
Ethyl amine on acetylation?
A. N-ethyl acetamide
B. Acetamide
C. Methyl acetamide
D. None
Answer
378.9k+ views
Hint: Acetylation is the addition of acetyl groups in the compound. Here, the amine group converts into the amide group with the substitution of the acetyl group in the compound.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Ethylamine has an amine group where nitrogen has a lone pair available for donation. Reagents used in acetylation reactions can be those containing acetyl functional groups like acid chloride, esters or anhydrides. Leaving group leaves the reagent and carbon of the carbonyl group becomes electron deficient. In the reaction called acetylation of amines, lone pair of nitrogen attacks on carbon of the carbonyl group and hydrogen of ethyl amine gets substituted with the acetyl functional group of a reagent. Nitrogen gets acetylated to give an amide product with the removal of HCl.
Ethyl amine on acetylation gives N-ethyl acetamide. In the given example reagent is acetyl chloride having Cl as a leaving group. The reaction is shown below:
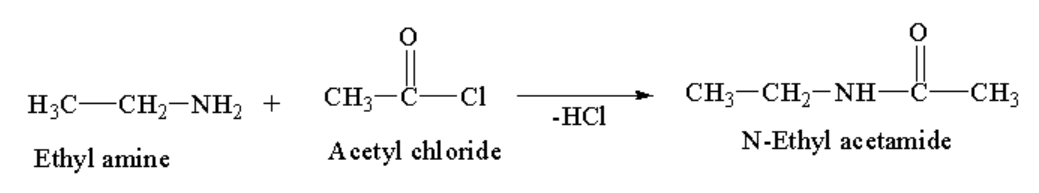
Image:Acetylation of ethyl amine
Initially the compound has an electronegative atom with no resonance in structure, but after acetylation, there is resonance in the system which stabilises the molecule. This is the driving force of the acetylation reaction.
So, the option A is correct.
Additional Information:Acetylation and deacetylation plays an important role in biological functions. Acetylation process can be seen in proteins during post translational modifications.
Acetylation brings stability to the system by converting the charged molecules into neutral ones.
Note: Firstly try to find the functional groups present in the reactant and their electron donor or accepting properties. Complete knowledge of amines, amides and their reaction will help to solve such types of reactions.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Ethylamine has an amine group where nitrogen has a lone pair available for donation. Reagents used in acetylation reactions can be those containing acetyl functional groups like acid chloride, esters or anhydrides. Leaving group leaves the reagent and carbon of the carbonyl group becomes electron deficient. In the reaction called acetylation of amines, lone pair of nitrogen attacks on carbon of the carbonyl group and hydrogen of ethyl amine gets substituted with the acetyl functional group of a reagent. Nitrogen gets acetylated to give an amide product with the removal of HCl.
Ethyl amine on acetylation gives N-ethyl acetamide. In the given example reagent is acetyl chloride having Cl as a leaving group. The reaction is shown below:

Image:Acetylation of ethyl amine
Initially the compound has an electronegative atom with no resonance in structure, but after acetylation, there is resonance in the system which stabilises the molecule. This is the driving force of the acetylation reaction.
So, the option A is correct.
Additional Information:Acetylation and deacetylation plays an important role in biological functions. Acetylation process can be seen in proteins during post translational modifications.
Acetylation brings stability to the system by converting the charged molecules into neutral ones.
Note: Firstly try to find the functional groups present in the reactant and their electron donor or accepting properties. Complete knowledge of amines, amides and their reaction will help to solve such types of reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




