
Explain the function of roots.
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: The root is the subterranean or underground part of a plant’s body. It is non-green due to the total absence of chlorophyll. It is positively geotropic i.e its growth is towards the direction of gravity.
Complete answer:
Some general functions of roots are:
-They provide anchorage of the plant in the ground so that the plant can stand upright properly.
-Any surplus or extra amount of sugars manufactured during photosynthesis is stored in the roots.
-It is the place of interaction between the soil microorganisms such as fungi or bacteria to provide essential or beneficial nutrients to the plant.
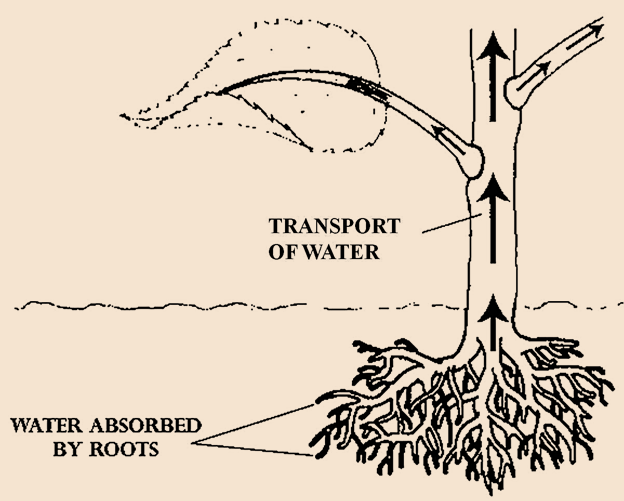
-Absorb water and minerals from the soil and transport it to all the cells of the plant body via xylem.
Some specialized functions of roots are:
-Mangroves such as Rhizophora growing in brackish water have upright, aerial roots called pneumatophores meant for gas exchange. These roots are negatively geotropic i.e against the gravity and positively phototropic i.e towards sunlight.
-In plants like carrot and potato, roots act as storage organs.
-Root nodule formation for nitrogen fixation in leguminous plants (Fabaceae). Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are present in the root nodules which convert the inert and abundant nitrogen in the atmosphere to usable forms such as nitrate.
-Coralloid roots of Cycas have cyanobacteria for nitrogen fixation.
-Higher plants have a symbiotic association with fungi via their roots. This mutual relationship is termed as Mycorrhiza. Fungi absorb useful nutrients particularly phosphorus to the plant and in return get shelter and protection by the plant.
Note:
There are three varieties of root systems in nature:
-In the tap root system, the primary root or taproot from the radicle persists, which is the thickest and largest of all. It penetrates deeper into the soil. Later, lateral roots i.e. primary and secondary roots develop from the main branch. This type of root system is observed in dicots e.g. Pea, Sunflower.
-In the fibrous root system, tufts of roots arise from a radicle which is nearly equal in size. The dense network of roots firmly holds the soil, thus, preventing soil erosion. The surface area for absorption substantially increases. Monocots usually portray the fibrous root system. E.g. wheat.
-Adventitious root system involves the growth of roots from parts other than radicle. They may be aerial or underground. E.g. Lower nodes of the stem bear roots to provide support to the plant in maize.
Complete answer:
Some general functions of roots are:
-They provide anchorage of the plant in the ground so that the plant can stand upright properly.
-Any surplus or extra amount of sugars manufactured during photosynthesis is stored in the roots.
-It is the place of interaction between the soil microorganisms such as fungi or bacteria to provide essential or beneficial nutrients to the plant.
-Absorb water and minerals from the soil and transport it to all the cells of the plant body via xylem.

Some specialized functions of roots are:
-Mangroves such as Rhizophora growing in brackish water have upright, aerial roots called pneumatophores meant for gas exchange. These roots are negatively geotropic i.e against the gravity and positively phototropic i.e towards sunlight.
-In plants like carrot and potato, roots act as storage organs.
-Root nodule formation for nitrogen fixation in leguminous plants (Fabaceae). Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are present in the root nodules which convert the inert and abundant nitrogen in the atmosphere to usable forms such as nitrate.
-Coralloid roots of Cycas have cyanobacteria for nitrogen fixation.
-Higher plants have a symbiotic association with fungi via their roots. This mutual relationship is termed as Mycorrhiza. Fungi absorb useful nutrients particularly phosphorus to the plant and in return get shelter and protection by the plant.
Note:
There are three varieties of root systems in nature:
-In the tap root system, the primary root or taproot from the radicle persists, which is the thickest and largest of all. It penetrates deeper into the soil. Later, lateral roots i.e. primary and secondary roots develop from the main branch. This type of root system is observed in dicots e.g. Pea, Sunflower.
-In the fibrous root system, tufts of roots arise from a radicle which is nearly equal in size. The dense network of roots firmly holds the soil, thus, preventing soil erosion. The surface area for absorption substantially increases. Monocots usually portray the fibrous root system. E.g. wheat.
-Adventitious root system involves the growth of roots from parts other than radicle. They may be aerial or underground. E.g. Lower nodes of the stem bear roots to provide support to the plant in maize.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




