
Explain how does (i) photoelectric current and kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted in a photocell vary if the frequency of incident radiation is doubled but keeping the intensity the same? Show the graphical variation in the above two cases.
Answer
561k+ views
Hint: As per Lernard study we have stopping potential is equal to the kinetic energy of the electrons ejected .
$V = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$ ,
Where,m is the mass, v is the velocity and V is stopping potential.
By experimental research done by scientists, we have two conclusions:
1. The maximum kinetic energy with which photoelectrons are emitted depends only on the frequency of the light incident.
2. The photoelectrons emitted per unit second depends on the intensity of incident light and is independent of its frequency.
Using the above conclusions we will solve the problem.
Complete step by step solution:
Photocurrent: maximum number of photoelectrons emitted per second is called photoelectric current .
By drawing the graph of photocurrent with frequency two different frequencies and providing the collector potential , we will make out a few conclusions:
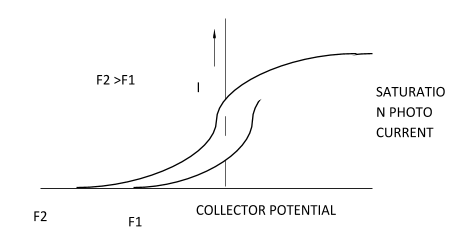
The graph explains us that photocurrent will remain unchanged , when light of different frequencies and different potentials is given to photoelectrons but of same intensity is provided.
Therefore, the number of photoelectrons emitted per second that is the photocurrent from the metal surface depends only on the intensity of the incident light and is independent of its frequency .
No matter what if the frequency is doubled, photocurrent remains the same, it depends only on the intensity of light .
Now, we will look at the kinetic energy .For kinetic energy we will redraw the graph with same frequencies and same stopping potential but with different intensities . To check the dependency of kinetic energy on frequency.
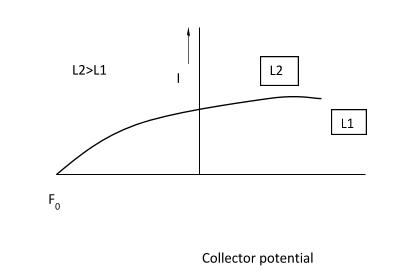
Now from the above graph ,having same frequency $f_0$ ,same collector potential and different intensities $I_1$ and $ l_2$ , concludes that the kinetic energy has no effect of intensity of light which is incident and is directly proportional to frequency ,therefore if frequency is doubled kinetic energy is also doubled.
Note:
Emission of photoelectrons takes place only when the frequency of the incident light is more than the certain minimum value called threshold frequency $f_0$. As soon as the incident light crosses the threshold frequency emission of photoelectrons takes place.
$V = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$ ,
Where,m is the mass, v is the velocity and V is stopping potential.
By experimental research done by scientists, we have two conclusions:
1. The maximum kinetic energy with which photoelectrons are emitted depends only on the frequency of the light incident.
2. The photoelectrons emitted per unit second depends on the intensity of incident light and is independent of its frequency.
Using the above conclusions we will solve the problem.
Complete step by step solution:
Photocurrent: maximum number of photoelectrons emitted per second is called photoelectric current .
By drawing the graph of photocurrent with frequency two different frequencies and providing the collector potential , we will make out a few conclusions:

The graph explains us that photocurrent will remain unchanged , when light of different frequencies and different potentials is given to photoelectrons but of same intensity is provided.
Therefore, the number of photoelectrons emitted per second that is the photocurrent from the metal surface depends only on the intensity of the incident light and is independent of its frequency .
No matter what if the frequency is doubled, photocurrent remains the same, it depends only on the intensity of light .

Now, we will look at the kinetic energy .For kinetic energy we will redraw the graph with same frequencies and same stopping potential but with different intensities . To check the dependency of kinetic energy on frequency.

Now from the above graph ,having same frequency $f_0$ ,same collector potential and different intensities $I_1$ and $ l_2$ , concludes that the kinetic energy has no effect of intensity of light which is incident and is directly proportional to frequency ,therefore if frequency is doubled kinetic energy is also doubled.
Note:
Emission of photoelectrons takes place only when the frequency of the incident light is more than the certain minimum value called threshold frequency $f_0$. As soon as the incident light crosses the threshold frequency emission of photoelectrons takes place.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




