
Cyclic hydrocarbon molecule A has all the carbon and hydrogen in a single plane. All the carbon-carbon bonds are of the same length and less than that $\text{1}\text{.54}\overset{\text{o}}{\mathop{\text{A}}}\,$ but more than $1.34\overset{o}{\mathop{A}}\,$. $C-C-C$ bond angle will be A. ${{120}^{O}}$
B. ${{180}^{O}}$
C. ${{100}^{O}}$
D. ${{109}^{O}}{{28}^{'}}$
Answer
361.5k+ views
Hint: Cyclic hydrocarbon molecule A has all the carbon and hydrogen in a single plane’ this statement suggests that cyclic hydrocarbon molecule A contains an unsaturated structure. Also, the data on the bond length of carbon-carbon bonds reveals that this hydrocarbon molecule has a partial double bond character.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Hydrocarbons are a type of compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen. The carbon atom in these compounds may share unsaturated bonds or single, double, and triple covalent bonds. Cyclic hydrocarbons with unsaturated bonds are aromatic hydrocarbons. An example of the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon is benzene.
Benzene with six carbon atoms has just one cyclic ring. The chemical formula of benzene is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$. The structure of benzene is shown in below:
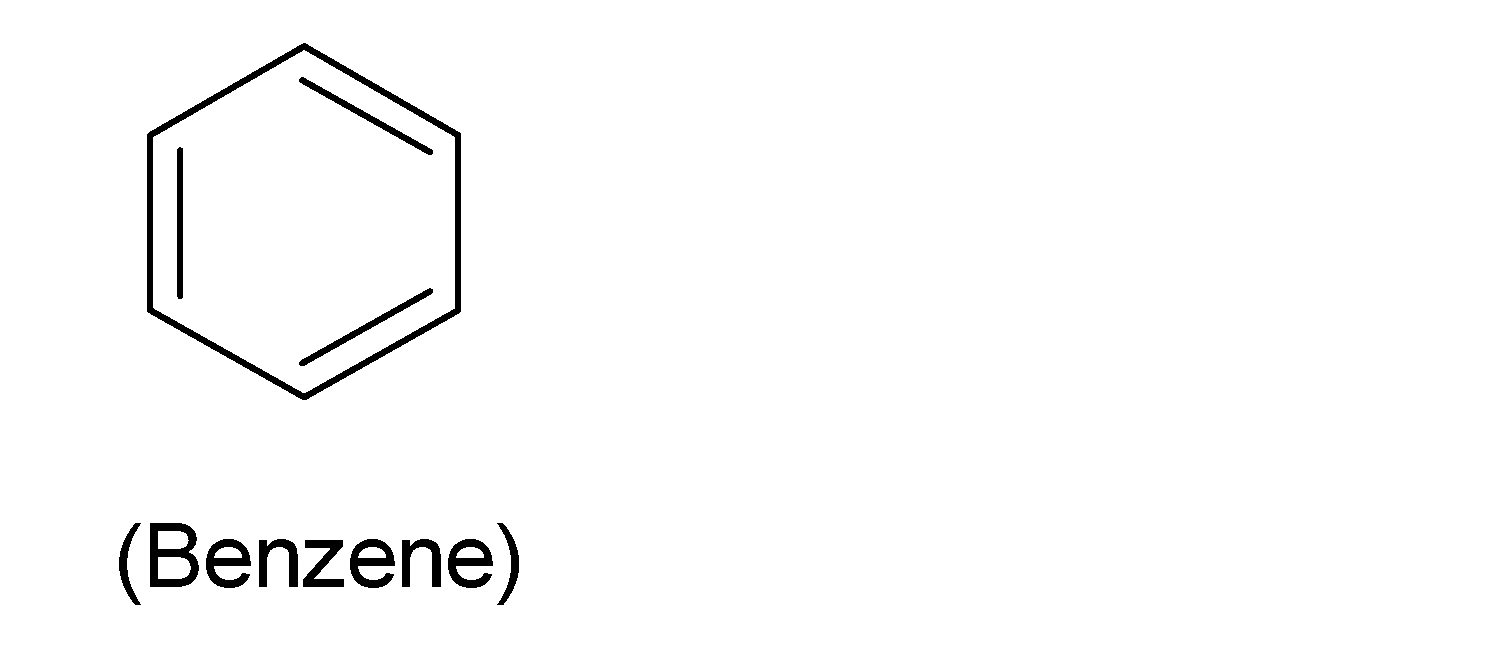
These hydrocarbons have six carbon atoms in a cyclic ring with alternating single and double bonds with $s{{p}^{2}}$hybridization and possessing alternating single and double bonds. Benzene has all the carbon-carbon bonds of the same length due to resonance and resulting in a partial double bond character. The resonance structures of benzene is shown in below:
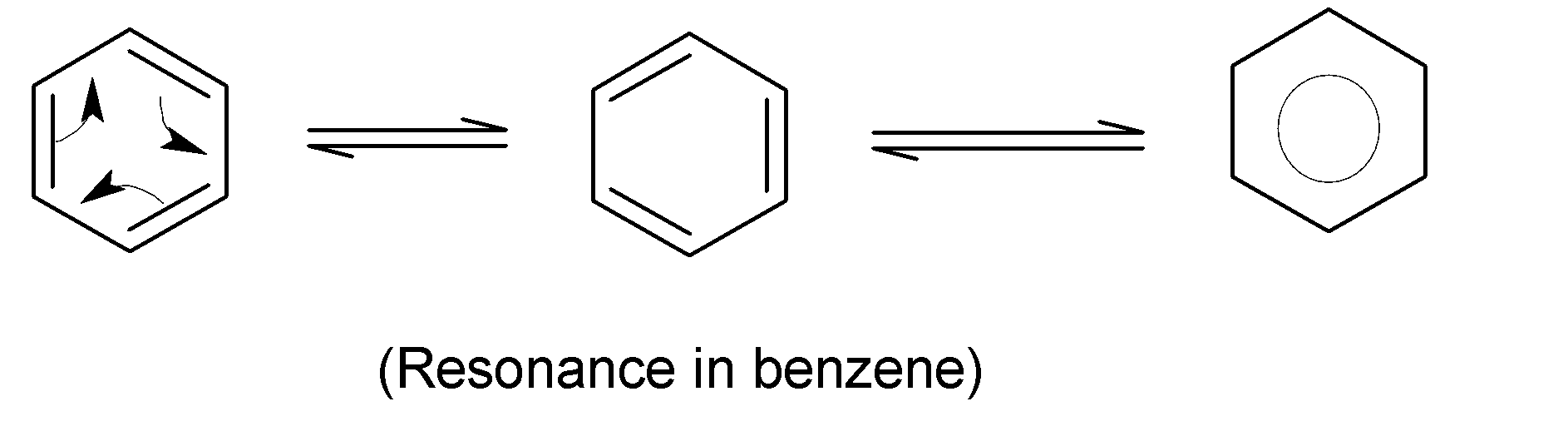
It is found that the $C-C$bond length in benzene $1.39\overset{O}{\mathop{A}}\,$ is a value between a single (bond length $1.54\overset{O}{\mathop{A}}\,$) and a double bond (bond length $1.34\overset{O}{\mathop{A}}\,$).
Now coming to the question, a cyclic hydrocarbon molecule A has all the carbon-hydrogen in a single plane I.e, planar. Also, all identical carbon-carbon bonds have a partial bond length (in between single and double bonds) and will participate in resonance. Therefore this cyclic hydrocarbon is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised and bond angle ${{120}^{O}}$.
