
Describe the various stages of the menstrual cycle emphasizing the role of hormones. What is the period when there is maximum chance of conception?
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: Menstruation is associated with puberty in females. The menstrual cycle is connected with ovulation and preparing the uterus for pregnancy and the support of the embryo. It continues until menopause sets in.
Complete Answer:
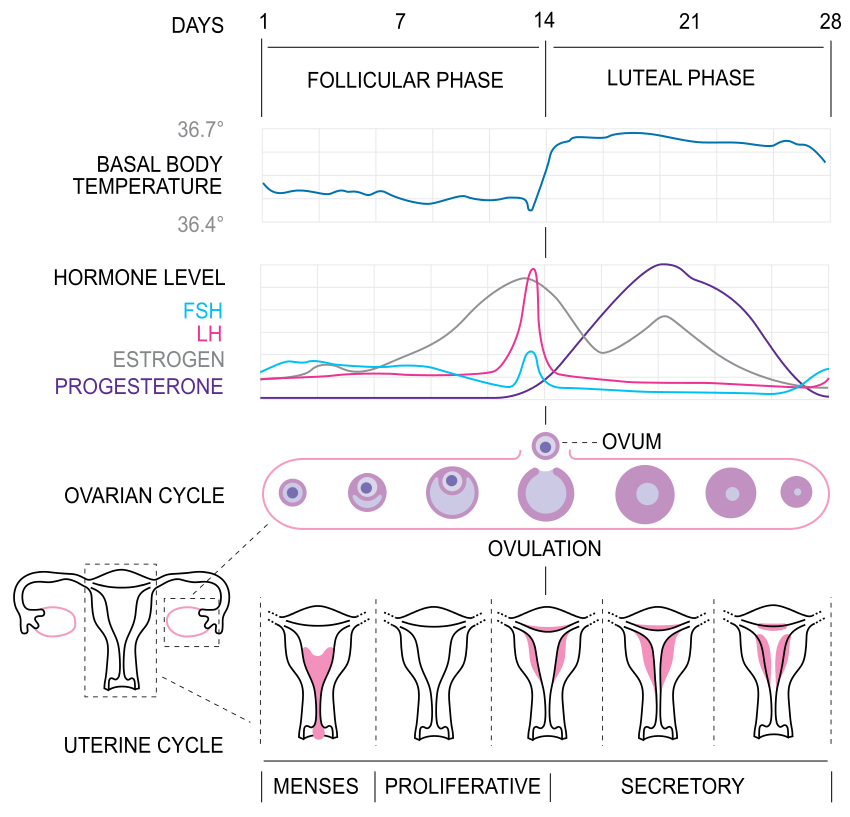
The menstrual cycle is divided into four phases. These are the menstrual, follicular, ovulation, and luteal phase. The cycle on average lasts around 28 days, but it can differ from individual to individual and vary with time.
The first phase, the menstrual phase, is the shedding of the thickened uterine lining. It includes tissues, blood, and mucus. This occurs when pregnancy has not happened. The phase can last from 3 to 7 days.
In the follicular phase, the ovaries prepare to release a mature egg. This starts on the first day of menstruation, and ends with ovulation. Release of follicular stimulating hormone from the pituitary gland signals the ovaries to start preparing an egg cell. As the follicle matures, it releases the hormone oestrogen which signals the uterus to start preparing the endometrial lining. Simultaneously, this then stimulates the pituitary to release luteinising hormone. The follicular phase lasts for about 14 days.
The ovulation phase starts around day 14, when the luteinising hormone from the pituitary causes a mature follicle to rupture, releasing an ovum or egg cell. This then travels down the fallopian tube to the uterus. A released ovum will survive for about 24 hours and die if it is not fertilised. Ovulation phase is thus day 14-15 of the menstrual cycle. This is the stage during which pregnancy is most likely to happen.
Simultaneously, the ruptured follicle or corpus luteum secretes progesterone and oestrogen to keep the thickened endometrium ready for implantation. If fertilisation and implantation takes place, the uterus then secretes human chorionic gonadotropin, the hormone tested for in pregnancy tests. This luteal phase lasts for about 14 days. If not, the corpus luteum then shrinks, resulting in a fall in levels of progesterone and oestrogen, and bringing you back to the menstrual phase.
Note: While an egg cell can survive only one day without fertilisation, sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to five days. So even if sperm has been deposited a few days prior to ovulation, pregnancy can still occur.
Complete Answer:
The menstrual cycle is divided into four phases. These are the menstrual, follicular, ovulation, and luteal phase. The cycle on average lasts around 28 days, but it can differ from individual to individual and vary with time.
The first phase, the menstrual phase, is the shedding of the thickened uterine lining. It includes tissues, blood, and mucus. This occurs when pregnancy has not happened. The phase can last from 3 to 7 days.
In the follicular phase, the ovaries prepare to release a mature egg. This starts on the first day of menstruation, and ends with ovulation. Release of follicular stimulating hormone from the pituitary gland signals the ovaries to start preparing an egg cell. As the follicle matures, it releases the hormone oestrogen which signals the uterus to start preparing the endometrial lining. Simultaneously, this then stimulates the pituitary to release luteinising hormone. The follicular phase lasts for about 14 days.
The ovulation phase starts around day 14, when the luteinising hormone from the pituitary causes a mature follicle to rupture, releasing an ovum or egg cell. This then travels down the fallopian tube to the uterus. A released ovum will survive for about 24 hours and die if it is not fertilised. Ovulation phase is thus day 14-15 of the menstrual cycle. This is the stage during which pregnancy is most likely to happen.
Simultaneously, the ruptured follicle or corpus luteum secretes progesterone and oestrogen to keep the thickened endometrium ready for implantation. If fertilisation and implantation takes place, the uterus then secretes human chorionic gonadotropin, the hormone tested for in pregnancy tests. This luteal phase lasts for about 14 days. If not, the corpus luteum then shrinks, resulting in a fall in levels of progesterone and oestrogen, and bringing you back to the menstrual phase.

Note: While an egg cell can survive only one day without fertilisation, sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to five days. So even if sperm has been deposited a few days prior to ovulation, pregnancy can still occur.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




