
What is equivalent resistance? Derive the expression for effective resistance of two resistors connected in parallel.
Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint:The word “equivalent” means the total. To derive the expression for effective resistance in the parallel combination of the two resistors, draw the circuit diagram of the two resistors connected parallel to each other. Use Kirchhoff’s current law to express the current at the junction to derive the expression.
Complete step by step answer:
Equivalent resistance is nothing but the total resistance in the circuit. If we connect the number of resistors one after another to the same wire, the total resistance of the wire increases because the resistance of each resistor adds up. Also, when we connect the number of resistors parallel to each other, the total resistance of the circuit decreases. Thus, we can say that the equivalent resistance is the resistance encountered by the whole circuit.Let the two resistors are connected in parallel combination as shown in the figure below.
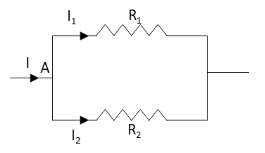
We know that the voltage in the parallel arm remains the same. Therefore, the voltage across the resistor \[{R_1}\] and the voltage across the resistor \[{R_2}\] is the same.Applying Kirchhoff’s current law at the junction A in the above circuit, we get,
\[I = {I_1} + {I_2}\]
Using Ohm’s law, we can write the above equation as,
\[\dfrac{V}{{{R_{eff}}}} = \dfrac{V}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{V}{{{R_2}}}\]
Here, \[{R_{eff}}\] is the effective resistance of the two resistors and V is the voltage which is the same across the two resistors.
Simplifying the above equation, we get,
\[\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eff}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}\]
\[ \therefore {R_{eff}} = \dfrac{{{R_1}{R_2}}}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}}\]
This is the required expression for the effective resistance of the two resistors connected parallel to each other.
Note:Students can also derive the expression for effective resistance in the series combination of the two resistors in the same manner as we have done in the above section. Remember, the current remains the same in series combination and the voltage remains the same in parallel combination. This is the key to derive the expression for both effective resistances in the series combination and the parallel combination. Also, students should remember KVL and KCL.
Complete step by step answer:
Equivalent resistance is nothing but the total resistance in the circuit. If we connect the number of resistors one after another to the same wire, the total resistance of the wire increases because the resistance of each resistor adds up. Also, when we connect the number of resistors parallel to each other, the total resistance of the circuit decreases. Thus, we can say that the equivalent resistance is the resistance encountered by the whole circuit.Let the two resistors are connected in parallel combination as shown in the figure below.

We know that the voltage in the parallel arm remains the same. Therefore, the voltage across the resistor \[{R_1}\] and the voltage across the resistor \[{R_2}\] is the same.Applying Kirchhoff’s current law at the junction A in the above circuit, we get,
\[I = {I_1} + {I_2}\]
Using Ohm’s law, we can write the above equation as,
\[\dfrac{V}{{{R_{eff}}}} = \dfrac{V}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{V}{{{R_2}}}\]
Here, \[{R_{eff}}\] is the effective resistance of the two resistors and V is the voltage which is the same across the two resistors.
Simplifying the above equation, we get,
\[\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eff}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}\]
\[ \therefore {R_{eff}} = \dfrac{{{R_1}{R_2}}}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}}\]
This is the required expression for the effective resistance of the two resistors connected parallel to each other.
Note:Students can also derive the expression for effective resistance in the series combination of the two resistors in the same manner as we have done in the above section. Remember, the current remains the same in series combination and the voltage remains the same in parallel combination. This is the key to derive the expression for both effective resistances in the series combination and the parallel combination. Also, students should remember KVL and KCL.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




