
Describe the life cycle of Plasmodium vivax in a man?
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint:
In Asia and South America, Plasmodium vivax accounts for 65% of malaria infections. Unlike Plasmodium falciparum at lower temperatures, P. vivax is capable of undergoing sporogonic growth in the mosquito.
Complete answer:
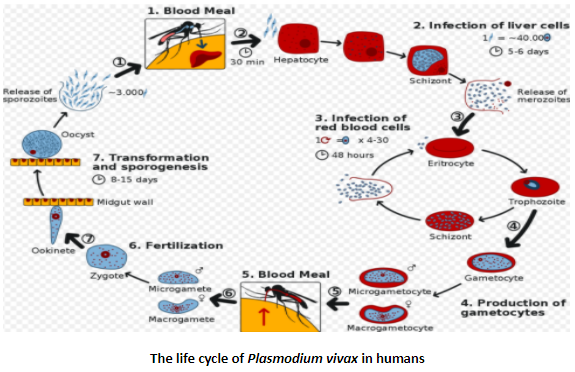
> Malaria's natural history includes cyclical colonization of Anopheles mosquitoes in humans and females. In humans, the parasites first develop and spread in the liver cells, and then in the blood's red cells.
> Within the red blood cells, successive broods of parasites develop and die in the blood, releasing daughter parasites ("merozoites") that begin the cycle by invading other red cells.
> Parasites in the blood stage are the ones that cause malaria symptoms. When certain types of blood-stage parasites (gametocytes that occur in both male and female types) are ingested by a female Anopheles mosquito during blood feeding, they fit in the gut of the mosquito and begin a growth and multiplication period in the mosquito.
> A type of the parasite named a sporozoite migrates to the salivary glands of the mosquito after 10-18 days. When the Anopheles mosquito takes a blood meal on another human, along with the sporozoites, anticoagulant saliva is injected, which migrates to the liver and thus starts a new cycle.
> Thereby, the mosquito bites bring the disease from one person to another (acting as a "vector"), while infected humans transmit the parasite to the mosquito, the mosquito vector does not suffer from the presence of the parasites, as opposed to the human host.
Note: Plasmodium vivax is a parasite of protozoa and a pathogen in humans. This parasite is the most widespread and widely spread cause of recurrent malaria. While less virulent than Plasmodium falciparum, it is the deadliest of the five parasites in human malaria.
In Asia and South America, Plasmodium vivax accounts for 65% of malaria infections. Unlike Plasmodium falciparum at lower temperatures, P. vivax is capable of undergoing sporogonic growth in the mosquito.
Complete answer:

> Malaria's natural history includes cyclical colonization of Anopheles mosquitoes in humans and females. In humans, the parasites first develop and spread in the liver cells, and then in the blood's red cells.
> Within the red blood cells, successive broods of parasites develop and die in the blood, releasing daughter parasites ("merozoites") that begin the cycle by invading other red cells.
> Parasites in the blood stage are the ones that cause malaria symptoms. When certain types of blood-stage parasites (gametocytes that occur in both male and female types) are ingested by a female Anopheles mosquito during blood feeding, they fit in the gut of the mosquito and begin a growth and multiplication period in the mosquito.
> A type of the parasite named a sporozoite migrates to the salivary glands of the mosquito after 10-18 days. When the Anopheles mosquito takes a blood meal on another human, along with the sporozoites, anticoagulant saliva is injected, which migrates to the liver and thus starts a new cycle.
> Thereby, the mosquito bites bring the disease from one person to another (acting as a "vector"), while infected humans transmit the parasite to the mosquito, the mosquito vector does not suffer from the presence of the parasites, as opposed to the human host.
Note: Plasmodium vivax is a parasite of protozoa and a pathogen in humans. This parasite is the most widespread and widely spread cause of recurrent malaria. While less virulent than Plasmodium falciparum, it is the deadliest of the five parasites in human malaria.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




