
Find the area between the curve $y=\dfrac{x}{\pi }+2{{\sin }^{2}}x$, the x-axis and the ordinates x= 0 and $x=\pi$.
Answer
607.2k+ views
Hint: Use the fact that if $f\left( x \right)\ge 0$ in the interval [a,b] then the area bounded by the curve y=f(x) and the x-axis and the ordinates x = a and x = b is given by $\int_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)dx}$. Observe that in the interval $\left[ 0,\pi \right]$, we have $\dfrac{x}{\pi }+2{{\sin }^{2}}x\ge 0$ and hence the area bounded by the curve $y=\dfrac{x}{\pi }+2{{\sin }^{2}}x$, the x-axis and the ordinates x = 0 and $x=\pi $ is given by $\int_{0}^{\pi }{\left( \dfrac{x}{\pi }+2{{\sin }^{2}}x \right)dx}$. Evaluate the integral and hence find the required area.
Complete step-by-step answer:
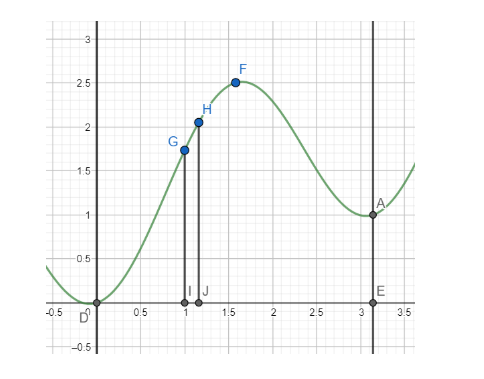
Consider the vertical strip GHJI
We have GI = y and IJ = dx
Hence the area of the strip is ydx.
The total area will be the sum of the area of the strips between D and E.
Hence, we have
Total area $=\int_{0}^{\pi }{ydx}$
We know that $y=\dfrac{x}{\pi }+2{{\sin }^{2}}x$
Hence, we have
Total area $=\int_{0}^{\pi }{\left( \dfrac{x}{\pi }+2{{\sin }^{2}}x \right)dx}$
We know that $\int_{a}^{b}{\left( f\left( x \right)+g\left( x \right) \right)dx}=\int_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)dx}+\int_{a}^{b}{g\left( x \right)dx}$
Hence, we have
Total area $=\int_{0}^{\pi }{\dfrac{x}{\pi }}dx+\int_{0}^{\pi }{2{{\sin }^{2}}xdx}={{I}_{1}}+{{I}_{2}}$, where ${{I}_{1}}=\int_{0}^{\pi }{\dfrac{x}{\pi }dx}$ and ${{I}_{2}}=\int_{0}^{\pi }{2{{\sin }^{2}}x}$
Finding the value of ${{I}_{1}}$:
We have ${{I}_{1}}=\int_{0}^{\pi }{\dfrac{x}{\pi }dx}$
We know that $\int_{a}^{b}{kf\left( x \right)dx}=k\int_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)dx}$
Hence, we have
${{I}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{\pi }\int_{0}^{\pi }{xdx}$
We know that $\int{{{x}^{n}}dx}=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}+C$
Hence, we have
${{I}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{\pi }\left( \left. \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2} \right|_{0}^{\pi } \right)=\dfrac{1}{\pi }\left( \dfrac{{{\pi }^{2}}}{2} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Hence, we have ${{I}_{1}}=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Finding the value of ${{I}_{2}}$:
We have ${{I}_{2}}=\int_{0}^{\pi }{2{{\sin }^{2}}xdx}$
We know that $\int_{a}^{b}{kf\left( x \right)dx}=k\int_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)dx}$
Hence, we have
${{I}_{2}}=2\int_{0}^{\pi }{{{\sin }^{2}}xdx}$
We know that if f(x) = f(2a-x), then $\int_{0}^{2a}{f\left( x \right)dx}=2\int_{0}^{a}{f\left( x \right)dx}$
Since ${{\sin }^{2}}\left( \pi -x \right)={{\sin }^{2}}x$, we have
$\int_{0}^{\pi }{{{\sin }^{2}}xdx}=2\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}{{{\sin }^{2}}xdx}$
Hence, we have
${{I}_{2}}=4\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}{{{\sin }^{2}}x}\text{ }\left( i \right)$
We know that $\int_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)dx}=\int_{a}^{b}{f\left( a+b-x \right)dx}$
Hence, we have
${{I}_{2}}=4\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}{{{\sin }^{2}}\left( \dfrac{\pi }{2}-x \right)dx}=4\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}{{{\cos }^{2}}xdx}\text{ }\left( ii \right)$
Adding equation (i) and equation (ii), we get
$2{{I}_{2}}=4\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}{\left( {{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x \right)dx}$
We know that ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x=1$
Hence, we have
$2{{I}_{2}}=4\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}{1dx}=4\left( \left. x \right|_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)=4\times \dfrac{\pi }{2}=2\pi $
Dividing both sides by 2, we get
${{I}_{2}}=\pi $
Hence we have
Total area $=\dfrac{\pi }{2}+\pi =\dfrac{3\pi }{2}$
Note: [1] We can calculate ${{I}_{2}}$ directly using the identity ${{\sin }^{2}}x=\dfrac{1-\cos 2x}{2}$
We have ${{I}_{2}}=2\int_{0}^{\pi }{{{\sin }^{2}}x=2\int_{0}^{\pi }{\dfrac{1-\cos 2x}{2}dx=\int_{0}^{\pi }{\left( 1-\cos 2x \right)dx}}}$
We know that $\int{\cos 2x}dx=\dfrac{\sin 2x}{2}+C$
Hence, we have
${{I}_{2}}=\left. x-\dfrac{\sin 2x}{2} \right|_{0}^{\pi }=\left( \pi -0 \right)-\left( \dfrac{\sin 2\pi }{2}-\dfrac{\sin 0}{2} \right)=\pi $, which is the same as obtained above.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Consider the vertical strip GHJI
We have GI = y and IJ = dx
Hence the area of the strip is ydx.
