
Define carbon fixation in plants. What was the contribution of Melvin Calvin? Describe the three phases of Calvin cycle.
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint:This is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. Utilization of $CO_2$ takes place during this process.
Complete Answer:
Autotrophic organisms have the capability to transform atmospheric $CO_2$ to a reduced state i.e. carbohydrate and, this process is known as carbon fixation or carbon assimilation. All the photosynthetic eukaryotes, from the most primitive alga to the most advanced angiosperm, reduce $CO_2$ to carbohydrate through the same basic mechanism.
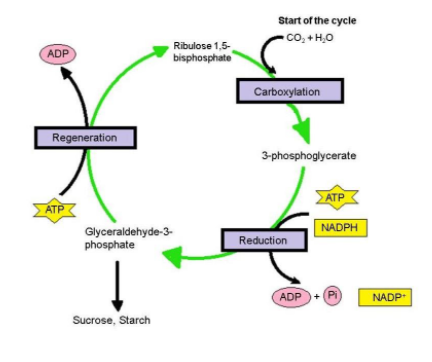
Contribution of Melvin Calvin: The complete biosynthetic pathway of photosynthetic carbon reduction cycle was for the first time elucidated by Melvin Calvin in and his colleagues in the 1950s that is why it is called the Calvin cycle. He inserted the radioactively labelled carbon (14C) into photosynthetic algae and analysed the pathway of carbon fixation in the plant by the method of two-dimensional paper chromatography. For this work he was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1961. He discovered that the first stable product formed during the process of carbon fixation is a 3-carbon organic acid, namely, 3-phosphoglyceric acid (PGA). Thus, it is also called the C3 cycle.
Three phases of Calvin cycle: The Calvin cycle proceeds in three stages –
1. Carboxylation: In this stage $CO_2$ and water from the environment enzymatically combine with a 5-carbon compound, Ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate (RuBP), and generates two molecules of a 3-carbon intermediate, 3- phosphoglycerate which is the first stable compound of the Calvin cycle.
2. Reduction: In this stage, 3-phosphoglycerate is reduced to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (a carbohydrate) by the use of ATP and NADPH which are produced during light reaction.
3. Regeneration: The cycle is completed by the regeneration of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate from glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. Ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate is the $CO_2$ acceptor.
Note:The $C_4$ photosynthetic carbon assimilation cycle and the photorespiratory carbon oxidation cycle ($C_2$ cycle) are either supplementary to or dependent on the basic $C_3$ cycle.
Complete Answer:
Autotrophic organisms have the capability to transform atmospheric $CO_2$ to a reduced state i.e. carbohydrate and, this process is known as carbon fixation or carbon assimilation. All the photosynthetic eukaryotes, from the most primitive alga to the most advanced angiosperm, reduce $CO_2$ to carbohydrate through the same basic mechanism.
Contribution of Melvin Calvin: The complete biosynthetic pathway of photosynthetic carbon reduction cycle was for the first time elucidated by Melvin Calvin in and his colleagues in the 1950s that is why it is called the Calvin cycle. He inserted the radioactively labelled carbon (14C) into photosynthetic algae and analysed the pathway of carbon fixation in the plant by the method of two-dimensional paper chromatography. For this work he was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1961. He discovered that the first stable product formed during the process of carbon fixation is a 3-carbon organic acid, namely, 3-phosphoglyceric acid (PGA). Thus, it is also called the C3 cycle.
Three phases of Calvin cycle: The Calvin cycle proceeds in three stages –
1. Carboxylation: In this stage $CO_2$ and water from the environment enzymatically combine with a 5-carbon compound, Ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate (RuBP), and generates two molecules of a 3-carbon intermediate, 3- phosphoglycerate which is the first stable compound of the Calvin cycle.
2. Reduction: In this stage, 3-phosphoglycerate is reduced to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (a carbohydrate) by the use of ATP and NADPH which are produced during light reaction.
3. Regeneration: The cycle is completed by the regeneration of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate from glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. Ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate is the $CO_2$ acceptor.

Note:The $C_4$ photosynthetic carbon assimilation cycle and the photorespiratory carbon oxidation cycle ($C_2$ cycle) are either supplementary to or dependent on the basic $C_3$ cycle.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




