
Explain the violet color of \[{\left[ {{\mathbf{Ti}}{{\left( {{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{2}}}{\mathbf{O}}} \right)}_{\mathbf{6}}}} \right]^{{\mathbf{3}} + }}\]complex on the basis of the Crystal Field theory?
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: In the given question we will discuss how the change of the color of the complex occurs on the basis of the crystal field theory. The CFT is a theory which is used to describe many spectroscopies of transition metal coordination complexes, in specific optical spectra that are colors.
Complete answer:
In the Coordination compounds they exhibit color, which is credited to the crystal field theory, that corresponds to the \[d - d\] transition of the elements. In ground state, the complex of Titanium has \[23\] electrons which have the outer shell electronic configuration that is \[3{d^3}4{s^2}\] and in the complex it is observed that titanium is in its \[ + 3\] oxidation state. This is accomplished by losing \[3\] electros. So, it has the configuration \[3{d^2}\]. Since it has \[2\] unpaired electrons and has the ability to undergo \[d - d\] transition, thus the complex is colored.
When light corresponding to the energy of the yellow-green region is absorbed by the complex, this would excite the electron from\[\;{t_{2g}}\;\] level to the \[{e_g}\;\] level. Thus, the complex occurs in violet color.
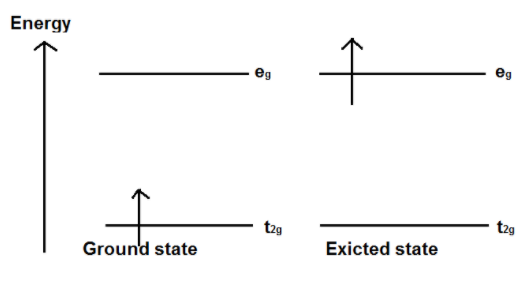
Figure 1 transition of electron in Ti complex
As though in the absence of ligands there will be no crystal field splitting and substance become colorless. when water molecules are removed it becomes colorless.
Note:When the excitation of an electron takes place from the ground state to excited state, electrons will absorb light that will excite the electron from one energy level to another and will return to ground state in the form of colors.
Complete answer:
In the Coordination compounds they exhibit color, which is credited to the crystal field theory, that corresponds to the \[d - d\] transition of the elements. In ground state, the complex of Titanium has \[23\] electrons which have the outer shell electronic configuration that is \[3{d^3}4{s^2}\] and in the complex it is observed that titanium is in its \[ + 3\] oxidation state. This is accomplished by losing \[3\] electros. So, it has the configuration \[3{d^2}\]. Since it has \[2\] unpaired electrons and has the ability to undergo \[d - d\] transition, thus the complex is colored.
When light corresponding to the energy of the yellow-green region is absorbed by the complex, this would excite the electron from\[\;{t_{2g}}\;\] level to the \[{e_g}\;\] level. Thus, the complex occurs in violet color.

Figure 1 transition of electron in Ti complex
As though in the absence of ligands there will be no crystal field splitting and substance become colorless. when water molecules are removed it becomes colorless.
Note:When the excitation of an electron takes place from the ground state to excited state, electrons will absorb light that will excite the electron from one energy level to another and will return to ground state in the form of colors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




