
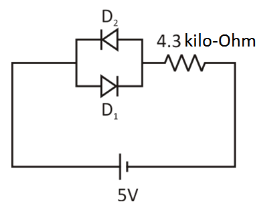
Diodes \[D - 1\] and \[{D_2}\] shown in circuit are silicon diodes. The voltage drop (\[V\]) across the diode \[{D_2}\] and the power dissipated (\[P\]) by this diode (\[{D_2}\]) are

Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint:First of all, we will analyze the given circuit, to look for the diode which is forward biased and the diode which is reversed biased. In a parallel connection the voltage remains the same in all the elements. However, that does not mean that current remains the same.
Complete answer:
In the given figure, we can see that the diode \[{D_1}\] is forward biased and diode \[{D_2}\] is reversed biased. Since the diode \[{D_1}\] is biased forward the voltage drop across it is \[5\,{\text{V}}\]. Since the \[{D_1}\] and \[{{\text{D}}_2}\] diodes are linked in parallel, the voltage drop across is equal to that across \[{D_1}\], i.e. \[5\,{\text{V}}\].
Since \[{{\text{D}}_2}\] is biased in reverse, no current flows through it and so the power dissipated by \[{{\text{D}}_2}\] is zero. As we know, that power is the product of voltage and current. Since, the current is zero in reversed biased condition, hence power is also zero.
Hence, the required answer is \[{V_{{D_2}}} = 5\,{\text{V}}\] and \[{P_{{D_2}}} = 0\,{\text{W}}\].
Additional information:
Forward bias: The external voltage is delivered through the P-N junction diode by forward bias or biasing. The P-side of the diode is connected to the positive terminal in a forward bias configuration, and the N-side is fixed to the battery's negative side.
Diode: A diode is a semiconductor device that basically functions as a one-way current switch. It makes it possible for current to flow freely in one direction, but seriously limits current from flowing in the opposite direction.
Note:Remember that in an electric circuit, a diode (PN junction) allows current to flow more quickly in one direction than in another. Forward biasing means placing a voltage across a diode that makes it easier for current to pass, while reverse biasing means putting a voltage in the opposite direction across a diode.
Complete answer:
In the given figure, we can see that the diode \[{D_1}\] is forward biased and diode \[{D_2}\] is reversed biased. Since the diode \[{D_1}\] is biased forward the voltage drop across it is \[5\,{\text{V}}\]. Since the \[{D_1}\] and \[{{\text{D}}_2}\] diodes are linked in parallel, the voltage drop across is equal to that across \[{D_1}\], i.e. \[5\,{\text{V}}\].
Since \[{{\text{D}}_2}\] is biased in reverse, no current flows through it and so the power dissipated by \[{{\text{D}}_2}\] is zero. As we know, that power is the product of voltage and current. Since, the current is zero in reversed biased condition, hence power is also zero.
Hence, the required answer is \[{V_{{D_2}}} = 5\,{\text{V}}\] and \[{P_{{D_2}}} = 0\,{\text{W}}\].
Additional information:
Forward bias: The external voltage is delivered through the P-N junction diode by forward bias or biasing. The P-side of the diode is connected to the positive terminal in a forward bias configuration, and the N-side is fixed to the battery's negative side.
Diode: A diode is a semiconductor device that basically functions as a one-way current switch. It makes it possible for current to flow freely in one direction, but seriously limits current from flowing in the opposite direction.
Note:Remember that in an electric circuit, a diode (PN junction) allows current to flow more quickly in one direction than in another. Forward biasing means placing a voltage across a diode that makes it easier for current to pass, while reverse biasing means putting a voltage in the opposite direction across a diode.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




