
How can I draw the following esters: ethyl butanoate, pentyl propanoate, propyl 3-ethylhexanoate?
Answer
555.3k+ views
Hint: We know that the ester is a chemical compound which is derived from an acid, in which an –OH group is replaced by –OR group. So, the structure of ether is RCOOR. Here, R represents the alkyl groups.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s discuss the naming of an ester. The naming of ester is done as if the alkyl chain from the alcohol is a substituent. Then, we do not need to assign numbers to the alkyl chain. Then, we have to name the parent chain from the carboxylic acid part of ester. Then, the ‘e’ of the parent should be replaced with ‘oate’. Then, the R group bonded to the O atom is named as substituent (prefix). Let’s understand with the help of an example,
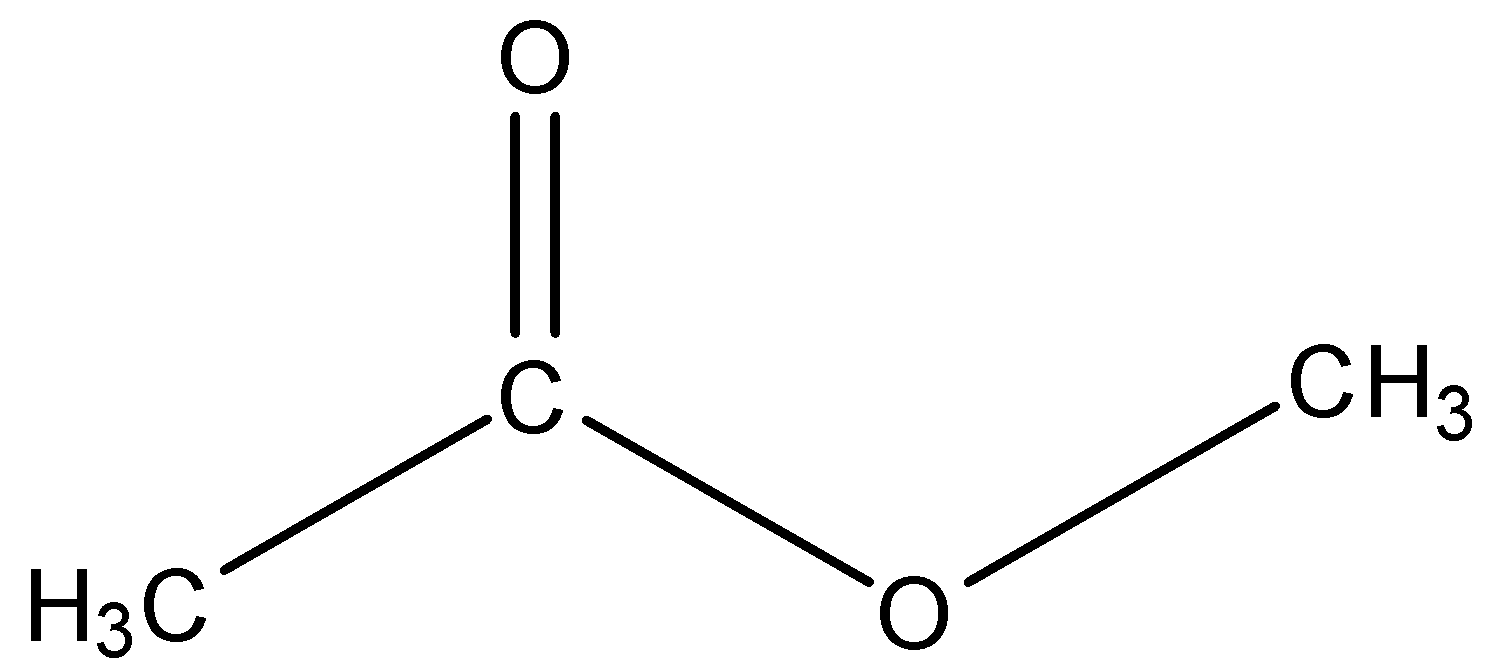
As the carboxylic part contains two carbon atoms. So, the name of the parent chain is ‘ethanoate’ and the methyl group is bonded to the O atom. So, the name of the ester is Methyl ethanoate.
