
Consider the reactions given below and identify A and B:
${\text{A}}\xleftarrow[{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}}}]{{{\text{B}}{{\text{D}}_3}/{\text{THF}}}}$Pentene$\xrightarrow[{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOD}}}]{{{\text{B}}{{\text{D}}_3}/{\text{THF}}}}{\text{B}}$
A. ${\text{A = }}$
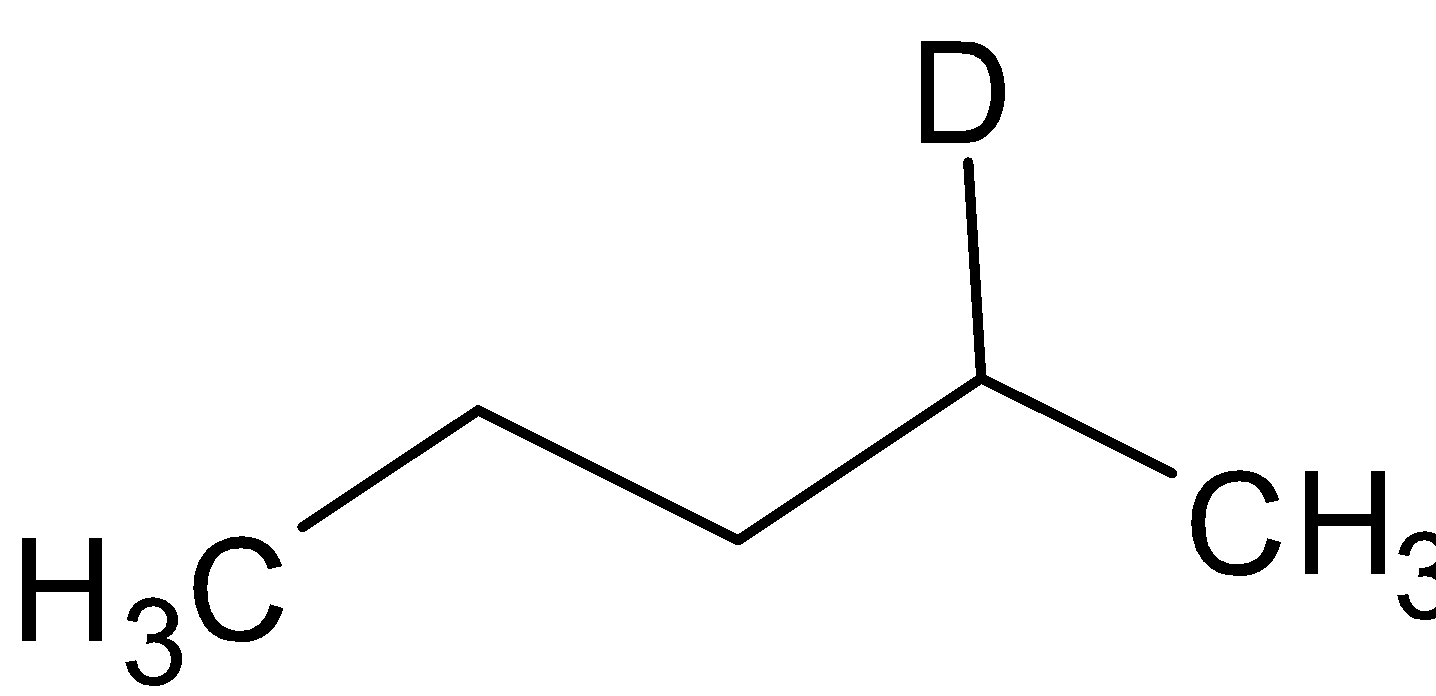 ${\text{B}} = $
${\text{B}} = $
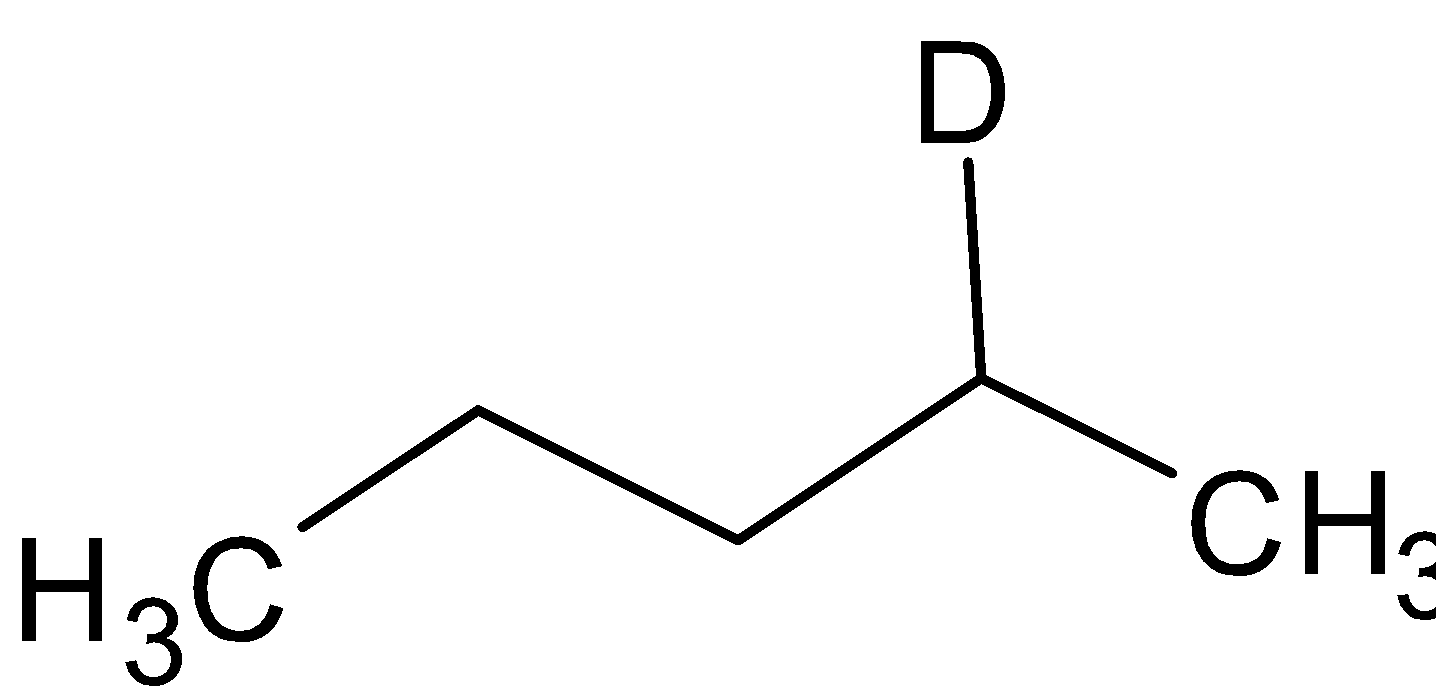
B. ${\text{A = }}$
