
Draw a plot showing the variation of (i) electric field (E) and (ii) electric potential (V) with the distance r for a point charge Q.
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: When a point charge particle is placed at a point, it creates a force field around it. This is called the electric field (E). Now, when you move a point unit charge under this field from infinity to a particular point, the work done by the particle is called electric potential. Electric potential difference between two points is equal to work done by the unit charge point particle moving one point to another.
Complete step by step answer:
A point particle with charge Q placed at origin. From Coulomb’s law, the electric field of the charge will be,\[=\dfrac{Q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{r}^{2}}}\widehat{r}\], assuming that it is placed in free space and \[{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\] is electric permittivity of free space. It is acting in the positive direction of r.
Now, according to definition above, the electric potential will be, \[V(r)=-\int\limits_{\infty }^{r}{}\cdot d\]. Now, putting the form of electric field and integrating over dr, we get that, \[V(r)=-\dfrac{Q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}r}\].
Now, plotting these two functions with respect to r, we get
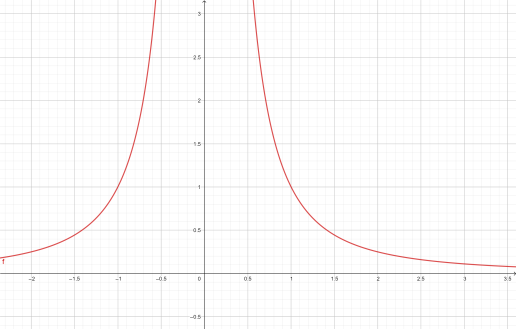
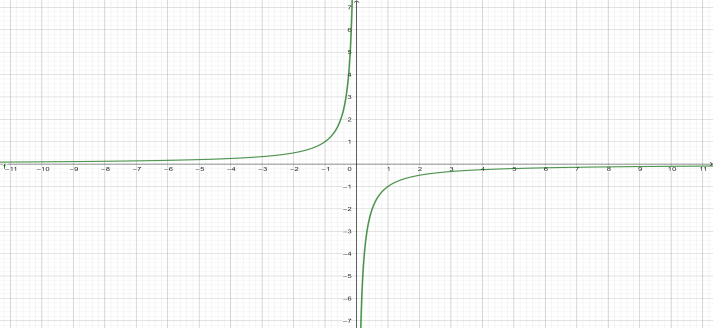
Fig-1: Electric field Fig-2: Electric potential
If we closely look at it we will see, in both cases if we take r close to origin value of potential and field goes very high. And we are ignoring the negative section of the plot, since in polar coordinates only positive values of r exist.
Note:
The S.I unit of the electric field is Newton/coulomb (N/C) which is the same as volt/meter (V/m). The S.I unit of electric potential is volt (V). In a cgs unit or Gaussian unit, the unit of electric field and electric potential is stat volt/stat coulomb and stat volt.
Complete step by step answer:
A point particle with charge Q placed at origin. From Coulomb’s law, the electric field of the charge will be,\[=\dfrac{Q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{r}^{2}}}\widehat{r}\], assuming that it is placed in free space and \[{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\] is electric permittivity of free space. It is acting in the positive direction of r.
Now, according to definition above, the electric potential will be, \[V(r)=-\int\limits_{\infty }^{r}{}\cdot d\]. Now, putting the form of electric field and integrating over dr, we get that, \[V(r)=-\dfrac{Q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}r}\].
Now, plotting these two functions with respect to r, we get


Fig-1: Electric field Fig-2: Electric potential
If we closely look at it we will see, in both cases if we take r close to origin value of potential and field goes very high. And we are ignoring the negative section of the plot, since in polar coordinates only positive values of r exist.
Note:
The S.I unit of the electric field is Newton/coulomb (N/C) which is the same as volt/meter (V/m). The S.I unit of electric potential is volt (V). In a cgs unit or Gaussian unit, the unit of electric field and electric potential is stat volt/stat coulomb and stat volt.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




