
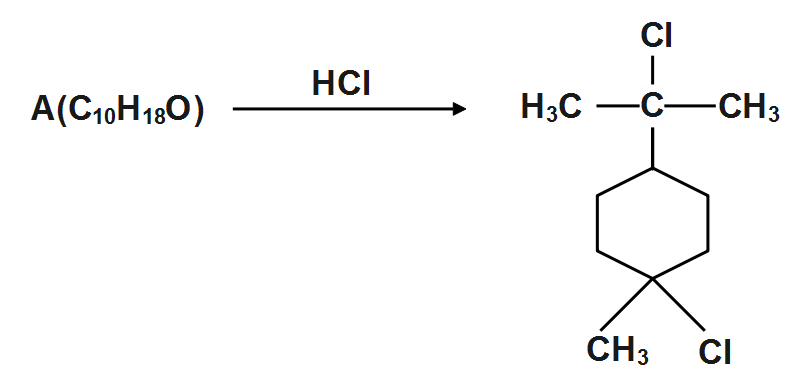
Degree of unsaturation of $ A=2 $ and it contains no double or triple bonds. Identify the structure of $ A $
(A)
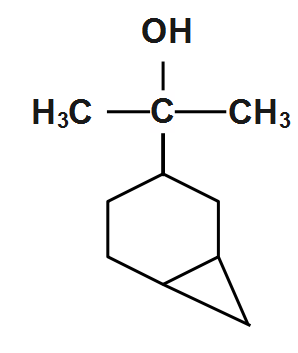
(B)
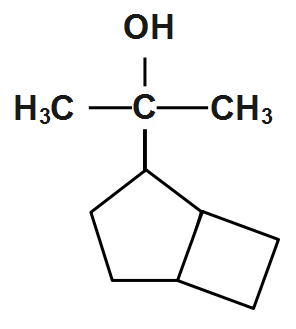
(C)
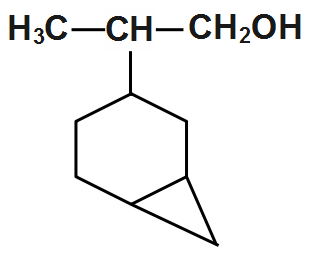
(D) None of these.




Answer
539.7k+ views
Hint : We know that the ketone is a structure with $ {{R}_{2}}C=O $ configuration and in this $ R $ can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. They are a carbonyl group which have a carbon-oxygen double bond. The simplest of ketone is called acetone. Ketones have a lot of industrial importance such as great importance in biology. Such as many sugars, steroids and solvent acetone.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The carbon is ketone has $ s{{p}^{2}} $ hybridization and that includes both their electronic and molecular structure. They are trigonal planar in structure and differ from aldehyde in that the carbonyl group $ O $ is bonded to two carbon within a carbon skeleton. Ketones are also distinct from other carbonyl-containing functional groups, such as carboxylic acids, esters and amides
Carbonyl groups are polar as the electronegativity of oxygen is more than that of carbon. This difference causes the polarity to arise. This means ketones are nucleophilic at oxygen and electrophilic at carbon. Ketones are water soluble and are hydrogen bond acceptors. They are not hydrogen-bond donors and thus cannot hydrogen-bond to themselves.
We can see that the degree of saturation is $ ~2 $ but it contains no double or triple bond. Thus we can see that there are two rings-one six membered as indicated by product and the other three membered which is cleaved by hydrochloric acid due to strain. This $ A $ has given the structure.
Note :
Note that the oxidation of hydrocarbons often with air is an important method known for ketone production. Cyclohexanone is produced annually by aerobic oxidation of cyclohexane. The preparation of Acetone occurs by air-oxidation of cumene. Because of their inability to serve both as hydrogen-bond donors and acceptors, ketones tend not to "self-associate" and are more volatile than alcohols and carboxylic acids of comparable molecular weights. Because the carbonyl group interacts with water by hydrogen bonding.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The carbon is ketone has $ s{{p}^{2}} $ hybridization and that includes both their electronic and molecular structure. They are trigonal planar in structure and differ from aldehyde in that the carbonyl group $ O $ is bonded to two carbon within a carbon skeleton. Ketones are also distinct from other carbonyl-containing functional groups, such as carboxylic acids, esters and amides
Carbonyl groups are polar as the electronegativity of oxygen is more than that of carbon. This difference causes the polarity to arise. This means ketones are nucleophilic at oxygen and electrophilic at carbon. Ketones are water soluble and are hydrogen bond acceptors. They are not hydrogen-bond donors and thus cannot hydrogen-bond to themselves.
We can see that the degree of saturation is $ ~2 $ but it contains no double or triple bond. Thus we can see that there are two rings-one six membered as indicated by product and the other three membered which is cleaved by hydrochloric acid due to strain. This $ A $ has given the structure.
Note :
Note that the oxidation of hydrocarbons often with air is an important method known for ketone production. Cyclohexanone is produced annually by aerobic oxidation of cyclohexane. The preparation of Acetone occurs by air-oxidation of cumene. Because of their inability to serve both as hydrogen-bond donors and acceptors, ketones tend not to "self-associate" and are more volatile than alcohols and carboxylic acids of comparable molecular weights. Because the carbonyl group interacts with water by hydrogen bonding.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




