\]
After arranging equation in a quadratic equation form, we can write
\[\Rightarrow 4{{x}^{2}}-20x+16=0\]
By taking a common factor of 4, we can write the above equation as
\[\Rightarrow 5\left( {{x}^{2}}-5x+4 \right)=0\]
The above equation can also be written as
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-5x+4=0\]
Now, using Sridharacharya method, the value of x will be
\[x=\dfrac{-\left( -5 \right)\pm \sqrt{{{\left( -5 \right)}^{2}}-4\times 1\times 4}}{2\times 1}=\dfrac{5\pm \sqrt{25-16}}{2}=\dfrac{5\pm \sqrt{9}}{2}=\dfrac{5\pm 3}{2}\]
Hence, the value of x will be\[\dfrac{5+3}{2}\] and \[\dfrac{5-3}{2}\] that is the value of x is \[\dfrac{8}{2}\] and\[\dfrac{2}{2}\].
So,
x=4 and x=1
If we put the value of x as 4 and 1 in the equation\[y=2x-4\], then we get the value of y as 4 and -2 respectively. We can take reference from the following figure.
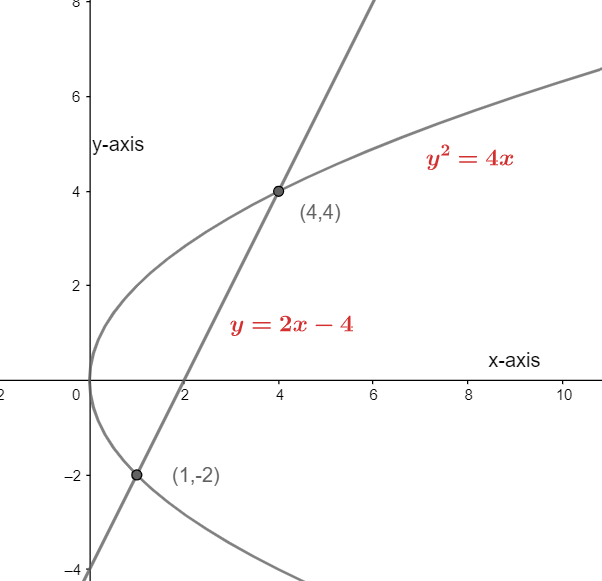
We have to find the area between the point (1,-2) and (4,4).
The equation \[y=2x-4\]can also be written as \[x=\dfrac{y+4}{2}\] and the equation\[{{y}^{2}}=4x\] can be written as \[x=\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}\].
So, the area between the curve \[{{y}^{2}}=4x\] and the line \[y=2x-4\]from y=-2 to y=4 will be
\[A=\int\limits_{-2}^{4}{\left[ \left( \dfrac{y+4}{2} \right)-\left( \dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4} \right) \right]dy}\]
The above integration can also be written as
\[A=\int\limits_{-2}^{4}{\left[ \dfrac{y}{2}+\dfrac{4}{2}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4} \right]dy}\]
As we know that \[\int{{{x}^{n}}dx}=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}\]
Using this formula, the above integration can also be written as
\[\Rightarrow A=\left[ \dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{2\times 2}+\dfrac{4}{2}y-\dfrac{{{y}^{3}}}{4\times 3} \right]_{-2}^{4}\]
We can write above equation as
\[\Rightarrow A=\left[ \dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}+2y-\dfrac{{{y}^{3}}}{12} \right]_{-2}^{4}\]
Now, putting the limits, we will get
\[\Rightarrow A=\left[ \dfrac{{{\left( 4 \right)}^{2}}}{4}+2\left( 4 \right)-\dfrac{{{\left( 4 \right)}^{3}}}{12} \right]-\left[ \dfrac{{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}}{4}+2\left( -2 \right)-\dfrac{{{\left( -2 \right)}^{3}}}{12} \right]\]
The above equation can also be written as
\[\Rightarrow A=\left[ 4+8-\dfrac{16}{3} \right]-\left[ 1-4+\dfrac{2}{3} \right]\]
The above equation can also be written as
\[\Rightarrow A=12-\dfrac{16}{3}+3-\dfrac{2}{3}=15-\dfrac{16}{3}-\dfrac{2}{3}=15-6=9\]
Hence, the area bounded between by \[{{y}^{2}}=4x\] and the line \[y=2x-4\] is 9 square units.
Note: We should have a better knowledge in the topic of calculus to solve this question easily.
Don’t forget the formula\[{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab\].
Always remember the Sridharacharya rule. The Sridharacharya rule says that the values of x of the equation \[a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0\] (let us consider this equation as a general equation) will be \[x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}\].
At the time of finding the area using the integration method, always remember the following points:
1) The formula of the bounded area is \[\int\limits_{a}^{b}{\left[ f\left( y \right)-g\left( y \right) \right]dy}\]. This value will always be positive. If it is negative, then make it positive, because the area quantity is always in the positive form.
2) The value of ‘a’ (lower limit of the integration) should always be less than the value of ‘b’ (upper limit of the integration).