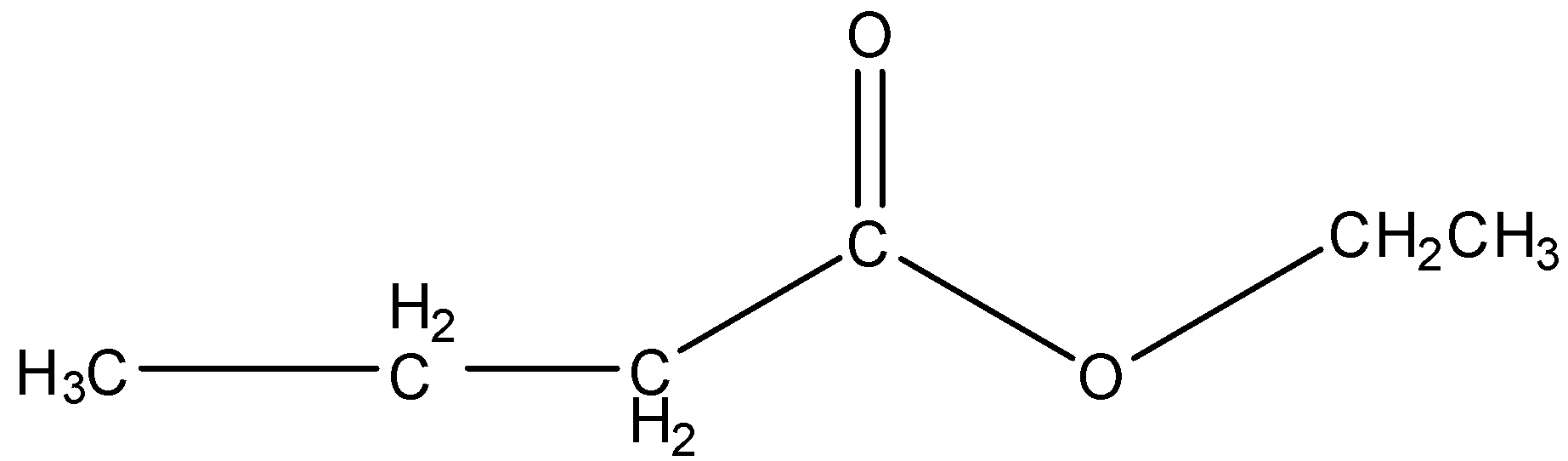
Now, come to the question. We have to draw the structure of ‘ethyl butanoate’. ‘Butanoate’ indicates that the carboxylic part of ester contains four carbon atoms and ethyl is the substituent bonded to the O atom. So, the structure of ethyl butanoate is,
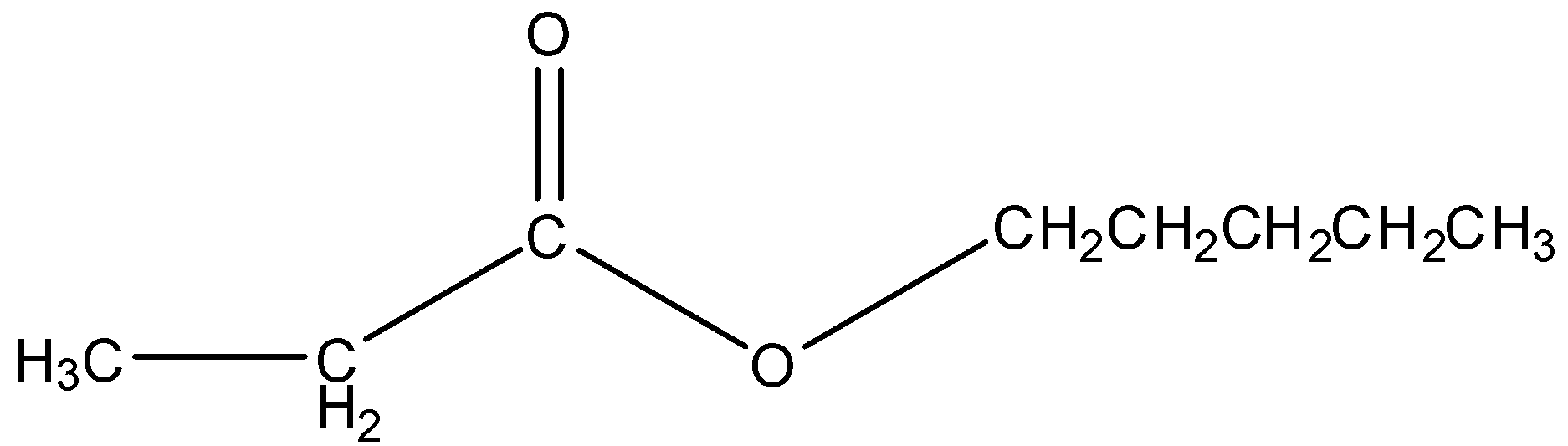
Similarly, in pentyl propanoate, a pentyl group is bonded to the O atom and there are three carbon atoms in the carboxyl part. So, the structure of pentyl propanoate is
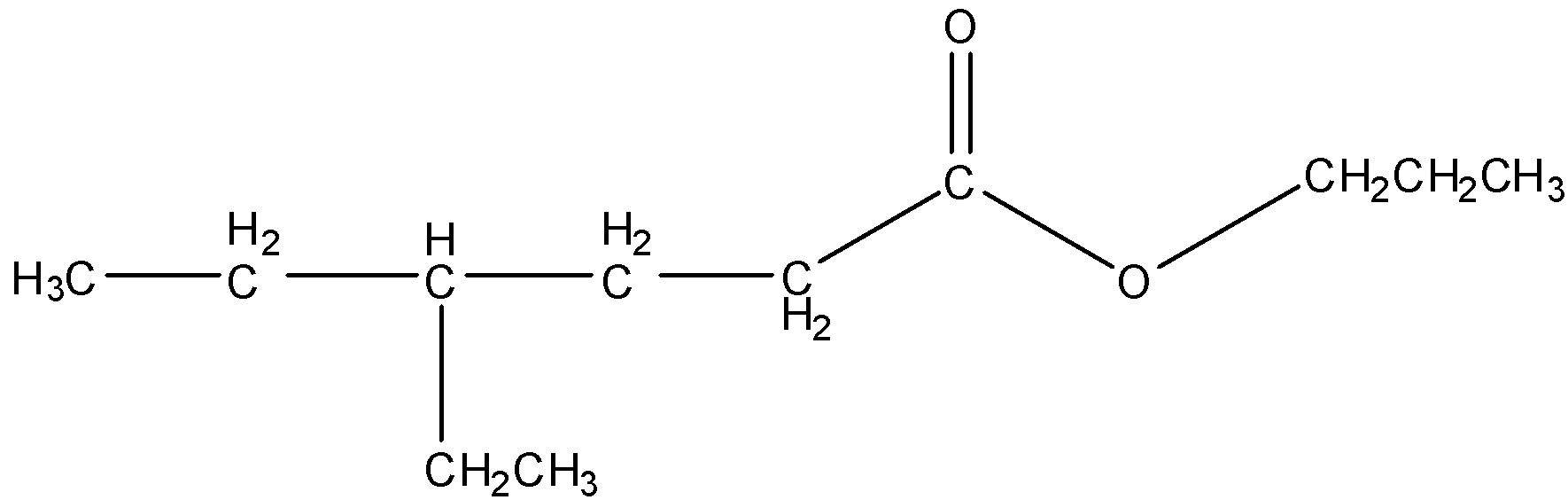
In propyl 3-ethylhexanoate, the carboxyl part contains a chain of six carbon atoms with an ethyl group on C3. And a propyl group is bonded to the O atom.
Note: It is to be noted that when carboxylic acid undergoes reaction with alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst, ester formation takes place. The acid catalyst that is commonly used in this reaction is concentrated sulphuric acid .
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s discuss the naming of an ester. The naming of ester is done as if the alkyl chain from the alcohol is a substituent. Then, we do not need to assign numbers to the alkyl chain. Then, we have to name the parent chain from the carboxylic acid part of ester. Then, the ‘e’ of the parent should be replaced with ‘oate’. Then, the R group bonded to the O atom is named as substituent (prefix). Let’s understand with the help of an example,

As the carboxylic part contains two carbon atoms. So, the name of the parent chain is ‘ethanoate’ and the methyl group is bonded to the O atom. So, the name of the ester is Methyl ethanoate.
Now, come to the question. We have to draw the structure of ‘ethyl butanoate’. ‘Butanoate’ indicates that the carboxylic part of ester contains four carbon atoms and ethyl is the substituent bonded to the O atom. So, the structure of ethyl butanoate is,

Similarly, in pentyl propanoate, a pentyl group is bonded to the O atom and there are three carbon atoms in the carboxyl part. So, the structure of pentyl propanoate is

In propyl 3-ethylhexanoate, the carboxyl part contains a chain of six carbon atoms with an ethyl group on C3. And a propyl group is bonded to the O atom.

Note: It is to be noted that when carboxylic acid undergoes reaction with alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst, ester formation takes place. The acid catalyst that is commonly used in this reaction is concentrated sulphuric acid .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




