
Find the area bounded by the curve \[y=\left( 4-{{x}^{2}} \right)\], the y-axis and the lines y= 1 and y=3.
Answer
606.9k+ views
Hint: Use the fact that the area bounded by the curve y = f(x), the x-axis and the ordinates x = a and x= b is given by $\int_{a}^{b}{\left| f\left( x \right) \right|dx}$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Hence, in this question, we are asked to find the area bounded by the curve \[y=\left( 4-{{x}^{2}} \right)\] and the y-axis which means that the region between the abscissas y=a and y=b, hence we can manipulate the above mentioned fact as follows
The area bounded by the curve x = f(y), the y-axis and the abscissas y = a and y= b is given by $\int_{a}^{b}{\left| f\left( y \right) \right|dy}$.
Now, we can write the curve as function of y as follows
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=\left( 4-{{x}^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}=4-y \\
& \Rightarrow x=\pm \sqrt{4-y} \\
& \Rightarrow f(y)=\pm \sqrt{4-y} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we can simply take the value of f(y) to be as positive by looking at the figure.
Hence the required area is given by $\int_{a}^{b}{f(y)dy}$.
As mentioned in the question, we have to find the area of the region that is bounded by the curve from the above and the y-axis from the lower side between the two abscissas 1 and 3 which can be seen from the lines which are y=1 and y=3.
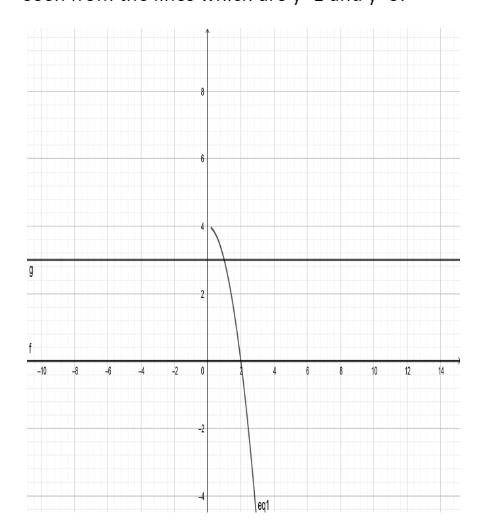
Hence, the values of y are 1 and 3 and these are the values of a and b respectively.
Now, we can simply form the integral as follows to get the required area of the region.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow Area=\int_{a}^{b}{f(y)dy} \\
& \Rightarrow Area=\int_{1}^{3}{\sqrt{\left( 4-y \right)}dy} \\
& \Rightarrow Area=\int_{1}^{3}{{{\left( 4-y \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}dy} \\
& \Rightarrow Area=\left[ \dfrac{{{\left( 4-y \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}{\dfrac{3}{2}} \right]_{1}^{3} \\
& \Rightarrow Area=\left[ \dfrac{{{\left( 4-3 \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}{\dfrac{3}{2}}-\dfrac{{{\left( 4-1 \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}{\dfrac{3}{2}} \right] \\
& \Rightarrow Area=\left[ \dfrac{{{\left( 1 \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}{\dfrac{3}{2}}-\dfrac{{{\left( 3 \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}{\dfrac{3}{2}} \right] \\
& \Rightarrow Area=\left[ \dfrac{2\left( 1-{{\left( 3 \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}} \right)}{3} \right] \\
\end{align}\]
(as we know that the integral of \[{{x}^{n}}\] is as follows
\[\int{{{x}^{n}}dx=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}}+c\]
Where c is the constant of integration )
Hence, we have
Total area \[=\left[ \dfrac{2\left( 1-{{\left( 3 \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}} \right)}{3} \right]\] square units
Note: The students can make an error if they don’t know the basic concepts of integration as without knowing them one could never get to the correct answer.
As in this question, it is very important to know the following result beforehand
The integral of \[{{x}^{n}}\] is as follows
\[\int{{{x}^{n}}dx=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}}+c\]
(Where c is the constant of integration)
Complete step-by-step answer:
Hence, in this question, we are asked to find the area bounded by the curve \[y=\left( 4-{{x}^{2}} \right)\] and the y-axis which means that the region between the abscissas y=a and y=b, hence we can manipulate the above mentioned fact as follows
The area bounded by the curve x = f(y), the y-axis and the abscissas y = a and y= b is given by $\int_{a}^{b}{\left| f\left( y \right) \right|dy}$.
Now, we can write the curve as function of y as follows
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=\left( 4-{{x}^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}=4-y \\
& \Rightarrow x=\pm \sqrt{4-y} \\
& \Rightarrow f(y)=\pm \sqrt{4-y} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we can simply take the value of f(y) to be as positive by looking at the figure.
Hence the required area is given by $\int_{a}^{b}{f(y)dy}$.
As mentioned in the question, we have to find the area of the region that is bounded by the curve from the above and the y-axis from the lower side between the two abscissas 1 and 3 which can be seen from the lines which are y=1 and y=3.

Hence, the values of y are 1 and 3 and these are the values of a and b respectively.
Now, we can simply form the integral as follows to get the required area of the region.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow Area=\int_{a}^{b}{f(y)dy} \\
& \Rightarrow Area=\int_{1}^{3}{\sqrt{\left( 4-y \right)}dy} \\
& \Rightarrow Area=\int_{1}^{3}{{{\left( 4-y \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}dy} \\
& \Rightarrow Area=\left[ \dfrac{{{\left( 4-y \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}{\dfrac{3}{2}} \right]_{1}^{3} \\
& \Rightarrow Area=\left[ \dfrac{{{\left( 4-3 \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}{\dfrac{3}{2}}-\dfrac{{{\left( 4-1 \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}{\dfrac{3}{2}} \right] \\
& \Rightarrow Area=\left[ \dfrac{{{\left( 1 \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}{\dfrac{3}{2}}-\dfrac{{{\left( 3 \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}{\dfrac{3}{2}} \right] \\
& \Rightarrow Area=\left[ \dfrac{2\left( 1-{{\left( 3 \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}} \right)}{3} \right] \\
\end{align}\]
(as we know that the integral of \[{{x}^{n}}\] is as follows
\[\int{{{x}^{n}}dx=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}}+c\]
Where c is the constant of integration )
Hence, we have
Total area \[=\left[ \dfrac{2\left( 1-{{\left( 3 \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}} \right)}{3} \right]\] square units
Note: The students can make an error if they don’t know the basic concepts of integration as without knowing them one could never get to the correct answer.
As in this question, it is very important to know the following result beforehand
The integral of \[{{x}^{n}}\] is as follows
\[\int{{{x}^{n}}dx=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}}+c\]
(Where c is the constant of integration)
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




