
Find acceleration in the given cases.
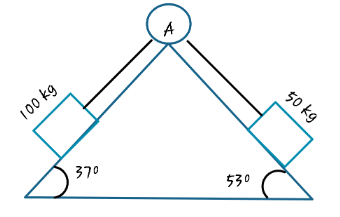

Answer
561k+ views
Hint: First write the equation of motion of each block. Take into consideration the tension produced in the string, weight (mg) component along the inclined plane.
TENSION: whenever any string is tight then the end of the string pulls whatever is connected to them in inward direction. This inward pulling force of the string on the object is called a tension force. It depends on mass, as mass increases tension also increases.
Remember that the heavy block will move down and the light block will slide up. According to this, it gives direction to the acceleration produced.
Complete step by step answer
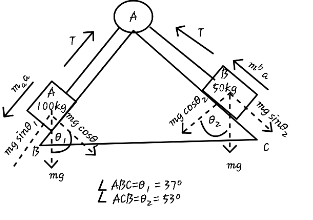
Let T, be the tension produced in the string and ‘a’ be the acceleration produced in each block.
Therefore, equation of motion of block A can be written as
$ \begin{align}
& {{m}_{A}}g\sin \theta -T={{m}_{A}}a \\
& {{m}_{A}}g\sin 37{}^\circ -T={{m}_{A}}a\text{ }............\text{(1)} \\
& \text{Equation of motion for block B is:-} \\
& T-{{m}_{B}}g\sin {{\theta }_{2}}={{m}_{B}}a\text{ } \\
& T-{{m}_{B}}g\sin 53{}^\circ ={{m}_{B}}a\text{ }.............\text{(2)} \\
\end{align} $
Adding equations 1. and 2. Gives,
$ \begin{align}
& g({{m}_{A}}\sin 37{}^\circ -{{m}_{b}}\sin 53{}^\circ )=({{m}_{A}}+{{m}_{B}})a \\
& g(100\times \dfrac{3}{5}-50\times \dfrac{4}{5})=(100+50)a \\
& 10(60-40)=150a \\
& a=\dfrac{200}{15}=\dfrac{4}{3}m/{{s}^{2}} \\
& \text{Thus acceleration of block= 4/3 ms}_{^{{}}}^{-2} \\
\end{align} $ .
Additional Information
Consider the situation as given in the following diagram.
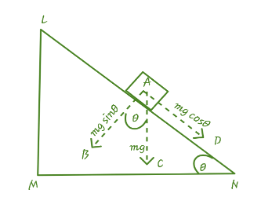
$ \begin{align}
& Here,\angle LMN=\angle BAC=\theta \\
& \\
\end{align} $
Because, the angle between the two lines is equal to the angle between the normal of that line.
$ \text{As here, MN}\bot \text{AC and BA}\bot \text{AD} $
Thus component along AN = mg $ \text{sin }\!\!\theta\!\!\text{ } $
Component along AB = mg $ \text{cos }\!\!\theta\!\!\text{ } $ .
Note
Equations 1 and 2 are taken according to the direction of acceleration produced in each block. Thus taking into account which force is dominant, according to which large value of force is to be subtracted from the small value, to get the resultant force.
Remember that the second law of Newton states that the acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables - the net force acting upon the object and the mass of the object.
TENSION: whenever any string is tight then the end of the string pulls whatever is connected to them in inward direction. This inward pulling force of the string on the object is called a tension force. It depends on mass, as mass increases tension also increases.
Remember that the heavy block will move down and the light block will slide up. According to this, it gives direction to the acceleration produced.
Complete step by step answer

Let T, be the tension produced in the string and ‘a’ be the acceleration produced in each block.
Therefore, equation of motion of block A can be written as
$ \begin{align}
& {{m}_{A}}g\sin \theta -T={{m}_{A}}a \\
& {{m}_{A}}g\sin 37{}^\circ -T={{m}_{A}}a\text{ }............\text{(1)} \\
& \text{Equation of motion for block B is:-} \\
& T-{{m}_{B}}g\sin {{\theta }_{2}}={{m}_{B}}a\text{ } \\
& T-{{m}_{B}}g\sin 53{}^\circ ={{m}_{B}}a\text{ }.............\text{(2)} \\
\end{align} $
Adding equations 1. and 2. Gives,
$ \begin{align}
& g({{m}_{A}}\sin 37{}^\circ -{{m}_{b}}\sin 53{}^\circ )=({{m}_{A}}+{{m}_{B}})a \\
& g(100\times \dfrac{3}{5}-50\times \dfrac{4}{5})=(100+50)a \\
& 10(60-40)=150a \\
& a=\dfrac{200}{15}=\dfrac{4}{3}m/{{s}^{2}} \\
& \text{Thus acceleration of block= 4/3 ms}_{^{{}}}^{-2} \\
\end{align} $ .
Additional Information
Consider the situation as given in the following diagram.

$ \begin{align}
& Here,\angle LMN=\angle BAC=\theta \\
& \\
\end{align} $
Because, the angle between the two lines is equal to the angle between the normal of that line.
$ \text{As here, MN}\bot \text{AC and BA}\bot \text{AD} $
Thus component along AN = mg $ \text{sin }\!\!\theta\!\!\text{ } $
Component along AB = mg $ \text{cos }\!\!\theta\!\!\text{ } $ .
Note
Equations 1 and 2 are taken according to the direction of acceleration produced in each block. Thus taking into account which force is dominant, according to which large value of force is to be subtracted from the small value, to get the resultant force.
Remember that the second law of Newton states that the acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables - the net force acting upon the object and the mass of the object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




