
Explain the mechanism of esterification. Write the reactions involved in dehydration of 1$^o$, 2$^o$, and 3$^o$ alcohols.
Answer
599.7k+ views
Hint: The mechanism of esterification involves the five steps. It is the conversion of carboxylic acids treated with primary alcohols to an ester. The dehydration of alcohols is an elimination reaction including the removal of hydrogen i.e. loose water molecules.
Complete step by step answer:
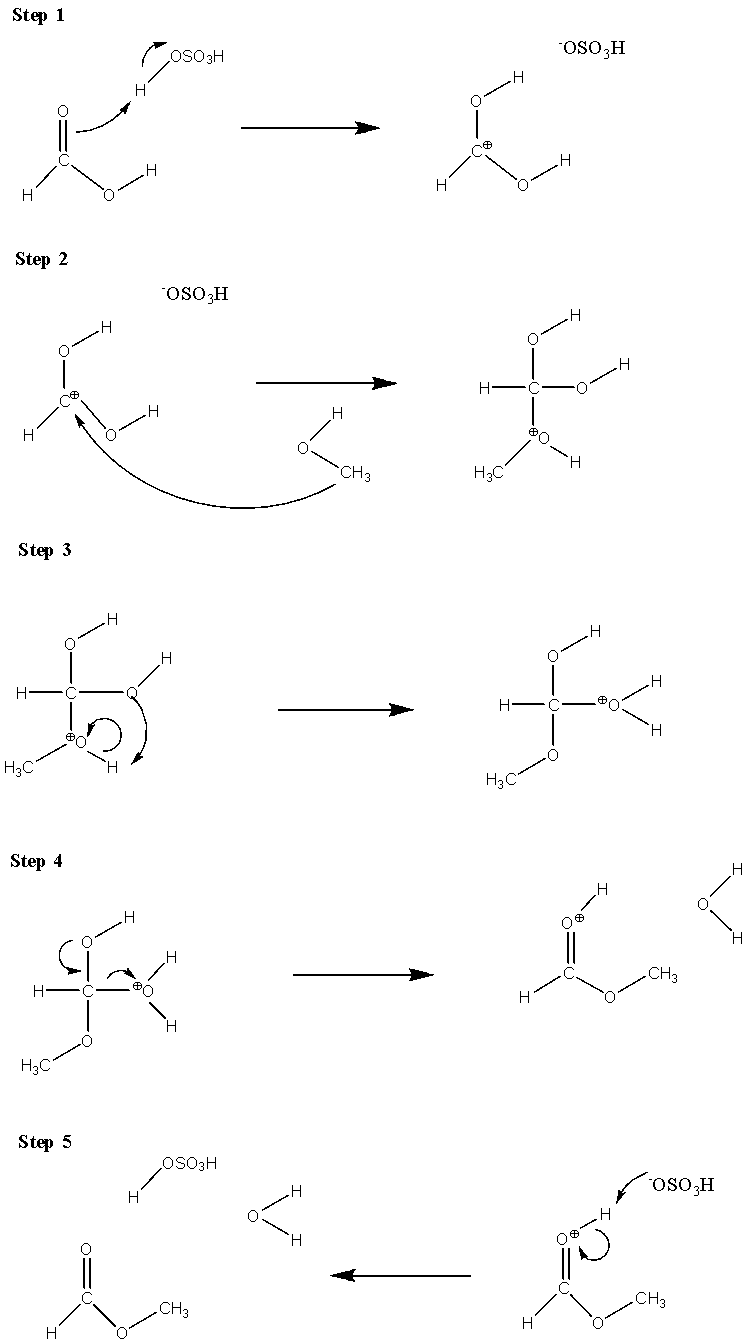
-Firstly, we will discuss the mechanism of esterification. This involves five steps
Cation formation
-Delocalized carbocation: Carboxyl oxygen gets protonated to give delocalized carbocation, making it a better electrophile.
-Transfer of proton: A proton is transferred to the hydroxyl group to form a good leaving group.
-Formation of pi bond: The hydroxyl group donates a pair of electrons to form a $\pi$ bond.
Ester formation: Deprotonation leads to the ester formation
The dehydration of alcohols is done by heating the alcohols in the presence of a strong acid, at high temperatures to form alkenes.
The reaction of dehydration of primary alcohols is:
CH$_3$-CH$_2$-OH $\xrightarrow[\text{443K}]{\text{95%H$_2$SO$_4$}}$ CH$_2$=CH$_2$ +H$_2$O
The reaction of dehydration of secondary alcohols is:
CH$_3$-CH(OH)-CH$_3$ $\xrightarrow[\text{373K}]{\text{60%H$_2$SO$_4$}}$ CH$_3$-CH=CH$_2$ +H$_2$O
The reaction of dehydration of tertiary alcohols is:
CH$_3$-CH(OH)(CH$_3$)-CH$_3$ $\xrightarrow[\text{423K}]{\text{ Al$_2$O$_3$}}$ CH$_3$-C(CH$_3$)=CH$_2$ +H$_2$O
From the above written we get to know the dehydration of alcohols, but there is a difference between three of the reactions, i.e. the temperature required to proceed the reaction.
Thus, in the last we conclude that the esterification leads to ester formation, and dehydration of alcohols to alkenes.
Note:
Don’t get confused between the esterification, and the dehydration of alcohols. The end product in both reactions is different, but the similarity is involvement of alcohols. The dehydration of alcohol involves various conditions; the end product is alkene by the removal of water.
Complete step by step answer:
-Firstly, we will discuss the mechanism of esterification. This involves five steps
Cation formation
-Delocalized carbocation: Carboxyl oxygen gets protonated to give delocalized carbocation, making it a better electrophile.
-Transfer of proton: A proton is transferred to the hydroxyl group to form a good leaving group.
-Formation of pi bond: The hydroxyl group donates a pair of electrons to form a $\pi$ bond.
Ester formation: Deprotonation leads to the ester formation

The dehydration of alcohols is done by heating the alcohols in the presence of a strong acid, at high temperatures to form alkenes.
The reaction of dehydration of primary alcohols is:
CH$_3$-CH$_2$-OH $\xrightarrow[\text{443K}]{\text{95%H$_2$SO$_4$}}$ CH$_2$=CH$_2$ +H$_2$O
The reaction of dehydration of secondary alcohols is:
CH$_3$-CH(OH)-CH$_3$ $\xrightarrow[\text{373K}]{\text{60%H$_2$SO$_4$}}$ CH$_3$-CH=CH$_2$ +H$_2$O
The reaction of dehydration of tertiary alcohols is:
CH$_3$-CH(OH)(CH$_3$)-CH$_3$ $\xrightarrow[\text{423K}]{\text{ Al$_2$O$_3$}}$ CH$_3$-C(CH$_3$)=CH$_2$ +H$_2$O
From the above written we get to know the dehydration of alcohols, but there is a difference between three of the reactions, i.e. the temperature required to proceed the reaction.
Thus, in the last we conclude that the esterification leads to ester formation, and dehydration of alcohols to alkenes.
Note:
Don’t get confused between the esterification, and the dehydration of alcohols. The end product in both reactions is different, but the similarity is involvement of alcohols. The dehydration of alcohol involves various conditions; the end product is alkene by the removal of water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




