
Establish the formula $\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{v}$ for a concave mirror, where symbols have their usual meanings.
Answer
601.2k+ views
Hint- A mirror formula can be defined as the formula that gives the relationship between object distance 'u', image distance 'v' and mirror focal length 'f'. The mirror formula is applicable for both plane mirrors and spherical mirrors (convex and concave mirrors).
Complete step-by-step solution -
The mirror formula is written as:
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{v}$
Let AB be an object placed on the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length f. u is the distance between the object and the mirror and v is the distance between the image and the mirror.
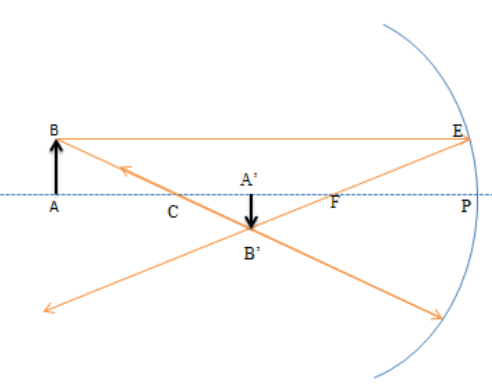
In the above figure
In $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta A'B'C$
$\Delta ABC \sim \Delta A'B'C$ (AA similarity rule)
$\dfrac{{AB}}{{A'B'}} = \dfrac{{AC}}{{A'C}}............\left( 1 \right)$
Similarly, in $\Delta FPE$ and $\Delta A'B'F$
$
\dfrac{{EP}}{{A'B'}} = \dfrac{{PF}}{{A'F}} \\
\dfrac{{AB}}{{A'B'}} = \dfrac{{PF}}{{A'F}}\left[ {AB = EP} \right].......\left( 2 \right) \\
$
From equation (1) and (2)
$
\dfrac{{AC}}{{A'C}} = \dfrac{{PF}}{{A'F}} \\
\dfrac{{A'C}}{{AC}} = \dfrac{{A'F}}{{PF}} \\
\dfrac{{\left( {CP - A'P} \right)}}{{\left( {AP - CP} \right)}} = \dfrac{{\left( {A'P - PF} \right)}}{{PF}} \\
$
Now, $PF = - f;CP = 2PF = -2f;AP = - u;A'P = - v$
Substituting the above values in the above relation, we will get the answer
$
\dfrac{{\left[ {\left( { - 2f} \right) - \left( { - v} \right)} \right]}}{{\left( { - u} \right) - \left( { - 2f} \right)}} = \dfrac{{\left[ {\left( { - v} \right) - \left( { - f} \right)} \right]}}{{\left( { - f} \right)}} \\
uv = fv + uf \\
\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{v} \\
$
Thus, the reciprocal of the focal length is numerically equal to the sum of the reciprocals of the distance of the object from the mirror and the distance of the image from the mirror.
Note- Assumptions for Derivation of Mirror Formula:
To obtain the mirror formula the following assumptions are taken. The distances are being measured from the pole of the mirror. According to the convention, the negative sign indicates the distance measured in the direction opposite to the incident ray while the positive sign indicates the distance measured in the direction of the incident ray. The distance below the axis is negative while the above distance is positive.
Complete step-by-step solution -
The mirror formula is written as:
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{v}$
Let AB be an object placed on the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length f. u is the distance between the object and the mirror and v is the distance between the image and the mirror.

In the above figure
In $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta A'B'C$
$\Delta ABC \sim \Delta A'B'C$ (AA similarity rule)
$\dfrac{{AB}}{{A'B'}} = \dfrac{{AC}}{{A'C}}............\left( 1 \right)$
Similarly, in $\Delta FPE$ and $\Delta A'B'F$
$
\dfrac{{EP}}{{A'B'}} = \dfrac{{PF}}{{A'F}} \\
\dfrac{{AB}}{{A'B'}} = \dfrac{{PF}}{{A'F}}\left[ {AB = EP} \right].......\left( 2 \right) \\
$
From equation (1) and (2)
$
\dfrac{{AC}}{{A'C}} = \dfrac{{PF}}{{A'F}} \\
\dfrac{{A'C}}{{AC}} = \dfrac{{A'F}}{{PF}} \\
\dfrac{{\left( {CP - A'P} \right)}}{{\left( {AP - CP} \right)}} = \dfrac{{\left( {A'P - PF} \right)}}{{PF}} \\
$
Now, $PF = - f;CP = 2PF = -2f;AP = - u;A'P = - v$
Substituting the above values in the above relation, we will get the answer
$
\dfrac{{\left[ {\left( { - 2f} \right) - \left( { - v} \right)} \right]}}{{\left( { - u} \right) - \left( { - 2f} \right)}} = \dfrac{{\left[ {\left( { - v} \right) - \left( { - f} \right)} \right]}}{{\left( { - f} \right)}} \\
uv = fv + uf \\
\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{v} \\
$
Thus, the reciprocal of the focal length is numerically equal to the sum of the reciprocals of the distance of the object from the mirror and the distance of the image from the mirror.
Note- Assumptions for Derivation of Mirror Formula:
To obtain the mirror formula the following assumptions are taken. The distances are being measured from the pole of the mirror. According to the convention, the negative sign indicates the distance measured in the direction opposite to the incident ray while the positive sign indicates the distance measured in the direction of the incident ray. The distance below the axis is negative while the above distance is positive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




