
How to determine whether $f\left( x \right) = 3\sin 2x + 5$ is one-to-one function. How to find the inverse of the function?
Answer
562.2k+ views
Hint: For checking whether a function is one-one or not, we need to check its graph. If we draw a horizontal line on the graph, which cuts it at more than one point, then we say that the function is not one—one. But if every possible horizontal line cuts the graph at most one point, then we say that the function is a one-to-one function.
Complete step-by-step solution:
According to the question, the function is
$f\left( x \right) = 3\sin 2x + 5$
Considering the graph of the above function, we have
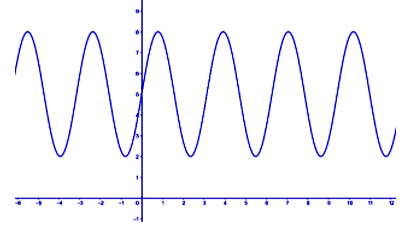
Now, we know that a one-to-one function is a function in which every value of the co domain is the image of at most one value of the domain. This means that every horizontal line drawn on the graph of a one-to-one function to intersect it, will cut it at most on point. So we draw a horizontal line, say
$y = 5$, on the above graph so that we get
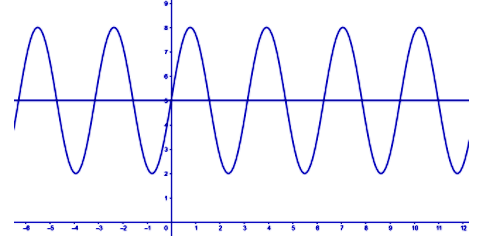
As we can see that the horizontal line $y = 5$ is cutting the graph at multiple points. So we can say that the given function is not a one-to-one function.
Now, we know that a function is invertible if and only if it is injective as well as subjective, that is, it is one-to-one as well as onto. But since we have shown above that the given function is not one-to-one, so it is not invertible.
Hence, the inverse of the given function does not exist.
Note:
We should keep in mind that the inverse of a function does not mean to simply express x in terms of y. The inverse of a function is itself a function and so it must follow all the properties of a function. Hence, for a function to be invertible, firstly it must be one-to-one as well as onto. The inverse of a function will only exist if it is a one-one function.
Complete step-by-step solution:
According to the question, the function is
$f\left( x \right) = 3\sin 2x + 5$
Considering the graph of the above function, we have

Now, we know that a one-to-one function is a function in which every value of the co domain is the image of at most one value of the domain. This means that every horizontal line drawn on the graph of a one-to-one function to intersect it, will cut it at most on point. So we draw a horizontal line, say
$y = 5$, on the above graph so that we get

As we can see that the horizontal line $y = 5$ is cutting the graph at multiple points. So we can say that the given function is not a one-to-one function.
Now, we know that a function is invertible if and only if it is injective as well as subjective, that is, it is one-to-one as well as onto. But since we have shown above that the given function is not one-to-one, so it is not invertible.
Hence, the inverse of the given function does not exist.
Note:
We should keep in mind that the inverse of a function does not mean to simply express x in terms of y. The inverse of a function is itself a function and so it must follow all the properties of a function. Hence, for a function to be invertible, firstly it must be one-to-one as well as onto. The inverse of a function will only exist if it is a one-one function.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




