
During meiotic division the
(a) Homologous chromosomes are separated
(b) The linkage is disturbed
(c) The Homologous chromosomes do not segregate
(d) All of the above
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: During the meiotic division, the diploid chromosome will get converted into the haploid chromosomes. For this process to occur, the paired chromosomes will come discrete.
During the anaphase I of the meiosis, the homologous chromosomes will get separated.
This kind of cell division occurs to reduce the chromosome number by half. It is involved in the production of haploid daughter cells. Meiosis will form haploid cells and during fertilization, the diploid phase will be restored.
Complete answer:
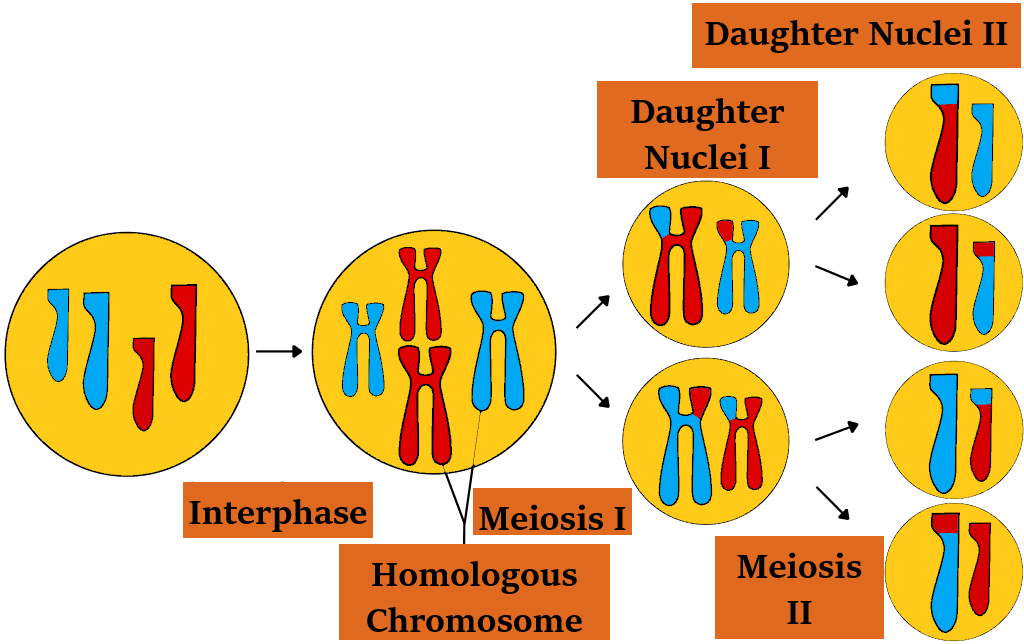
Meiosis is divided into two phases. Meiosis I and meiosis II. The homologous chromosomes will get separated at meiosis I and thus this answer is mainly concentrated only on Meiosis I.
Meiosis I
Prophase I: Prophase I is the first phase of meiosis I. Prophase I has five phases based on chromosomal behavior. They are Leptotene, Zygotene, Pachytene, Diplotene, and Diakinesis.
Leptotene: The chromosome undergoes compaction.
Zygotene: The chromosome starts to pair with each other and this is called synapsis. The paired chromosomes are called a Homologous chromosome. The complex formed by this pair of the synapsed chromosome is known as a bivalent or tetrad.
Pachytene: The bivalent chromosomes appear to be more prominent and are called tetrads. Recombination nodules will appear and the cross over will take place between the non-sister chromatids of the homologous chromosome. The crossing over is responsible for genetic material exchange.
Diplotene: The synaptonemal complex undergoes dissolution and the recombined chromosome will get separated except at the cross over the site. The chromosome appears to be X in shape and is called chiasmata.
Diakinesis: The chiasmata termination occurs. The fully condensed chromosomes are formed and the meiotic spindle will get prepared and assembled for the separation of Homologous chromosomes. The nucleolus will disappear and the nuclear envelope forms.
Metaphase I: The alignment of the bivalent chromosomes occurs on the equatorial plane. The microtubules from opposite poles will attach to each of the homologous chromosomes.
Anaphase I: During this phase, the homologous chromosome gets separated but the sister chromatids will be attached to the centromere.
Telophase l: The nuclear membrane as well as the nucleolus will reappear. Cytokinesis occurs and thus two daughter cells are formed.
Meiosis II: prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II will take place. At the end of the meiosis II, 4 haploid daughter cells will be formed.
So, the correct answer is, ‘The homologous chromosomes are separated’.
Note: Before the start of the cell division, the cells will remain in the interphase. The longest step of the cell cycle is interphase. The cell grows to its full size during this process, performs its normal cellular functions, replicates its DNA, and prepares for cell division.
During the anaphase I of the meiosis, the homologous chromosomes will get separated.
This kind of cell division occurs to reduce the chromosome number by half. It is involved in the production of haploid daughter cells. Meiosis will form haploid cells and during fertilization, the diploid phase will be restored.
Complete answer:
Meiosis is divided into two phases. Meiosis I and meiosis II. The homologous chromosomes will get separated at meiosis I and thus this answer is mainly concentrated only on Meiosis I.
Meiosis I
Prophase I: Prophase I is the first phase of meiosis I. Prophase I has five phases based on chromosomal behavior. They are Leptotene, Zygotene, Pachytene, Diplotene, and Diakinesis.
Leptotene: The chromosome undergoes compaction.
Zygotene: The chromosome starts to pair with each other and this is called synapsis. The paired chromosomes are called a Homologous chromosome. The complex formed by this pair of the synapsed chromosome is known as a bivalent or tetrad.
Pachytene: The bivalent chromosomes appear to be more prominent and are called tetrads. Recombination nodules will appear and the cross over will take place between the non-sister chromatids of the homologous chromosome. The crossing over is responsible for genetic material exchange.
Diplotene: The synaptonemal complex undergoes dissolution and the recombined chromosome will get separated except at the cross over the site. The chromosome appears to be X in shape and is called chiasmata.
Diakinesis: The chiasmata termination occurs. The fully condensed chromosomes are formed and the meiotic spindle will get prepared and assembled for the separation of Homologous chromosomes. The nucleolus will disappear and the nuclear envelope forms.
Metaphase I: The alignment of the bivalent chromosomes occurs on the equatorial plane. The microtubules from opposite poles will attach to each of the homologous chromosomes.
Anaphase I: During this phase, the homologous chromosome gets separated but the sister chromatids will be attached to the centromere.
Telophase l: The nuclear membrane as well as the nucleolus will reappear. Cytokinesis occurs and thus two daughter cells are formed.
Meiosis II: prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II will take place. At the end of the meiosis II, 4 haploid daughter cells will be formed.

So, the correct answer is, ‘The homologous chromosomes are separated’.
Note: Before the start of the cell division, the cells will remain in the interphase. The longest step of the cell cycle is interphase. The cell grows to its full size during this process, performs its normal cellular functions, replicates its DNA, and prepares for cell division.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