3) f(y) and g(y) are the functions of y (or, we can say the value of x in term of y) taken from both the equations (we have take a curve and a line here)
And, also don’t forget the formula of integration that is \[\int{{{x}^{n}}dx}=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us solve this question.
In this question, we have to find the area bounded by the curve \[{{y}^{2}}=4x\]and the line\[y=2x-4\].
We will simplify both the equation to check where the curve and the line meet.
By putting the value of y from the equation\[y=2x-4\] in the equation\[{{y}^{2}}=4x\], we get
\[{{\left( 2x-4 \right)}^{2}}=4x\]
Using the formula \[{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab\] in the above equation, we can write
\[\Rightarrow 4{{x}^{2}}+16-16x=4x\]
The above equation can also be written as
\[\Rightarrow 4{{x}^{2}}+16-16x-4x=0\]
The above equation can also be written as
\[\Rightarrow 4{{x}^{2}}+16-20x=0\]
After arranging equation in a quadratic equation form, we can write
\[\Rightarrow 4{{x}^{2}}-20x+16=0\]
By taking a common factor of 4, we can write the above equation as
\[\Rightarrow 5\left( {{x}^{2}}-5x+4 \right)=0\]
The above equation can also be written as
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-5x+4=0\]
Now, using Sridharacharya method, the value of x will be
\[x=\dfrac{-\left( -5 \right)\pm \sqrt{{{\left( -5 \right)}^{2}}-4\times 1\times 4}}{2\times 1}=\dfrac{5\pm \sqrt{25-16}}{2}=\dfrac{5\pm \sqrt{9}}{2}=\dfrac{5\pm 3}{2}\]
Hence, the value of x will be\[\dfrac{5+3}{2}\] and \[\dfrac{5-3}{2}\] that is the value of x is \[\dfrac{8}{2}\] and\[\dfrac{2}{2}\].
So,
x=4 and x=1
If we put the value of x as 4 and 1 in the equation\[y=2x-4\], then we get the value of y as 4 and -2 respectively. We can take reference from the following figure.

We have to find the area between the point (1,-2) and (4,4).
The equation \[y=2x-4\]can also be written as \[x=\dfrac{y+4}{2}\] and the equation\[{{y}^{2}}=4x\] can be written as \[x=\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}\].
So, the area between the curve \[{{y}^{2}}=4x\] and the line \[y=2x-4\]from y=-2 to y=4 will be
\[A=\int\limits_{-2}^{4}{\left[ \left( \dfrac{y+4}{2} \right)-\left( \dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4} \right) \right]dy}\]
The above integration can also be written as
\[A=\int\limits_{-2}^{4}{\left[ \dfrac{y}{2}+\dfrac{4}{2}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4} \right]dy}\]
As we know that \[\int{{{x}^{n}}dx}=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}\]
Using this formula, the above integration can also be written as
\[\Rightarrow A=\left[ \dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{2\times 2}+\dfrac{4}{2}y-\dfrac{{{y}^{3}}}{4\times 3} \right]_{-2}^{4}\]
We can write above equation as
\[\Rightarrow A=\left[ \dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}+2y-\dfrac{{{y}^{3}}}{12} \right]_{-2}^{4}\]
Now, putting the limits, we will get
\[\Rightarrow A=\left[ \dfrac{{{\left( 4 \right)}^{2}}}{4}+2\left( 4 \right)-\dfrac{{{\left( 4 \right)}^{3}}}{12} \right]-\left[ \dfrac{{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}}{4}+2\left( -2 \right)-\dfrac{{{\left( -2 \right)}^{3}}}{12} \right]\]
The above equation can also be written as
\[\Rightarrow A=\left[ 4+8-\dfrac{16}{3} \right]-\left[ 1-4+\dfrac{2}{3} \right]\]
The above equation can also be written as
\[\Rightarrow A=12-\dfrac{16}{3}+3-\dfrac{2}{3}=15-\dfrac{16}{3}-\dfrac{2}{3}=15-6=9\]
Hence, the area bounded between by \[{{y}^{2}}=4x\] and the line \[y=2x-4\] is 9 square units.
Note: We should have a better knowledge in the topic of calculus to solve this question easily.
Don’t forget the formula\[{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab\].
Always remember the Sridharacharya rule. The Sridharacharya rule says that the values of x of the equation \[a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0\] (let us consider this equation as a general equation) will be \[x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}\].
At the time of finding the area using the integration method, always remember the following points:
1) The formula of the bounded area is \[\int\limits_{a}^{b}{\left[ f\left( y \right)-g\left( y \right) \right]dy}\]. This value will always be positive. If it is negative, then make it positive, because the area quantity is always in the positive form.
2) The value of ‘a’ (lower limit of the integration) should always be less than the value of ‘b’ (upper limit of the integration).
3) f(y) and g(y) are the functions of y (or, we can say the value of x in term of y) taken from both the equations (we have take a curve and a line here)
And, also don’t forget the formula of integration that is \[\int{{{x}^{n}}dx}=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




