
Describe the different types of lipids.
Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint:Organic compounds that are made up of hydrogen, carbon, oxygen atoms associated with various groups are known as lipids. They can be of different types based on their functions. They form the framework for the structure and function of living organisms.
Complete answer:Lipids are molecules that contain hydrocarbons and make up the building blocks of the structure and function of living cells. They are formed of fatty acids chain and glycerol. They are non-polar organic molecules that are soluble in only certain non-polar solvents and are insoluble in water because of their polar nature. The lipid molecules are synthesized in the liver in the human body. They yield high energy and have various functions in the human body. They are mostly stored in the adipose tissue of the body. They are a heterogeneous group of compounds that provide energy for different cellular processes. They are significant in the biological system and act as a mechanical barrier that divides the cell from the external atmosphere. They are a major part of the plasma membrane. They are classified into two main classes- non-saponifiable and saponifiable. They are of different types such as simple, complex, derived, precursor, saturated, and unsaturated.
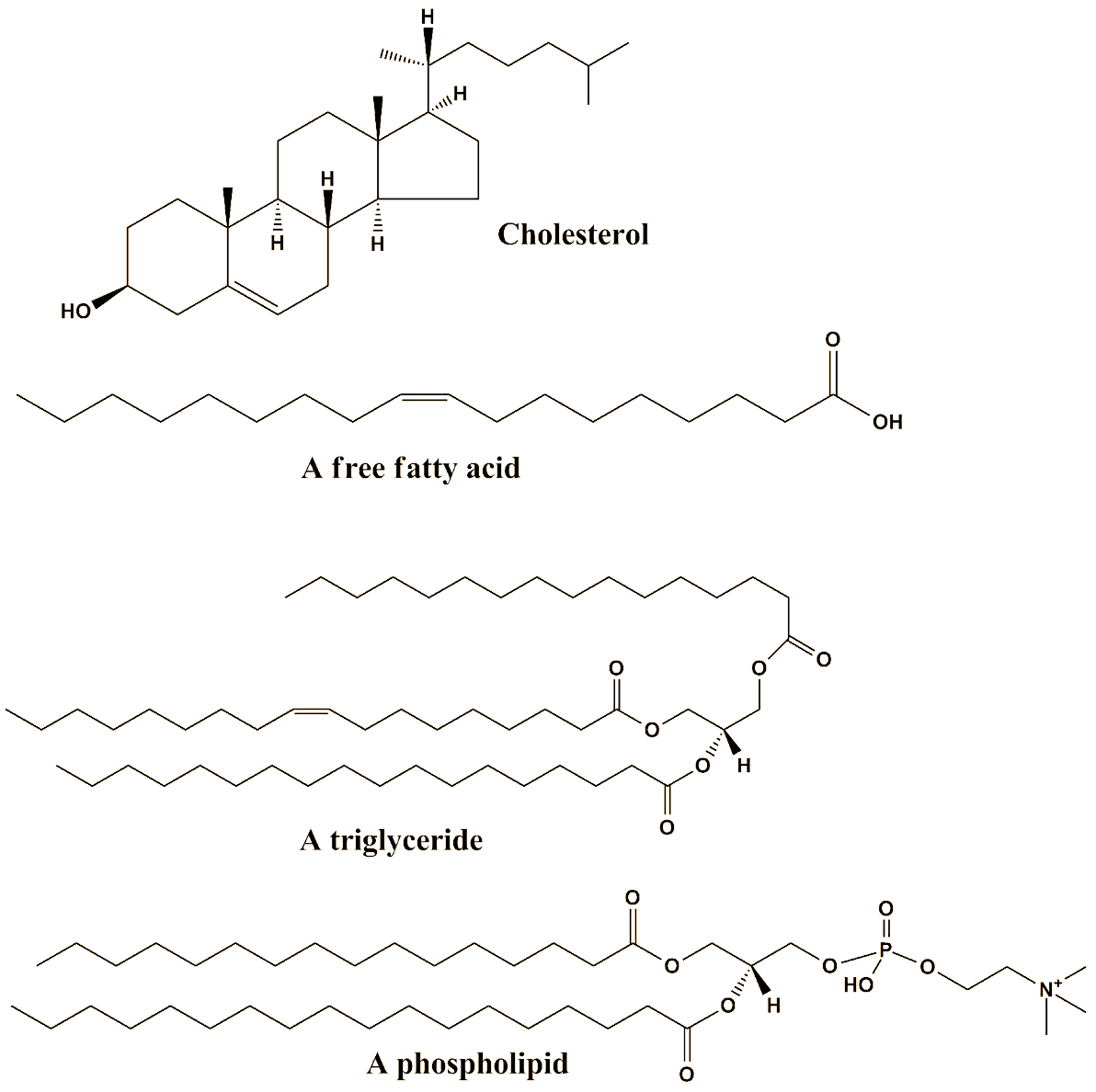
Simple lipids are the esters of fatty acids with various alcohols. Fats and waxes are common simple lipids. Complex lipids are the esters of fatty acids having other groups in addition to alcohol or fatty acids. Phospholipids, glycolipids, sulfolipids, and amino lipids are common examples of complex lipids. Lipid soluble vitamins, hormones, ketone bodies, fatty aldehydes, etc, are common precursors or derived lipids.
Note: Lipids are made up of a glycerol molecule joined with three molecules of fatty acids. They form the structural component of the cell membrane. They can be of different types depending upon the side chain or group joined with them.
Complete answer:Lipids are molecules that contain hydrocarbons and make up the building blocks of the structure and function of living cells. They are formed of fatty acids chain and glycerol. They are non-polar organic molecules that are soluble in only certain non-polar solvents and are insoluble in water because of their polar nature. The lipid molecules are synthesized in the liver in the human body. They yield high energy and have various functions in the human body. They are mostly stored in the adipose tissue of the body. They are a heterogeneous group of compounds that provide energy for different cellular processes. They are significant in the biological system and act as a mechanical barrier that divides the cell from the external atmosphere. They are a major part of the plasma membrane. They are classified into two main classes- non-saponifiable and saponifiable. They are of different types such as simple, complex, derived, precursor, saturated, and unsaturated.

Simple lipids are the esters of fatty acids with various alcohols. Fats and waxes are common simple lipids. Complex lipids are the esters of fatty acids having other groups in addition to alcohol or fatty acids. Phospholipids, glycolipids, sulfolipids, and amino lipids are common examples of complex lipids. Lipid soluble vitamins, hormones, ketone bodies, fatty aldehydes, etc, are common precursors or derived lipids.
Note: Lipids are made up of a glycerol molecule joined with three molecules of fatty acids. They form the structural component of the cell membrane. They can be of different types depending upon the side chain or group joined with them.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