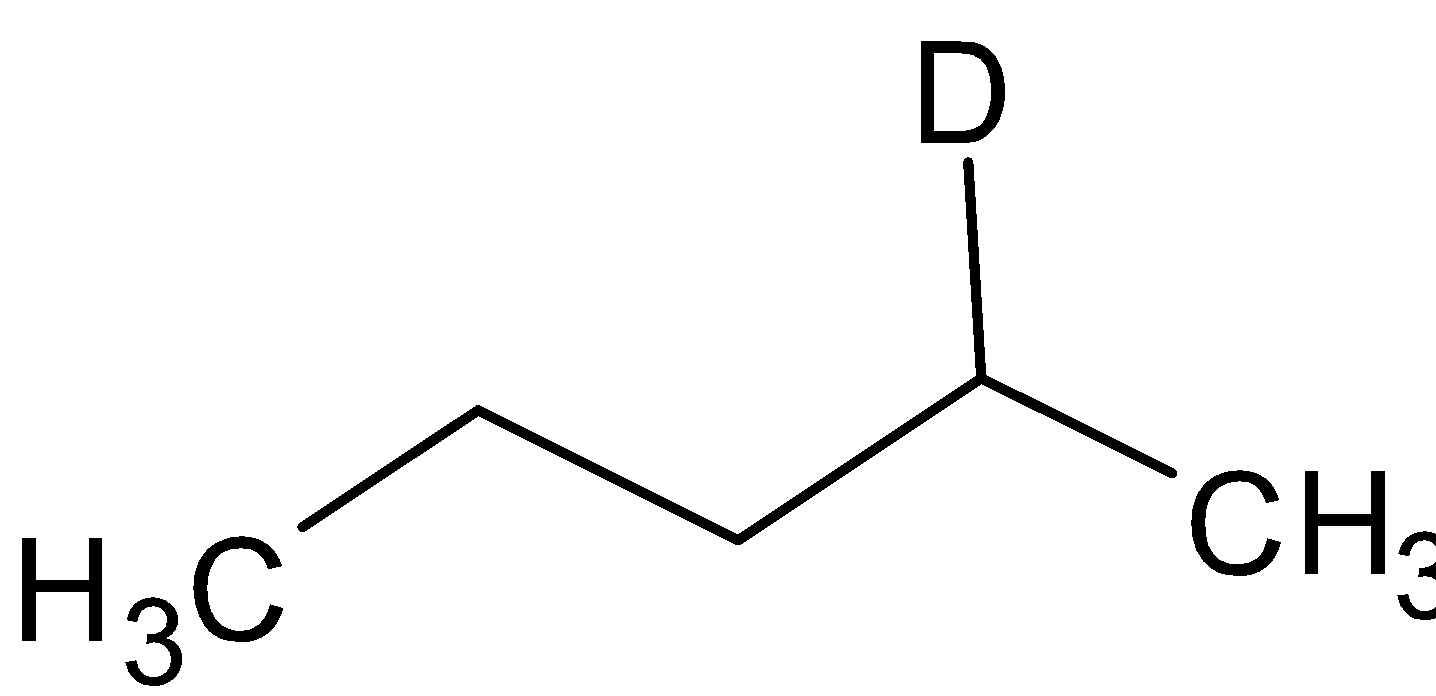 ${\text{B}} = $
${\text{B}} = $
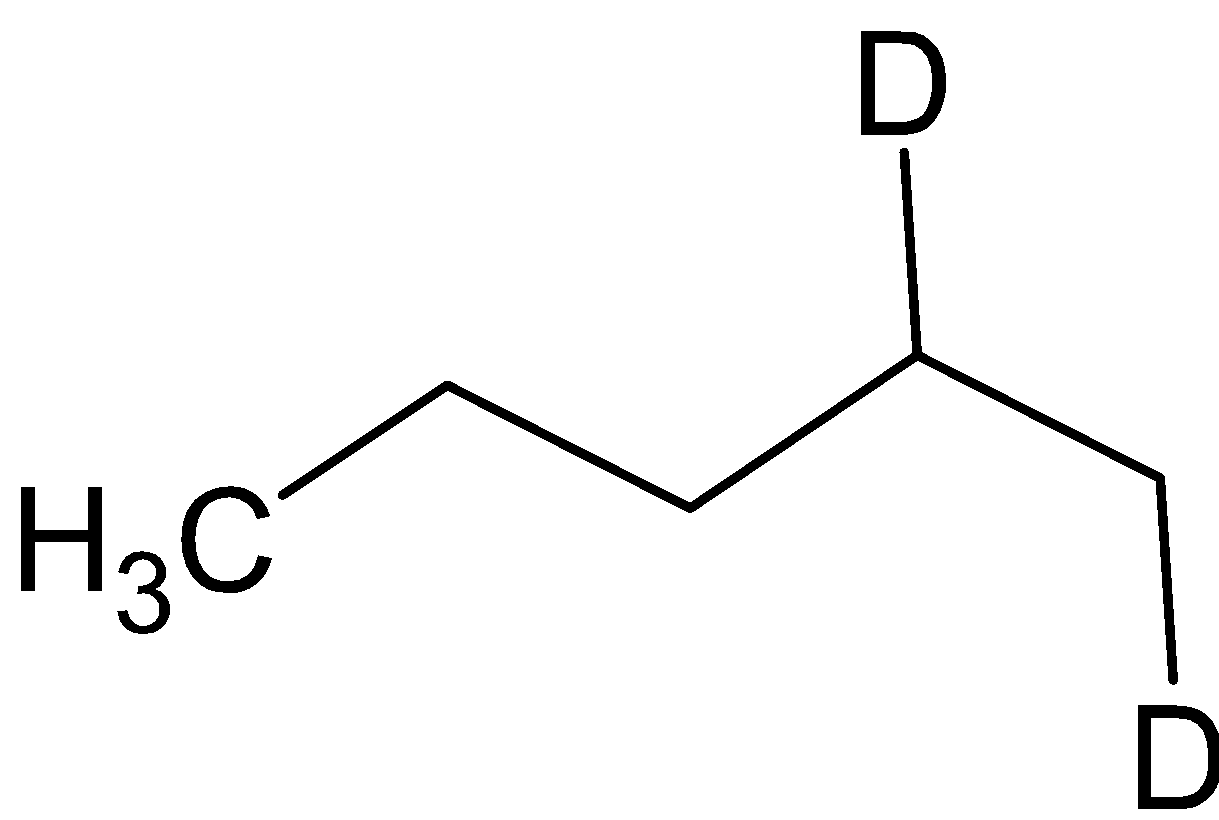
C. ${\text{A = }}$
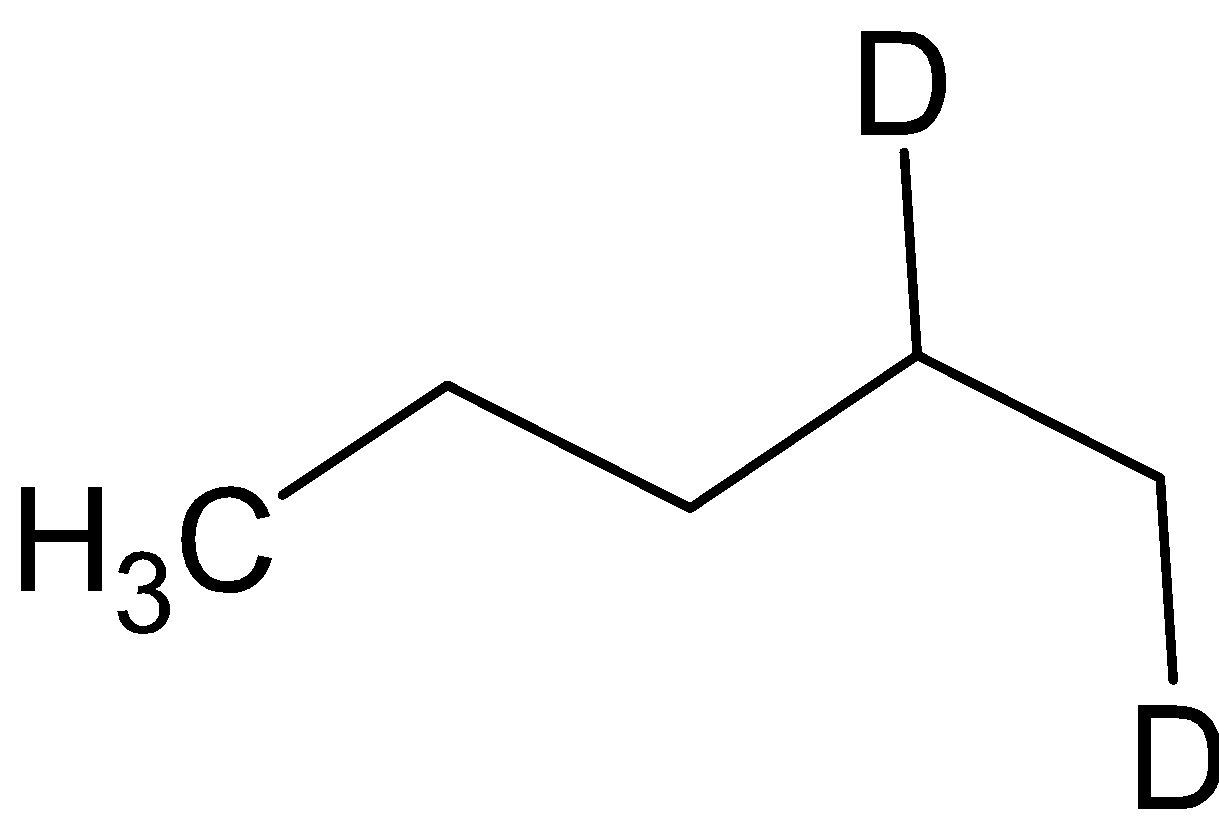 ${\text{B}} = $
${\text{B}} = $
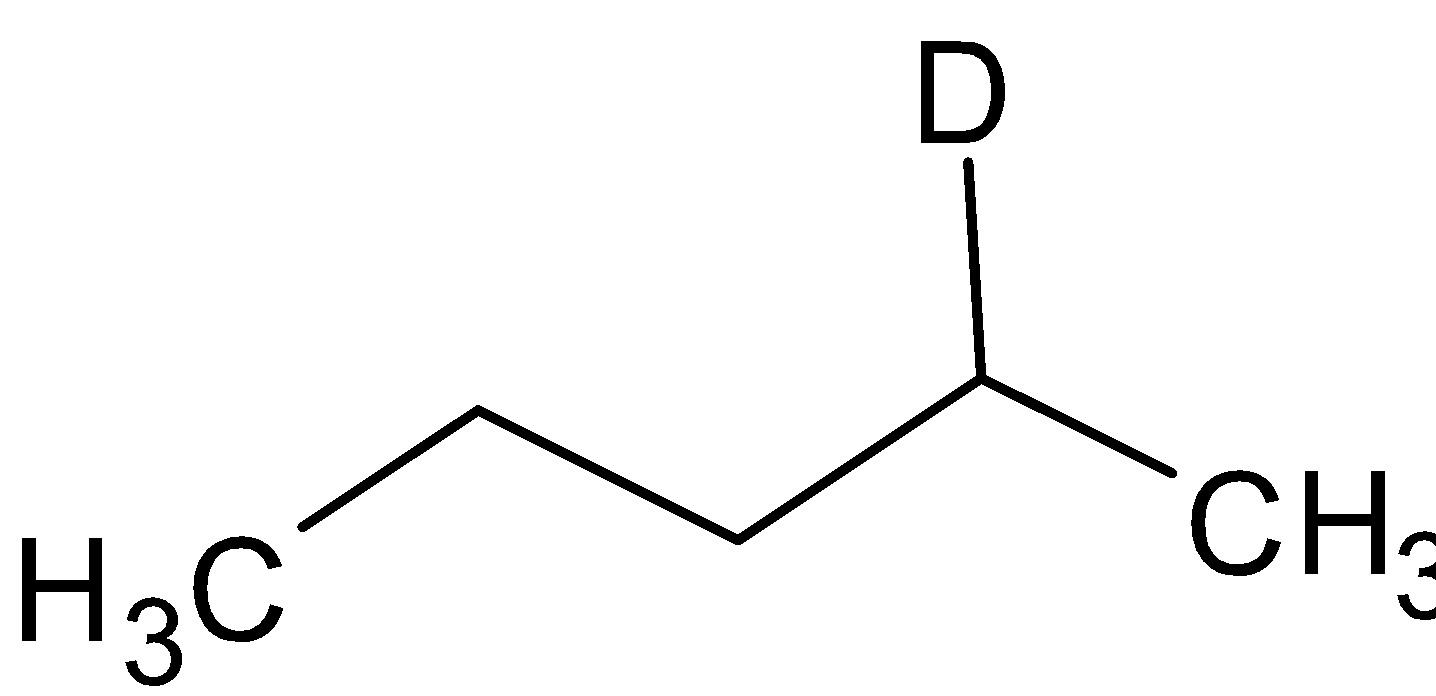
D. ${\text{A = }}$
