
D-glucose and D-galactose are components of lactose
A) True
B) False
Answer
513.9k+ views
Hint: Lactose is known as milk sugar. It is a disaccharide that is composed of two molecules of monosaccharide. Starch is an example of a polysaccharide. Glucose and galactose are the examples of a monosaccharide.
Complete answer:
The carbohydrates are divided into monosaccharide, disaccharide and polysaccharide depending on the repeating units present in the molecule. For example, Lactose is a disaccharide sugar composed of galactose and glucose subunits. Lactose is present in milk and makes up around 2–8% of milk (by weight).
The name Lactose comes from lac (gen. lactis) the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix -ose used to name sugars It is used in the food industry. In lactose glucose and galactose are bound together by beta 1,4 glycosidic linkage. The figure below shows the structure of lactose. The bond is formed between D-galactose and D-glucose.
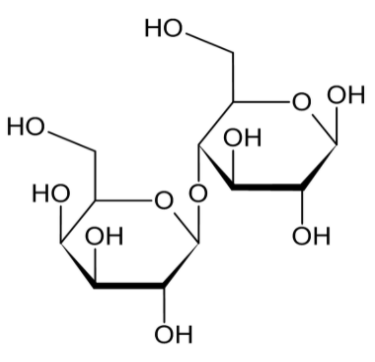
D-glucose is a short form of dextrorotatory glucose. It is one of the two stereoisomers of glucose and it is biologically active. It is produced in plants as a product of photosynthesis. In animals and fungi, it is the result of the breakdown of glycogen. It is a monosaccharide. Galactose is a sugar found in milk. Galactose is a monosaccharide. So, it is true that D-glucose and galactose are components of lactose.
Thus, the correct option is ‘A’ i.e True.
Note: The only difference between D-glucose and D-galactose is in the carbon-4. In the case of D-glucose, the -OH is on the right in Fischer Projection, and in the case of D-galactose, the -OH group is on the left. This is the only difference between D-glucose and D-galactose epimers. They are neither enantiomers nor diastereomers or isomers, they are only epimers.
Complete answer:
The carbohydrates are divided into monosaccharide, disaccharide and polysaccharide depending on the repeating units present in the molecule. For example, Lactose is a disaccharide sugar composed of galactose and glucose subunits. Lactose is present in milk and makes up around 2–8% of milk (by weight).
The name Lactose comes from lac (gen. lactis) the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix -ose used to name sugars It is used in the food industry. In lactose glucose and galactose are bound together by beta 1,4 glycosidic linkage. The figure below shows the structure of lactose. The bond is formed between D-galactose and D-glucose.

D-glucose is a short form of dextrorotatory glucose. It is one of the two stereoisomers of glucose and it is biologically active. It is produced in plants as a product of photosynthesis. In animals and fungi, it is the result of the breakdown of glycogen. It is a monosaccharide. Galactose is a sugar found in milk. Galactose is a monosaccharide. So, it is true that D-glucose and galactose are components of lactose.
Thus, the correct option is ‘A’ i.e True.
Note: The only difference between D-glucose and D-galactose is in the carbon-4. In the case of D-glucose, the -OH is on the right in Fischer Projection, and in the case of D-galactose, the -OH group is on the left. This is the only difference between D-glucose and D-galactose epimers. They are neither enantiomers nor diastereomers or isomers, they are only epimers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




