
Cyclohexanol on reaction with $ PB{r_3} $ in the presence of pyridine gives:
(A) Bromocyclohexene
(B) Bromocyclohexane
(C) $ 1 - $ bromocyclohexanol
(D) None of the above
Answer
528.9k+ views
Hint :Nucleophilic reactions: These are the type of organic reactions in which a nucleophile i.e., an electron rich species attacks the electron deficient carbon atom and the functional group attached to that carbon is replaced.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As per given reaction conditions, when cyclohexanol reacts with $ PB{r_3} $ in the presence of pyridine, it follows $ S{N_2} $ nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Bimolecular nucleophilic reaction $ (S{N_2}) $ : These are the nucleophilic reactions in which the rate of reaction depends on both, the nucleophile as well as the reactant taken. In these reactions, bond formation and breaking of bonds takes place simultaneously. So, it is a single step or concerted reaction.
The reaction mechanism is as follows:
Step-1: The lone pair of electrons present on the oxygen atom attack the phosphorus atom and removal of bromine ion takes place. The reaction is as follows:
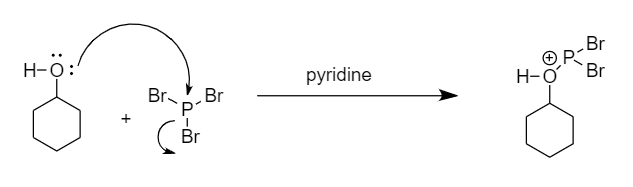
Step-2: The bromine ion will act as a nucleophile and will attack the carbon atom to replace the unstable functional group formed in the transition state. The reaction is as follows:
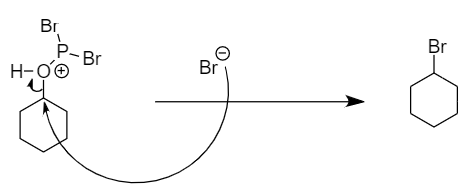
Hence, bromocyclohexane is the final product.
Thus, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note :
In $ S{N_2} $ reaction, the nucleophile attacks from the opposite plane relative to the plane in which the functional group is present. Hence a complete inversion in the configuration of the product is observed. The most common example of $ S{N_2} $ reaction is the Walden inversion in which an inversion of configuration for asymmetric carbon is observed.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As per given reaction conditions, when cyclohexanol reacts with $ PB{r_3} $ in the presence of pyridine, it follows $ S{N_2} $ nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Bimolecular nucleophilic reaction $ (S{N_2}) $ : These are the nucleophilic reactions in which the rate of reaction depends on both, the nucleophile as well as the reactant taken. In these reactions, bond formation and breaking of bonds takes place simultaneously. So, it is a single step or concerted reaction.
The reaction mechanism is as follows:
Step-1: The lone pair of electrons present on the oxygen atom attack the phosphorus atom and removal of bromine ion takes place. The reaction is as follows:

Step-2: The bromine ion will act as a nucleophile and will attack the carbon atom to replace the unstable functional group formed in the transition state. The reaction is as follows:

Hence, bromocyclohexane is the final product.
Thus, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note :
In $ S{N_2} $ reaction, the nucleophile attacks from the opposite plane relative to the plane in which the functional group is present. Hence a complete inversion in the configuration of the product is observed. The most common example of $ S{N_2} $ reaction is the Walden inversion in which an inversion of configuration for asymmetric carbon is observed.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




