
What is the energy stored in the capacitor between the terminals a and b of the network shown in the figure?
Capacitance of each capacitor $C=1\mu F$)
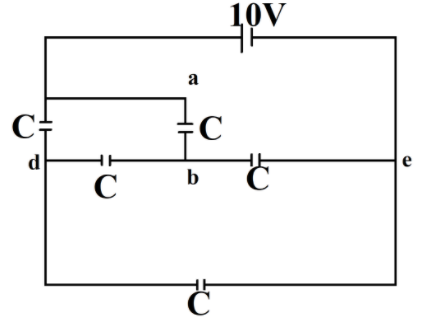
A. $12.5\mu J$
B. Zero
C. $25\mu J$
D. $50\mu J$

Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: If you look closely at the diagram, you will notice that there is a wheatstone network in here. It is a balanced Wheatstone network. So, it can easily be solved using the concept of a wheatstone bridge. In a balanced Wheatstone Bridge, It is said that both sides of the parallel bridge network are balanced since the voltage at point C is equal to the voltage at point D, with zero being the difference.
Formula used:
For solving this question, we will be using the formula
Q = CV
Step by step solution:
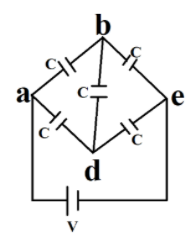
First, let us redraw the diagram to make it a Wheatstone network
Now, Applying the concept of the balanced Wheatstone bridge,
${{C}_{eq}}=C$
Now, The Charge on capacitor between the terminals a and b
$\dfrac{Q}{2}=\dfrac{CV}{2}$
Now, for the energy stored in the capacitor between a and b,
\[=\dfrac{{{(\dfrac{Q}{2})}^{2}}}{2C}=\dfrac{{{Q}^{2}}}{8C}\]
Now, using
Q = CV
We have
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow Q=\dfrac{{{C}^{2}}{{V}^{2}}}{8C} \\
& \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow Q=\dfrac{C{{V}^{2}}}{8}$
Now, as
$C=1\mu F$
And, V = 10 V
Takin the given values,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow U=\dfrac{(1\times {{10}^{-6}})\times {{10}^{2}}}{2C} \\
& \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow U=\dfrac{100}{8}\times {{10}^{-6}}$
$\Rightarrow U=12.5\mu J$
So, the energy stored in the capacitor between the terminals a and b of the network shown in the figure will be $12.5\mu J$, i.e., Option – A.
Note:
The network (or bridge) of Wheatstone is a circuit for indirect resistance calculation by a null reference approach relative to an established normal resistance. It consists of four R1, R2, R3 and R4 resistors connected to a quadrilateral ABCD. The Wheatstone bridge was created by the British Scientist, mathematician and physicist, Samuel Hunter Christie in 1843.
Formula used:
For solving this question, we will be using the formula
Q = CV
Step by step solution:
First, let us redraw the diagram to make it a Wheatstone network
Now, Applying the concept of the balanced Wheatstone bridge,
${{C}_{eq}}=C$
Now, The Charge on capacitor between the terminals a and b

$\dfrac{Q}{2}=\dfrac{CV}{2}$
Now, for the energy stored in the capacitor between a and b,
\[=\dfrac{{{(\dfrac{Q}{2})}^{2}}}{2C}=\dfrac{{{Q}^{2}}}{8C}\]
Now, using
Q = CV
We have
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow Q=\dfrac{{{C}^{2}}{{V}^{2}}}{8C} \\
& \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow Q=\dfrac{C{{V}^{2}}}{8}$
Now, as
$C=1\mu F$
And, V = 10 V
Takin the given values,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow U=\dfrac{(1\times {{10}^{-6}})\times {{10}^{2}}}{2C} \\
& \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow U=\dfrac{100}{8}\times {{10}^{-6}}$
$\Rightarrow U=12.5\mu J$
So, the energy stored in the capacitor between the terminals a and b of the network shown in the figure will be $12.5\mu J$, i.e., Option – A.
Note:
The network (or bridge) of Wheatstone is a circuit for indirect resistance calculation by a null reference approach relative to an established normal resistance. It consists of four R1, R2, R3 and R4 resistors connected to a quadrilateral ABCD. The Wheatstone bridge was created by the British Scientist, mathematician and physicist, Samuel Hunter Christie in 1843.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




