
Derive Einstein’s photoelectric equation $\dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} = hv - h{v_o}$.
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint:Photoelectric effect is the phenomenon in which when the light strikes the metal plate and then it releases the electrons. When a light strikes the surface then some of the light is absorbed, some gets reflected, the absorbed light is responsible for the electron emission.
Formula used:The formula of the kinetic energy is given by,
$ \Rightarrow K \cdot E = \dfrac{1}{2}m \times {v^2}$
Where the mass of the object is equal to m and the velocity of the object is equal to v.
The formula of the incident photon is given by,
$ \Rightarrow E = hv$
Where the Planck’s constant is h and the frequency is equal to v.
Complete step by step solution:
It is asked in the problem to derive Einstein's photoelectric equation.
When a beam of light strikes the surface of the metal then the electrons will release from the surface of the electron. The energy of the photon which is required to eject the electrons is equal to threshold energy for the removal of the electron and also the kinetic energy of the electron with which the electron leaves the metal surface. The electron must have some kinetic energy when it leaves the surface of the metal if the electrons don’t have the required kinetic energy then there is no use of the ejection of electron and therefore the energy of the electron must be given such that it has threshold energy for the ejection of electron and also it has the energy that the electrons leaves the metal surface with maximum kinetic energy.
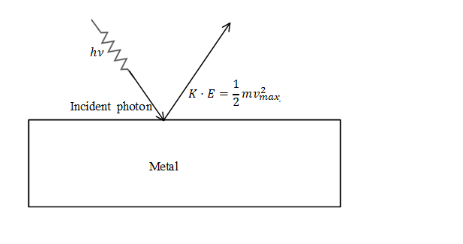
The energy of the photons is equal to,
Energy of the photon= Energy required to eject the electrons Maximum kinetic energy of electron.
$ \Rightarrow E = W + K \cdot {E_e}$
The energy of the photon is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow E = hv$
Where Planck’s constant is h and frequency is v.
$ \Rightarrow E = W + K \cdot {E_{\max .}}$
$ \Rightarrow hv = W + \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
The energy required for the ejection of the electrons is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow W = h{v_o}$
Where Planck’s constant is h and the minimum threshold frequency is ${v_o}$.
$ hv = W + \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max .}^2$
$ \Rightarrow hv = h{v_o} + \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max .}^2$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max .}^2 = h{v_o} - hv$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max .}^2 = h\left( {{v_o} - v} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow K \cdot {E_{\max .}} = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max .}^2 = h\left( {{v_o} - v} \right)$
The equation of the Einstein’s photoelectric equation is equal to,
$ \therefore K \cdot {E_{\max .}} = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max .}^2 = h\left( {{v_o} - v} \right)$.
Note:The students are advised to understand and remember the formula of the kinetic energy and also the formula of the energy of the photon as these formulas are very important in solving these types of problems.
Formula used:The formula of the kinetic energy is given by,
$ \Rightarrow K \cdot E = \dfrac{1}{2}m \times {v^2}$
Where the mass of the object is equal to m and the velocity of the object is equal to v.
The formula of the incident photon is given by,
$ \Rightarrow E = hv$
Where the Planck’s constant is h and the frequency is equal to v.
Complete step by step solution:
It is asked in the problem to derive Einstein's photoelectric equation.
When a beam of light strikes the surface of the metal then the electrons will release from the surface of the electron. The energy of the photon which is required to eject the electrons is equal to threshold energy for the removal of the electron and also the kinetic energy of the electron with which the electron leaves the metal surface. The electron must have some kinetic energy when it leaves the surface of the metal if the electrons don’t have the required kinetic energy then there is no use of the ejection of electron and therefore the energy of the electron must be given such that it has threshold energy for the ejection of electron and also it has the energy that the electrons leaves the metal surface with maximum kinetic energy.

The energy of the photons is equal to,
Energy of the photon= Energy required to eject the electrons Maximum kinetic energy of electron.
$ \Rightarrow E = W + K \cdot {E_e}$
The energy of the photon is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow E = hv$
Where Planck’s constant is h and frequency is v.
$ \Rightarrow E = W + K \cdot {E_{\max .}}$
$ \Rightarrow hv = W + \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
The energy required for the ejection of the electrons is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow W = h{v_o}$
Where Planck’s constant is h and the minimum threshold frequency is ${v_o}$.
$ hv = W + \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max .}^2$
$ \Rightarrow hv = h{v_o} + \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max .}^2$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max .}^2 = h{v_o} - hv$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max .}^2 = h\left( {{v_o} - v} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow K \cdot {E_{\max .}} = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max .}^2 = h\left( {{v_o} - v} \right)$
The equation of the Einstein’s photoelectric equation is equal to,
$ \therefore K \cdot {E_{\max .}} = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max .}^2 = h\left( {{v_o} - v} \right)$.
Note:The students are advised to understand and remember the formula of the kinetic energy and also the formula of the energy of the photon as these formulas are very important in solving these types of problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




