
How does glucose convert to pyruvate?
Answer
519.9k+ views
Hint: Glycolysis is the process of breakdown of glucose or similar hexose sugar into two molecules of pyruvic acid through a series of enzyme mediated reactions releasing some energy in the form of ATP and reducing power as NADH. This reaction takes place in the cytoplasm.
Complete answer:
To begin with, we must know the discoverer. It was discovered by Embden, Meyerhof and Parnas and so the process of glycolysis is also known as the EMP pathway.
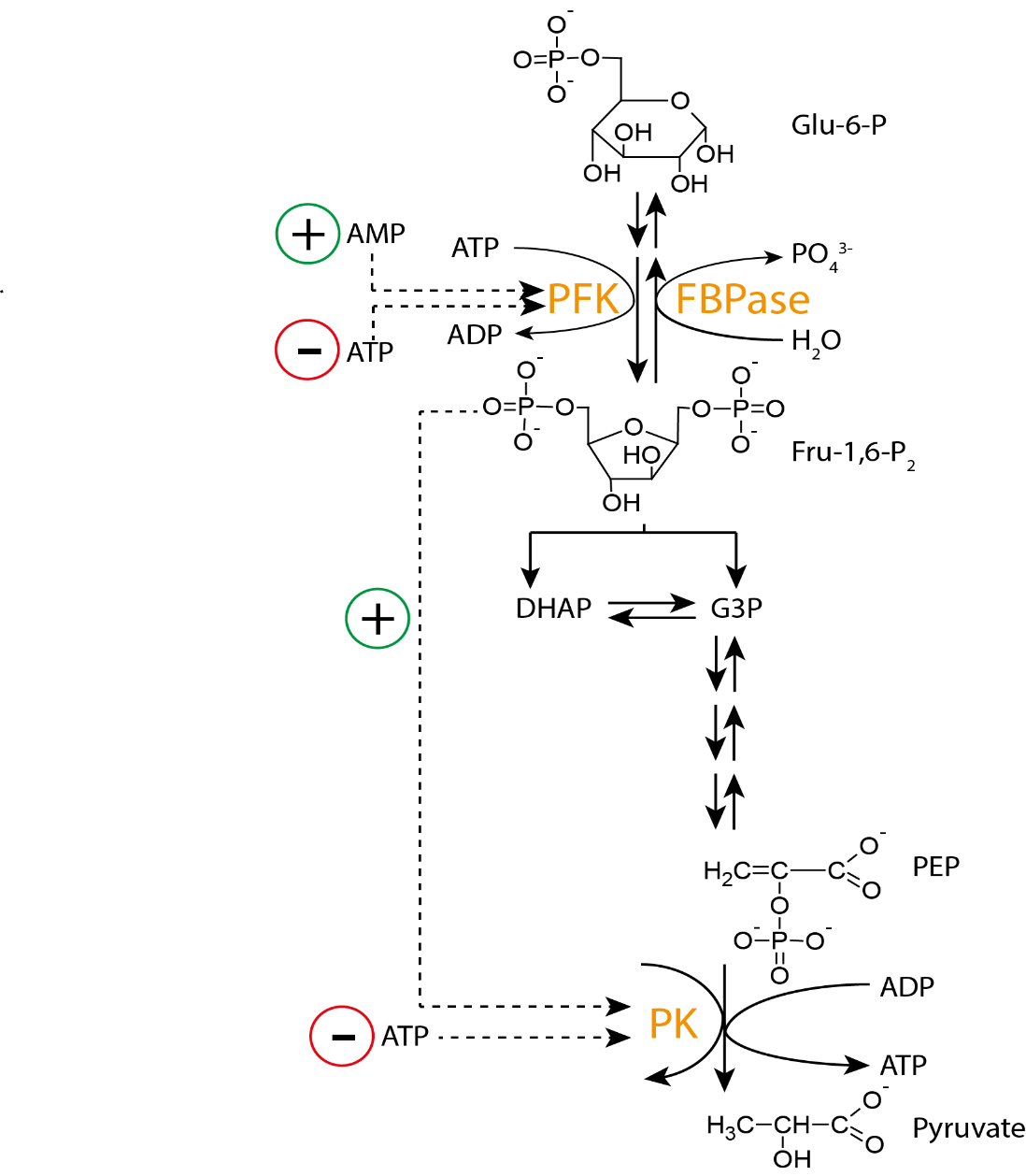
It begins with breaking of glucose into glucose-6-phosphate in the presence of hexokinase and mg, which in turns get isomerized to fructose-6-phosphate in the presence of phosphate isomerase.
Now this fructose-6-phosphate gets converted into fructose-1,6-bisphosphate in the presence of phosphofructokinase, which in the presence of enzyme aldolase, splits into – 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde (3 PGAL) and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP), that are interconvertible.
In the next step, we will see phosphoglycerate kinase catalysis which is the formation of 1-3 diphosphoglycerate from 3-PGAL.
Consequently, 3-phosphoglycerate is converted into 2-phosphoglycerate and phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). Using PEP, the enzyme pyruvate kinase catalyses the formation of pyruvate and liberates ATP.
This is a schematic diagram of conversion of glucose to pyruvic acid or pyruvate. This step by step breakdown will make the conversion even more clear to you.
Note:
Glycolysis is the common phase of aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
It is a series of 10 biochemical reactions which occur in cytoplasm . In this process 10 enzymes are used forming 11 substrates.
The conversion of glucose to fructose 1,6 – Bisphosphate is known as phosphorylation.
Complete answer:
To begin with, we must know the discoverer. It was discovered by Embden, Meyerhof and Parnas and so the process of glycolysis is also known as the EMP pathway.
It begins with breaking of glucose into glucose-6-phosphate in the presence of hexokinase and mg, which in turns get isomerized to fructose-6-phosphate in the presence of phosphate isomerase.
Now this fructose-6-phosphate gets converted into fructose-1,6-bisphosphate in the presence of phosphofructokinase, which in the presence of enzyme aldolase, splits into – 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde (3 PGAL) and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP), that are interconvertible.
In the next step, we will see phosphoglycerate kinase catalysis which is the formation of 1-3 diphosphoglycerate from 3-PGAL.
Consequently, 3-phosphoglycerate is converted into 2-phosphoglycerate and phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). Using PEP, the enzyme pyruvate kinase catalyses the formation of pyruvate and liberates ATP.
This is a schematic diagram of conversion of glucose to pyruvic acid or pyruvate. This step by step breakdown will make the conversion even more clear to you.

Note:
Glycolysis is the common phase of aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
It is a series of 10 biochemical reactions which occur in cytoplasm . In this process 10 enzymes are used forming 11 substrates.
The conversion of glucose to fructose 1,6 – Bisphosphate is known as phosphorylation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




