
what is ferromagnetism? Iron is strongly ferromagnetic. Explain.
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: This question is based on the unique properties of the substances that contain unpaired electrons, depending upon the number of unpaired electrons substance will behave accordingly, Higher the number of unpaired electrons, higher the chances of getting attracted into the magnetic field.
Complete step by step solution:
Ferromagnetic materials: Ferromagnetic materials are those materials which exhibit a spontaneous net magnetization at the atomic level, even in the absence of an external magnetic field because they contain quite a few unpaired electrons. When placed in an external magnetic field, ferromagnetic materials are strongly magnetized in the direction of the field. Ferromagnetic materials are strongly attracted to a magnetic field. These materials will retain their magnetization for some time even after the external magnetizing field is removed. That’s why they are permanent magnets. Transition metals Fe, H, Co, Ni; alloys of ferromagnetic elements; some alloys of Mn like MnBi show ferromagnetism.
- Ferromagnetism is defined as the phenomenon by which a material in an external magnetic field becomes magnetized and remains magnetized even after the removal of the external magnetic field.
Electronic configuration of Iron:
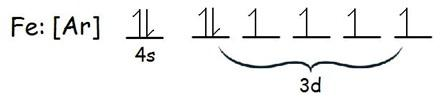
Clearly iron atoms have 4 unpaired electrons and because of them it has a net magnetic moment greater than zero even in the absence of magnetic field.
- In solid state, the iron atoms are grouped together in small regions called domains. In an unmagnetized piece of iron all the domains are randomly oriented and their magnetic moments get cancelled. When it is placed in a magnetic field all the domains get oriented in the direction of the magnetic field and strong magnetization takes place and they become magnet.
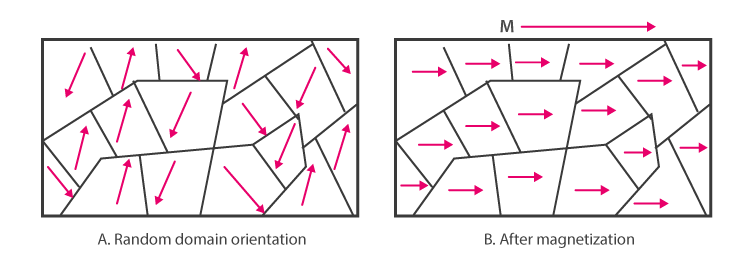
- This ordering of domain persists even after the removal of the magnetic field, that’s why ferromagnetic substances become permanent magnets.
Additional Information:
Ferromagnetic materials are used to make permanent magnet, electromagnet, core of transformer, to build memory stores in modern computers, for coating magnetic tapes etc.
Note: It is a property not just of the chemical make-up of a material, but of its crystalline structure and microstructure. There are ferromagnetic metal alloys whose constituents are not themselves ferromagnetic, called Heusler alloys. Conversely there are non-magnetic alloys, such as types of stainless steel composed almost exclusively of ferromagnetic metals. A new class of exceptionally strong ferromagnetic materials is the rare-earth magnets. They contain lanthanide elements that are known for their ability to carry large magnetic moments in well-localized f-orbitals.
Complete step by step solution:
Ferromagnetic materials: Ferromagnetic materials are those materials which exhibit a spontaneous net magnetization at the atomic level, even in the absence of an external magnetic field because they contain quite a few unpaired electrons. When placed in an external magnetic field, ferromagnetic materials are strongly magnetized in the direction of the field. Ferromagnetic materials are strongly attracted to a magnetic field. These materials will retain their magnetization for some time even after the external magnetizing field is removed. That’s why they are permanent magnets. Transition metals Fe, H, Co, Ni; alloys of ferromagnetic elements; some alloys of Mn like MnBi show ferromagnetism.
- Ferromagnetism is defined as the phenomenon by which a material in an external magnetic field becomes magnetized and remains magnetized even after the removal of the external magnetic field.
Electronic configuration of Iron:
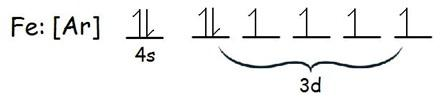
Clearly iron atoms have 4 unpaired electrons and because of them it has a net magnetic moment greater than zero even in the absence of magnetic field.
- In solid state, the iron atoms are grouped together in small regions called domains. In an unmagnetized piece of iron all the domains are randomly oriented and their magnetic moments get cancelled. When it is placed in a magnetic field all the domains get oriented in the direction of the magnetic field and strong magnetization takes place and they become magnet.

- This ordering of domain persists even after the removal of the magnetic field, that’s why ferromagnetic substances become permanent magnets.
Additional Information:
Ferromagnetic materials are used to make permanent magnet, electromagnet, core of transformer, to build memory stores in modern computers, for coating magnetic tapes etc.
Note: It is a property not just of the chemical make-up of a material, but of its crystalline structure and microstructure. There are ferromagnetic metal alloys whose constituents are not themselves ferromagnetic, called Heusler alloys. Conversely there are non-magnetic alloys, such as types of stainless steel composed almost exclusively of ferromagnetic metals. A new class of exceptionally strong ferromagnetic materials is the rare-earth magnets. They contain lanthanide elements that are known for their ability to carry large magnetic moments in well-localized f-orbitals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




