
Describe the structure of the human eye.
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: The structure of the eye is important to study as it is one of the important sensory organs of human beings. Vision is the sensation possible due to the eyes. The structure of the human eye can be compared to a camera. Both of these work by gathering, focusing, and transmitting light through a lens to create images.
Complete answer: The human eye is one of the most complex and sensitive parts of the body. It is a visual sensory organ which means that it enables us to see the beautiful world around us. The human eye looks simple from the outside. It seems like a sphere but is composed of various sensitive parts like ocular muscles, tissues, nerves, etc.
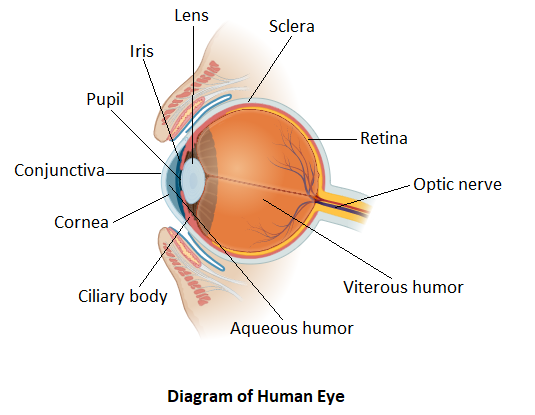
Every part of the human eye performs a specific function and these functions sum up to give the resultant image. The eye is made of two main parts called internal structure and external structure.
Let us understand both one by one.
The external structure of the eye consists of sclera, conjunctiva, cornea, iris, and pupil respectively. The sclera is the outer covering which is white and is made of dense connective tissue. It functions to protect the inner parts of the eye. The conjunctiva is a layer above the sclera and is made of stratified squamous epithelium. It functions to keep our eyes moist and clear. It provides lubrication by secreting tears and mucus. The transparent front part of the eye is termed as the cornea. It covers the iris and pupil. Its function is to refract light along with the lens of the eye. Iris is the pigmented portion of the eye that is responsible for determining the eye color. It is the visible central part of the outer eye. Its function is to maintain the diameter of the pupil as per the light source. The pupil is the small aperture present in the center of the iris. It allows the light to enter the eye. It focuses the entering light on the retina.
The internal structure of the eye is a little complex. It consists of lens, retina, optic nerve, aqueous humor, and vitreous humor. The lens is the transparent biconvex structure that is attached to the ciliary body by ligament tissue. The lens along with the cornea refracts the entering light and helps to focus it on the retina. The retina is the main visionary part of the eye. It is the innermost layer of the eye. It is light sensitive and resembles the film of the camera. Photoreceptor cells that detect colors are present in the retina. The retina converts the image into electrical signals. These electrical signals are then processed by the brain. The optic nerve which lies in the posterior portion of the eyes is responsible for carrying nerve impulses from the retina to the brain. The aqueous humor is the watery fluid that is present between the lens and the cornea. It nourishes the eye while keeping it inflated. Vitreous humor on the other side is a transparent jelly-like substance that lies between the retina and lens. Its function is to provide protection to the eye and maintain the spherical shape of the eye.
Note: As of popular belief the eye is considered a perfect sphere. But it is not a perfect sphere. It is made up of two parts fused along with several muscles and tissues. The two main parts are called internal and external structures. So, it is roughly a spherical structure.
Complete answer: The human eye is one of the most complex and sensitive parts of the body. It is a visual sensory organ which means that it enables us to see the beautiful world around us. The human eye looks simple from the outside. It seems like a sphere but is composed of various sensitive parts like ocular muscles, tissues, nerves, etc.

Every part of the human eye performs a specific function and these functions sum up to give the resultant image. The eye is made of two main parts called internal structure and external structure.
Let us understand both one by one.
The external structure of the eye consists of sclera, conjunctiva, cornea, iris, and pupil respectively. The sclera is the outer covering which is white and is made of dense connective tissue. It functions to protect the inner parts of the eye. The conjunctiva is a layer above the sclera and is made of stratified squamous epithelium. It functions to keep our eyes moist and clear. It provides lubrication by secreting tears and mucus. The transparent front part of the eye is termed as the cornea. It covers the iris and pupil. Its function is to refract light along with the lens of the eye. Iris is the pigmented portion of the eye that is responsible for determining the eye color. It is the visible central part of the outer eye. Its function is to maintain the diameter of the pupil as per the light source. The pupil is the small aperture present in the center of the iris. It allows the light to enter the eye. It focuses the entering light on the retina.
The internal structure of the eye is a little complex. It consists of lens, retina, optic nerve, aqueous humor, and vitreous humor. The lens is the transparent biconvex structure that is attached to the ciliary body by ligament tissue. The lens along with the cornea refracts the entering light and helps to focus it on the retina. The retina is the main visionary part of the eye. It is the innermost layer of the eye. It is light sensitive and resembles the film of the camera. Photoreceptor cells that detect colors are present in the retina. The retina converts the image into electrical signals. These electrical signals are then processed by the brain. The optic nerve which lies in the posterior portion of the eyes is responsible for carrying nerve impulses from the retina to the brain. The aqueous humor is the watery fluid that is present between the lens and the cornea. It nourishes the eye while keeping it inflated. Vitreous humor on the other side is a transparent jelly-like substance that lies between the retina and lens. Its function is to provide protection to the eye and maintain the spherical shape of the eye.
Note: As of popular belief the eye is considered a perfect sphere. But it is not a perfect sphere. It is made up of two parts fused along with several muscles and tissues. The two main parts are called internal and external structures. So, it is roughly a spherical structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