The total area will be the sum of the area of the strips between D and E.
Hence, we have
Total area $=\int_{0}^{\pi }{ydx}$
We know that $y=\dfrac{x}{\pi }+2{{\sin }^{2}}x$
Hence, we have
Total area $=\int_{0}^{\pi }{\left( \dfrac{x}{\pi }+2{{\sin }^{2}}x \right)dx}$
We know that $\int_{a}^{b}{\left( f\left( x \right)+g\left( x \right) \right)dx}=\int_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)dx}+\int_{a}^{b}{g\left( x \right)dx}$
Hence, we have
Total area $=\int_{0}^{\pi }{\dfrac{x}{\pi }}dx+\int_{0}^{\pi }{2{{\sin }^{2}}xdx}={{I}_{1}}+{{I}_{2}}$, where ${{I}_{1}}=\int_{0}^{\pi }{\dfrac{x}{\pi }dx}$ and ${{I}_{2}}=\int_{0}^{\pi }{2{{\sin }^{2}}x}$
Finding the value of ${{I}_{1}}$:
We have ${{I}_{1}}=\int_{0}^{\pi }{\dfrac{x}{\pi }dx}$
We know that $\int_{a}^{b}{kf\left( x \right)dx}=k\int_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)dx}$
Hence, we have
${{I}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{\pi }\int_{0}^{\pi }{xdx}$
We know that $\int{{{x}^{n}}dx}=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}+C$
Hence, we have
${{I}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{\pi }\left( \left. \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2} \right|_{0}^{\pi } \right)=\dfrac{1}{\pi }\left( \dfrac{{{\pi }^{2}}}{2} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Hence, we have ${{I}_{1}}=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Finding the value of ${{I}_{2}}$:
We have ${{I}_{2}}=\int_{0}^{\pi }{2{{\sin }^{2}}xdx}$
We know that $\int_{a}^{b}{kf\left( x \right)dx}=k\int_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)dx}$
Hence, we have
${{I}_{2}}=2\int_{0}^{\pi }{{{\sin }^{2}}xdx}$
We know that if f(x) = f(2a-x), then $\int_{0}^{2a}{f\left( x \right)dx}=2\int_{0}^{a}{f\left( x \right)dx}$
Since ${{\sin }^{2}}\left( \pi -x \right)={{\sin }^{2}}x$, we have
$\int_{0}^{\pi }{{{\sin }^{2}}xdx}=2\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}{{{\sin }^{2}}xdx}$
Hence, we have
${{I}_{2}}=4\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}{{{\sin }^{2}}x}\text{ }\left( i \right)$
We know that $\int_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)dx}=\int_{a}^{b}{f\left( a+b-x \right)dx}$
Hence, we have
${{I}_{2}}=4\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}{{{\sin }^{2}}\left( \dfrac{\pi }{2}-x \right)dx}=4\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}{{{\cos }^{2}}xdx}\text{ }\left( ii \right)$
Adding equation (i) and equation (ii), we get
$2{{I}_{2}}=4\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}{\left( {{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x \right)dx}$
We know that ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x=1$
Hence, we have
$2{{I}_{2}}=4\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}{1dx}=4\left( \left. x \right|_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)=4\times \dfrac{\pi }{2}=2\pi $
Dividing both sides by 2, we get
${{I}_{2}}=\pi $
Hence we have
Total area $=\dfrac{\pi }{2}+\pi =\dfrac{3\pi }{2}$
Note: [1] We can calculate ${{I}_{2}}$ directly using the identity ${{\sin }^{2}}x=\dfrac{1-\cos 2x}{2}$
We have ${{I}_{2}}=2\int_{0}^{\pi }{{{\sin }^{2}}x=2\int_{0}^{\pi }{\dfrac{1-\cos 2x}{2}dx=\int_{0}^{\pi }{\left( 1-\cos 2x \right)dx}}}$
We know that $\int{\cos 2x}dx=\dfrac{\sin 2x}{2}+C$
Hence, we have
${{I}_{2}}=\left. x-\dfrac{\sin 2x}{2} \right|_{0}^{\pi }=\left( \pi -0 \right)-\left( \dfrac{\sin 2\pi }{2}-\dfrac{\sin 0}{2} \right)=\pi $, which is the same as obtained above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




