
Explain the principle of paper chromatography.
Answer
592.5k+ views
Hint:This technique is classified under the chromatography for the separation of a mixture. From the name itself we can say that it is based on the use of paper, and it is relatable to the adsorption process. So, we can explain the principle of paper chromatography.
Complete step by step answer:
-First, let us define paper chromatography. As mentioned it involves the use of paper, or strips, that acts as an adsorbent, and stationary phase. So, the solution is allowed to pass through the stationary phase, i.e. paper. Thus, it is termed as paper chromatography.
-Talking more about it, we can say that this process is not costly, and considered to be a powerful analytical tool. In this technique, chemical substances with the different migration rates are passed through the paper for separation.
-It was discovered by Synge, and Martin.
-Now, the principle involved in paper chromatography is related to the adsorption process, or the partition technique.
-Let us discuss the partition technique. In this technique, substances are being distributed between the two liquid phases.
- One phase is stationary i.e. pores of filter paper holding the water, and other one is a mobile phase which is passing through the paper. Thus, the separation of mixture will take place by the movement of the mobile phase.
-Now, if we talk about the adsorption techniques, then it is between one solid phase, and the liquid phase. The stationary phase is the solid surface of the paper, and the mobile phase is the liquid that will be passed through it.
The schematic representation is shown below in the diagram
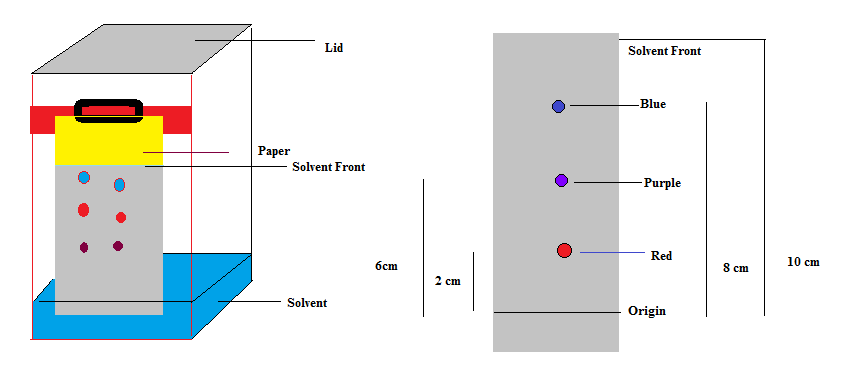
Now, in the last we can conclude that paper chromatography involves the use of paper, and in both the techniques it acts as a stationary phase for the separation of mixture.
Note:
Don’t get confused between the partition technique, and adsorption technique. Partition techniques are liquid-liquid separation, whereas adsorption technique is solid-liquid separation.
Complete step by step answer:
-First, let us define paper chromatography. As mentioned it involves the use of paper, or strips, that acts as an adsorbent, and stationary phase. So, the solution is allowed to pass through the stationary phase, i.e. paper. Thus, it is termed as paper chromatography.
-Talking more about it, we can say that this process is not costly, and considered to be a powerful analytical tool. In this technique, chemical substances with the different migration rates are passed through the paper for separation.
-It was discovered by Synge, and Martin.
-Now, the principle involved in paper chromatography is related to the adsorption process, or the partition technique.
-Let us discuss the partition technique. In this technique, substances are being distributed between the two liquid phases.
- One phase is stationary i.e. pores of filter paper holding the water, and other one is a mobile phase which is passing through the paper. Thus, the separation of mixture will take place by the movement of the mobile phase.
-Now, if we talk about the adsorption techniques, then it is between one solid phase, and the liquid phase. The stationary phase is the solid surface of the paper, and the mobile phase is the liquid that will be passed through it.
The schematic representation is shown below in the diagram

Now, in the last we can conclude that paper chromatography involves the use of paper, and in both the techniques it acts as a stationary phase for the separation of mixture.
Note:
Don’t get confused between the partition technique, and adsorption technique. Partition techniques are liquid-liquid separation, whereas adsorption technique is solid-liquid separation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




