
Explain the $s{p^2}$ hybridisation?
Answer
553.2k+ views
Hint: As we know that the atomic orbitals combine to form a new set of equivalent orbitals known as the hybrid orbitals and it helps in explaining the shape of molecules and equivalency of bonds. It can be classified into $sp,s{p^2},s{p^3}$ and so on which involves one s-orbital and one p-orbital, one s and two p-orbitals etc.
Complete answer:
As we know that hybridisation is a theoretical concept which has been introduced to explain the structural properties such as shape of molecule and equivalency of bonds etc which cannot be explained by simple theories of valency.
We also know that there are many different types of hybridisation depending upon the types of orbitals involved in mixing like $sp,s{p^2},s{p^3},s{p^3}d$ etc. let us talk about $s{p^2}$ hybridisation among these.
We can see that in $s{p^2}$ hybridisation, one s-orbital and two p- $({p_x}\;\& \;{p_y})$ orbitals of one atom hybridise to give three equivalent $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbitals. These three $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbitals are directed towards the three corners of an equilateral triangle with an angle of ${120^\circ }$ and give a triangular geometry to the molecule. We can represent it as:
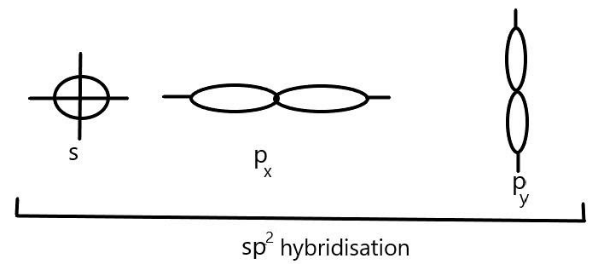
$s{p^2}$ hybrid orbitals are larger in size than the $sp$-hybrid orbitals but slightly smaller than that of $s{p^3}$. Examples of $s{p^2}$ hybridisation includes the compounds of boron like $B{F_3},BC{l_3}$ and $B{H_3}$ as well as aluminium and carbon containing compounds such as $AlC{l_3}$ and $C{H_2} = C{H_2}$respectively.
Note:Always remember that $s{p^2}$ hybridisation involves the mixing of one s-orbital and two p-orbitals which includes the promotion of one electron in the s-orbital and the one to the any one of the p-orbital whose combination creates a three new hybrid orbitals of equivalent energy levels. The $s{p^2}$ hybridised orbitals possess a trigonal planar geometry of molecules and these hybrid orbitals are more effective in forming stable bonds than the pure atomic orbitals.
Complete answer:
As we know that hybridisation is a theoretical concept which has been introduced to explain the structural properties such as shape of molecule and equivalency of bonds etc which cannot be explained by simple theories of valency.
We also know that there are many different types of hybridisation depending upon the types of orbitals involved in mixing like $sp,s{p^2},s{p^3},s{p^3}d$ etc. let us talk about $s{p^2}$ hybridisation among these.
We can see that in $s{p^2}$ hybridisation, one s-orbital and two p- $({p_x}\;\& \;{p_y})$ orbitals of one atom hybridise to give three equivalent $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbitals. These three $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbitals are directed towards the three corners of an equilateral triangle with an angle of ${120^\circ }$ and give a triangular geometry to the molecule. We can represent it as:

$s{p^2}$ hybrid orbitals are larger in size than the $sp$-hybrid orbitals but slightly smaller than that of $s{p^3}$. Examples of $s{p^2}$ hybridisation includes the compounds of boron like $B{F_3},BC{l_3}$ and $B{H_3}$ as well as aluminium and carbon containing compounds such as $AlC{l_3}$ and $C{H_2} = C{H_2}$respectively.
Note:Always remember that $s{p^2}$ hybridisation involves the mixing of one s-orbital and two p-orbitals which includes the promotion of one electron in the s-orbital and the one to the any one of the p-orbital whose combination creates a three new hybrid orbitals of equivalent energy levels. The $s{p^2}$ hybridised orbitals possess a trigonal planar geometry of molecules and these hybrid orbitals are more effective in forming stable bonds than the pure atomic orbitals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




