
What effect does the concentration of H+ (aq) ions have on the nature of the solution?
Answer
607.2k+ views
Hint: ${H^ + }$ is the representation of the isolated hydrogen ion. It is used to represent protons as well.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The following are the effects of ${H^ + }$ concentration on the nature of the solution:
The concentration of ${H^ + }$ (aq) ions determine the acidic nature of the solution. Hence, the acidity of a solution increases with increase in the concentration of ${H^ + }$ (aq) ions.
The acidity of a solution decreases with decrease in the concentration of ${H^ + }$ (aq) ions.
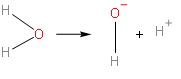
$\left[ {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O} \right]\text{ }\xrightarrow{\text{ionization}}\text{ }{{\left[ \text{OH} \right]}^{-}}\text{ + }{{\left[ \text{H} \right]}^{\text{+}}}$
Hydrogen ions are created when hydrogen atoms lose or gain an electron. A positively charged hydrogen ion or proton can readily combine with other particles and therefore is only seen isolated when it is in a gaseous state or a nearby particle-free space.
Therefore, we can say that the presence of ${H^ + }$ (aq) ions increases the acidic nature of the solution.
Additional Information:
If the pH of a solution is less than 7 the solution is acidic.
If the pH is about 7 the solution is neutral.
If the pH is greater than 7 the solution is basic.
If the soil is acidic then it should be treated with quicklime or slaked lime to make it neutralize so that soil can be made proper for cultivation.
Note: Basic solutions also have ${H^ + }$ (aq) ions. But the concentration of the ${H^ + }$ (aq) ions is less than the concentration of OH- ions. So the solutions are basic in nature.
The atomic number of hydrogen is 1 and mass number is also 1. So in an hydrogen atom, there is 1 proton, 0 neutrons, and 1 electron. After losing 1 electron, it is left with only 1 proton.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The following are the effects of ${H^ + }$ concentration on the nature of the solution:
The concentration of ${H^ + }$ (aq) ions determine the acidic nature of the solution. Hence, the acidity of a solution increases with increase in the concentration of ${H^ + }$ (aq) ions.
The acidity of a solution decreases with decrease in the concentration of ${H^ + }$ (aq) ions.

$\left[ {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O} \right]\text{ }\xrightarrow{\text{ionization}}\text{ }{{\left[ \text{OH} \right]}^{-}}\text{ + }{{\left[ \text{H} \right]}^{\text{+}}}$
Hydrogen ions are created when hydrogen atoms lose or gain an electron. A positively charged hydrogen ion or proton can readily combine with other particles and therefore is only seen isolated when it is in a gaseous state or a nearby particle-free space.
Therefore, we can say that the presence of ${H^ + }$ (aq) ions increases the acidic nature of the solution.
Additional Information:
If the pH of a solution is less than 7 the solution is acidic.
If the pH is about 7 the solution is neutral.
If the pH is greater than 7 the solution is basic.
If the soil is acidic then it should be treated with quicklime or slaked lime to make it neutralize so that soil can be made proper for cultivation.
Note: Basic solutions also have ${H^ + }$ (aq) ions. But the concentration of the ${H^ + }$ (aq) ions is less than the concentration of OH- ions. So the solutions are basic in nature.
The atomic number of hydrogen is 1 and mass number is also 1. So in an hydrogen atom, there is 1 proton, 0 neutrons, and 1 electron. After losing 1 electron, it is left with only 1 proton.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




