
Conversion of ethyl alcohol into acetaldehyde is an example of ?
A. hydrolysis
B. oxidation
C. reduction
D. molecular rearrangement.
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: In order to answer this question, you need to think about how aldehydes are prepared from alcohols. Aldehydes have the $CHO$ group, whereas, the alcohols have an $OH$ functional group.
Complete step by step answer:
In order to answer this question, we need to learn how reactions occur in aldehydes and ketones and structure of carbonyl groups. In order to solve this question, we need to learn about aldol condensation reactions. Carbon atom of the carbonyl group is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised having triangular planar geometry. Carbon atoms form three sigma bonds and one n(pi) bond, out of which 3 sigma bonds are located in the same plane whereas the fourth it bond, which is formed by lateral or sideways overlapping, is situated above and below the plane. Bond angles are approximately ${{120}^{0}}$.Carbonyl group is polarised due to difference in electronegativity between carbon and oxygen. Oxygen being more electronegative pulls the shared pair of electrons more towards itself making oxygen as a nucleophilic centre and carbon as an electrophilic centre. Hence carbonyl compounds have substantial dipole moments and their polarity can be expressed on the basis of resonance.
Let us see the mechanism of PCC oxidation, we have used propanol instead of ethanol for better clarity:
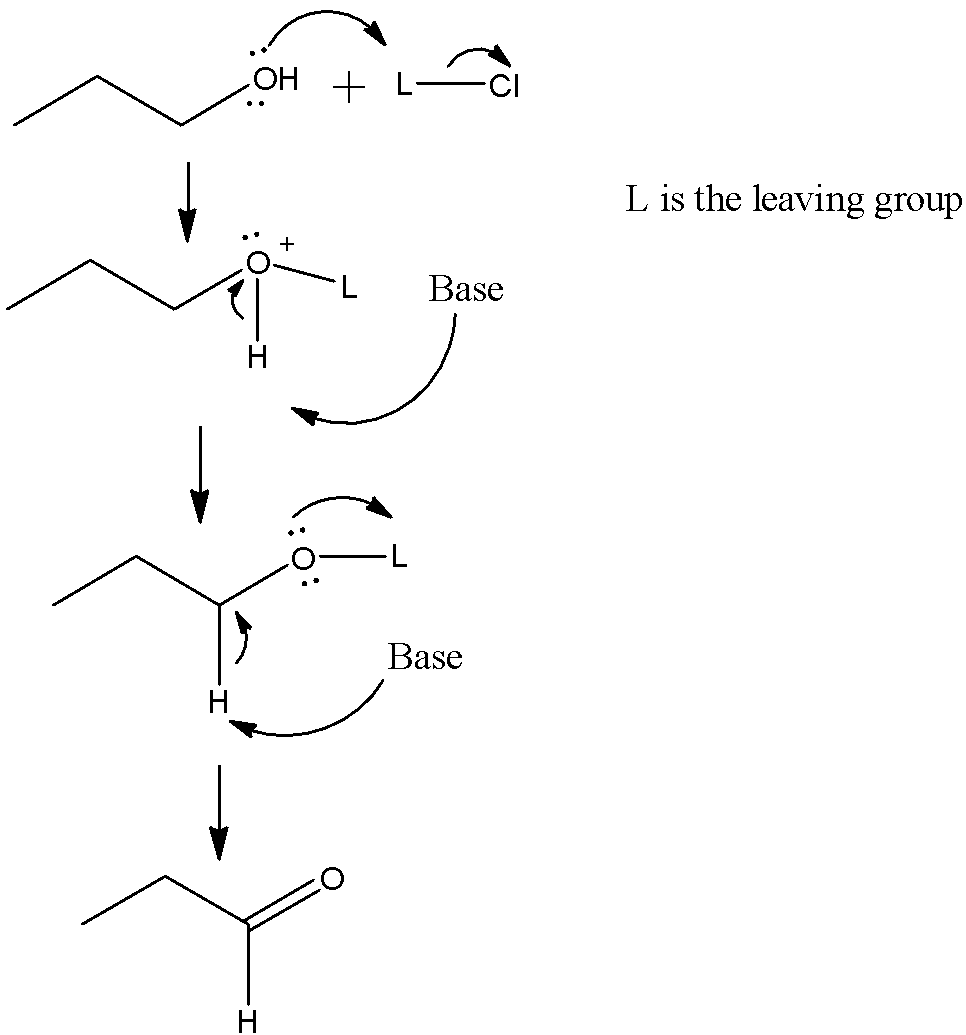
The formula of ethanol is $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$ and the formula of acetaldehyde is $C{{H}_{3}}CHO$. From the formula, we can see that ethanol is getting oxidised to form the aldehyde. So, we can represent the reaction as:
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH\xrightarrow{PCC}C{{H}_{3}}CHO(oxidation)\]
Here, the oxidising agent used in pyridinium chlorochromate. So, as it is getting oxidised,
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Aldehydes formed are prone to further oxidation and form carboxylic acid. To prevent this aldehydes are distilled off as soon as possible. Whereas ketones cannot be oxidised further easily, hence their yield is quite high in the reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
In order to answer this question, we need to learn how reactions occur in aldehydes and ketones and structure of carbonyl groups. In order to solve this question, we need to learn about aldol condensation reactions. Carbon atom of the carbonyl group is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised having triangular planar geometry. Carbon atoms form three sigma bonds and one n(pi) bond, out of which 3 sigma bonds are located in the same plane whereas the fourth it bond, which is formed by lateral or sideways overlapping, is situated above and below the plane. Bond angles are approximately ${{120}^{0}}$.Carbonyl group is polarised due to difference in electronegativity between carbon and oxygen. Oxygen being more electronegative pulls the shared pair of electrons more towards itself making oxygen as a nucleophilic centre and carbon as an electrophilic centre. Hence carbonyl compounds have substantial dipole moments and their polarity can be expressed on the basis of resonance.
Let us see the mechanism of PCC oxidation, we have used propanol instead of ethanol for better clarity:

The formula of ethanol is $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$ and the formula of acetaldehyde is $C{{H}_{3}}CHO$. From the formula, we can see that ethanol is getting oxidised to form the aldehyde. So, we can represent the reaction as:
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH\xrightarrow{PCC}C{{H}_{3}}CHO(oxidation)\]
Here, the oxidising agent used in pyridinium chlorochromate. So, as it is getting oxidised,
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Aldehydes formed are prone to further oxidation and form carboxylic acid. To prevent this aldehydes are distilled off as soon as possible. Whereas ketones cannot be oxidised further easily, hence their yield is quite high in the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