Thus, option (A) is correct.
Note: Cyclic hydrocarbon represents a ring-containing structure composed of carbon atoms attached by covalent bonds. They are extremely used in biological reactions and industry. It can also be used as a solvent in many chemical reactions.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Hydrocarbons are a type of compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen. The carbon atom in these compounds may share unsaturated bonds or single, double, and triple covalent bonds. Cyclic hydrocarbons with unsaturated bonds are aromatic hydrocarbons. An example of the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon is benzene.
Benzene with six carbon atoms has just one cyclic ring. The chemical formula of benzene is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$. The structure of benzene is shown in below:

These hydrocarbons have six carbon atoms in a cyclic ring with alternating single and double bonds with $s{{p}^{2}}$hybridization and possessing alternating single and double bonds. Benzene has all the carbon-carbon bonds of the same length due to resonance and resulting in a partial double bond character. The resonance structures of benzene is shown in below:

It is found that the $C-C$bond length in benzene $1.39\overset{O}{\mathop{A}}\,$ is a value between a single (bond length $1.54\overset{O}{\mathop{A}}\,$) and a double bond (bond length $1.34\overset{O}{\mathop{A}}\,$).
Now coming to the question, a cyclic hydrocarbon molecule A has all the carbon-hydrogen in a single plane I.e, planar. Also, all identical carbon-carbon bonds have a partial bond length (in between single and double bonds) and will participate in resonance. Therefore this cyclic hydrocarbon is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised and bond angle ${{120}^{O}}$.
Thus, option (A) is correct.
Note: Cyclic hydrocarbon represents a ring-containing structure composed of carbon atoms attached by covalent bonds. They are extremely used in biological reactions and industry. It can also be used as a solvent in many chemical reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell




