
Define menstrual cycle and explain its various phases with diagram.
Answer
597.6k+ views
Hint:It is a developmental cycle that occurs in the females of the primate population. This cycle is complicated and regulated by several different glands and hormones released by these glands.
Complete answer:
The menstrual cycle is a biofeedback mechanism, which means that each function and gland is influenced by the activity of others. The average duration of the menstrual cycle is 28-29 days, although this will vary between women and from one cycle to another. The length of your menstrual cycle is measured from the first day of the phase to the day before the next period begins.
There are four main phases of the menstrual cycle. They are- menstruation, follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase.
Mensuration- Menstruation is the removal from the body of the thickened lining of the uterus by the vagina. Menstrual fluid includes blood, uterine lining cell, and mucus. The average duration of the period is between three days to one week.
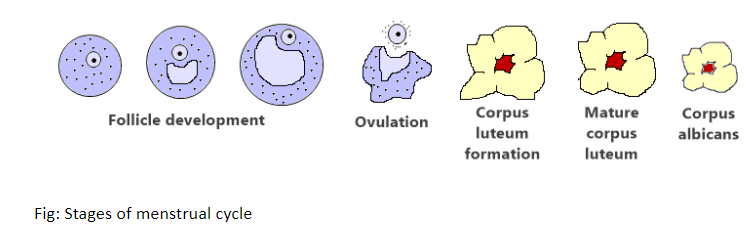
Follicular phase- The follicular process begins on the first day of menstruation and concludes with ovulation. Produced by hypothalamus, the pituitary gland releases follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). FSH hormone activates the ovary to develop about five to 20 follicles of the bead on the top. Each follicle produces an immature egg. Typically, only one follicle matures into an egg, while the others die. This will happen on the 10th day of a 28-day cycle. The follicle development induces the lining of the uterus to thicken in anticipation for future birth.
Ovulation- Ovulation is the removal of a mature egg from the ovary surface. This usually happens in the middle of the cycle, about two weeks or so before menstruation begins. During the follicular process, the growth of the follicle induces a raise in the estrogen level. The brain hypothalamus detects these rising levels and releases a chemical called gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). This hormone stimulates the pituitary gland to develop elevated levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and FSH. Within two days, ovulation is caused by a higher level of LH. The egg is consumed in the fallopian tube and in the direction of the uterus by waves of tiny, hair-like projections. The life cycle of the average egg is just 24 hours. If it does not reach the sperm at this period, it will die.
Luteal phase- The egg explodes from its follicle after ovulation, but the damaged follicle rests on the surface of the ovary. For the next two weeks or so, the follicle is converted into a structure known as the corpus luteum. This arrangement continues to release progesterone, along with small levels of estrogen. This mix of hormones preserves the thickened lining of the uterus, preparing for the fertilised egg to stick. If the egg implant is fertilised in the lining of the uterus, it releases the hormones required to sustain the luteum of the corpus. This includes human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), a hormone that is found in the pregnancy test in the urine. The corpus luteum continues to release elevated levels of progesterone required to sustain the thickened lining of the uterus. If there is no pregnancy, the corpus luteum will wither and die, normally about day 22 of the 28-day period. A reduction in the progesterone amount allows the lining of the uterus to break apart. It's known as menstruation. Then the loop repeats itself.
Note:Girls have their first cycle (menarche) on average between the ages of 11 and 14. Other sexual characteristics have developed at this stage, like pubic hair and budding breasts.
Complete answer:
The menstrual cycle is a biofeedback mechanism, which means that each function and gland is influenced by the activity of others. The average duration of the menstrual cycle is 28-29 days, although this will vary between women and from one cycle to another. The length of your menstrual cycle is measured from the first day of the phase to the day before the next period begins.
There are four main phases of the menstrual cycle. They are- menstruation, follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase.
Mensuration- Menstruation is the removal from the body of the thickened lining of the uterus by the vagina. Menstrual fluid includes blood, uterine lining cell, and mucus. The average duration of the period is between three days to one week.
Follicular phase- The follicular process begins on the first day of menstruation and concludes with ovulation. Produced by hypothalamus, the pituitary gland releases follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). FSH hormone activates the ovary to develop about five to 20 follicles of the bead on the top. Each follicle produces an immature egg. Typically, only one follicle matures into an egg, while the others die. This will happen on the 10th day of a 28-day cycle. The follicle development induces the lining of the uterus to thicken in anticipation for future birth.
Ovulation- Ovulation is the removal of a mature egg from the ovary surface. This usually happens in the middle of the cycle, about two weeks or so before menstruation begins. During the follicular process, the growth of the follicle induces a raise in the estrogen level. The brain hypothalamus detects these rising levels and releases a chemical called gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). This hormone stimulates the pituitary gland to develop elevated levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and FSH. Within two days, ovulation is caused by a higher level of LH. The egg is consumed in the fallopian tube and in the direction of the uterus by waves of tiny, hair-like projections. The life cycle of the average egg is just 24 hours. If it does not reach the sperm at this period, it will die.
Luteal phase- The egg explodes from its follicle after ovulation, but the damaged follicle rests on the surface of the ovary. For the next two weeks or so, the follicle is converted into a structure known as the corpus luteum. This arrangement continues to release progesterone, along with small levels of estrogen. This mix of hormones preserves the thickened lining of the uterus, preparing for the fertilised egg to stick. If the egg implant is fertilised in the lining of the uterus, it releases the hormones required to sustain the luteum of the corpus. This includes human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), a hormone that is found in the pregnancy test in the urine. The corpus luteum continues to release elevated levels of progesterone required to sustain the thickened lining of the uterus. If there is no pregnancy, the corpus luteum will wither and die, normally about day 22 of the 28-day period. A reduction in the progesterone amount allows the lining of the uterus to break apart. It's known as menstruation. Then the loop repeats itself.

Note:Girls have their first cycle (menarche) on average between the ages of 11 and 14. Other sexual characteristics have developed at this stage, like pubic hair and budding breasts.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




