
Find compound ‘D’.

Answer
505.2k+ views
Hint: In order to find the unknown compound ‘D’, all the intermediate reactions need to be performed theoretically so as to reach the final product. Identify the role of each reagent and the transformation it brings, make a product for each step and reach the final answer.
Complete answer:
The starting reactant of the given organic reaction is an aromatic amine known as aniline. The following steps can be followed to reach the compound ‘D’:
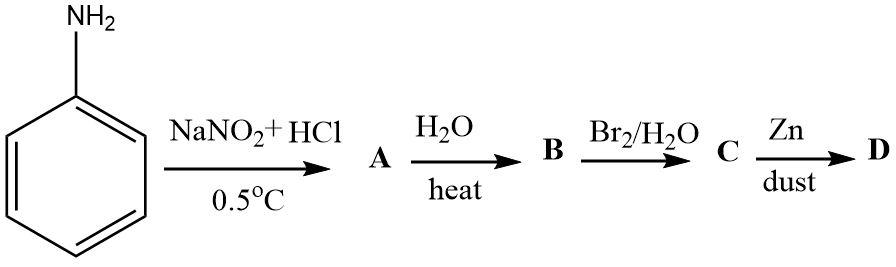
1.Diazotization: aromatic amines can be easily transformed into the diazonium salts. Sodium nitrite along with hydrochloric acid combine in situ to give nitrous acid as the effective diazotization reagent. The nitrosyl cation formed in the reaction medium transforms the amino group into the diazonium ion.
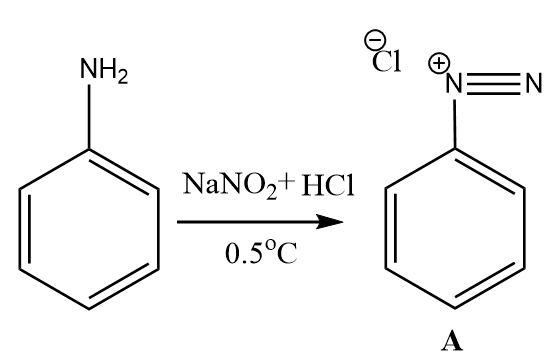
2.The benzene diazonium salt upon treatment with water and heat gets converted into phenol. The role of water is to provide hydroxide ions (which become the hydroxyl functional group on attaching with the carbon atom) that replace the diazonium ion group attached to the benzene ring.
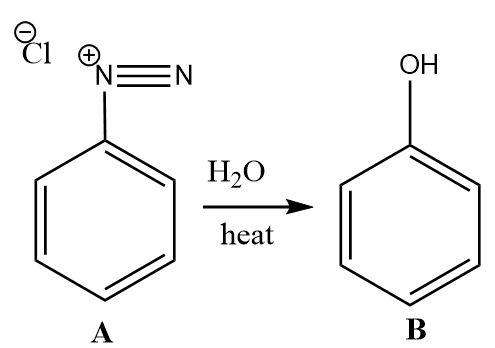
3.Phenol is very electron rich and reacts vigorously with electrophiles. The reaction between phenol and bromine water is an electrophilic substitution reaction. Due to the high sensitivity of phenol towards electrophiles, it gets tri-substituted by bromine electrophiles.
4.The tri-substituted bromo phenol undergoes a reduction on treatment with zinc dust. Zinc is a strong reducing agent that selectively reduces the hydroxyl group on the benzene ring into a hydrogen atom without affecting the other substituents attached.
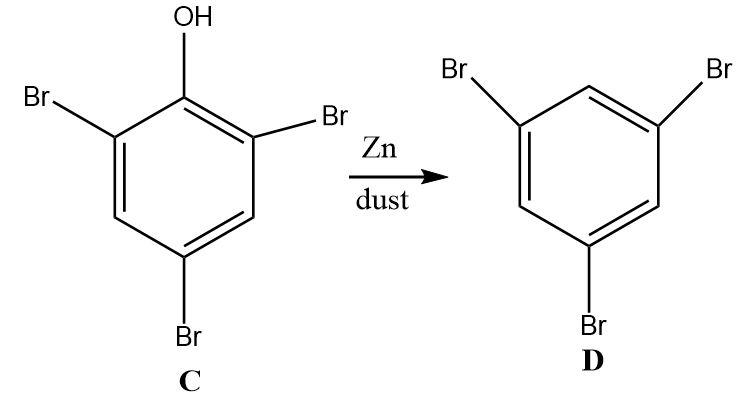
Hence, the final product ‘D’ is \[1,3,5 - tribromobenzene\].
Note:
The electrophilic substitution reaction of phenol is vigorous in the presence of a protic solvent like water. The incoming electrophiles only attack the active sites i.e. ortho and meta positions. The high reactivity is a consequence of the strong electron donating effect of the \[ - OH\] group.
Complete answer:
The starting reactant of the given organic reaction is an aromatic amine known as aniline. The following steps can be followed to reach the compound ‘D’:
1.Diazotization: aromatic amines can be easily transformed into the diazonium salts. Sodium nitrite along with hydrochloric acid combine in situ to give nitrous acid as the effective diazotization reagent. The nitrosyl cation formed in the reaction medium transforms the amino group into the diazonium ion.

2.The benzene diazonium salt upon treatment with water and heat gets converted into phenol. The role of water is to provide hydroxide ions (which become the hydroxyl functional group on attaching with the carbon atom) that replace the diazonium ion group attached to the benzene ring.

3.Phenol is very electron rich and reacts vigorously with electrophiles. The reaction between phenol and bromine water is an electrophilic substitution reaction. Due to the high sensitivity of phenol towards electrophiles, it gets tri-substituted by bromine electrophiles.

4.The tri-substituted bromo phenol undergoes a reduction on treatment with zinc dust. Zinc is a strong reducing agent that selectively reduces the hydroxyl group on the benzene ring into a hydrogen atom without affecting the other substituents attached.

Hence, the final product ‘D’ is \[1,3,5 - tribromobenzene\].
Note:
The electrophilic substitution reaction of phenol is vigorous in the presence of a protic solvent like water. The incoming electrophiles only attack the active sites i.e. ortho and meta positions. The high reactivity is a consequence of the strong electron donating effect of the \[ - OH\] group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 12 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE