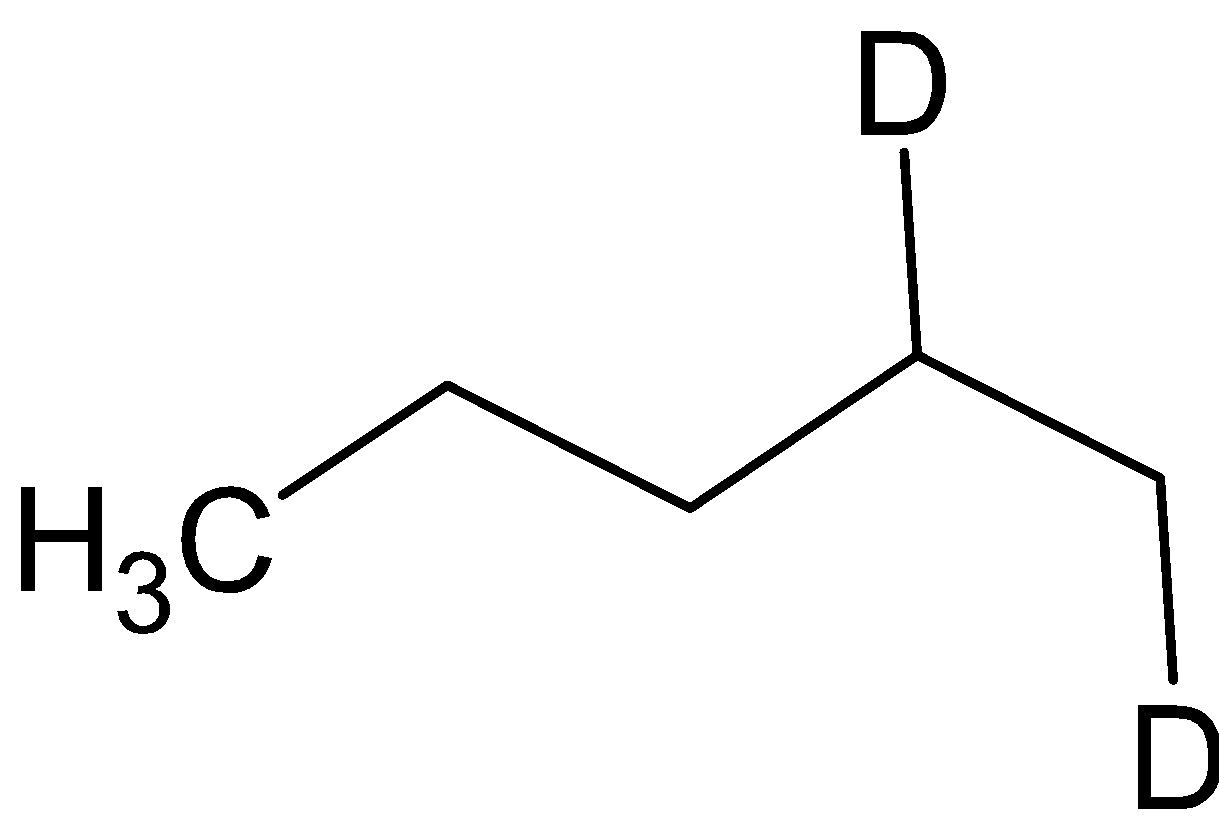 ${\text{B}} = $
${\text{B}} = $
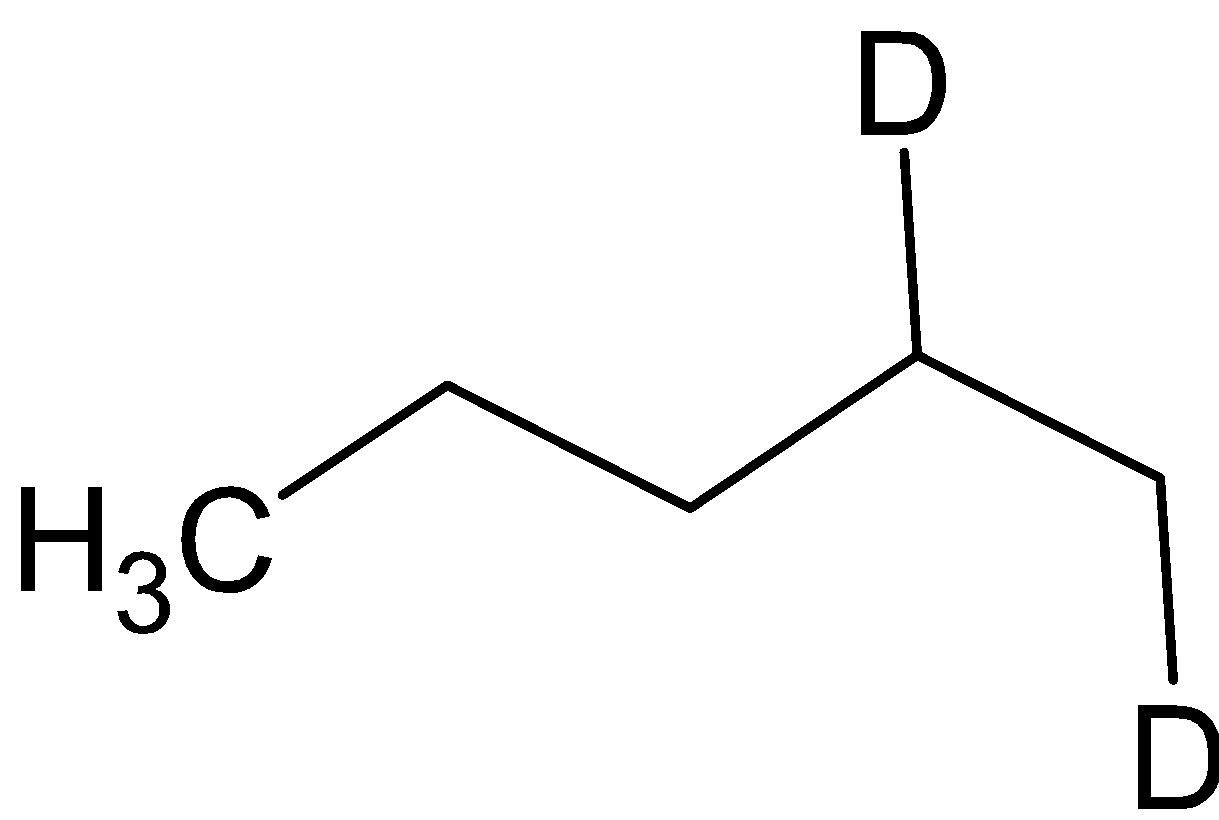








Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: Borane dissolved in THF undergoes additional reactions rapidly with most alkenes. This reaction is called hydroboration. Hydroboration produces an organoborane. This is a very useful intermediate in organic synthesis.
Complete step by step answer:
Alkenes are also called olefins. They contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. In such compounds, carbon is ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$ hybridized.
One of the major reactions of alkenes is hydroboration reaction. It is the addition of hydrogen-boron bonds to carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-oxygen double bonds, as well as triple bonds. This chemical reaction is used for organic synthesis of compounds.
Here, instead of ${\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_3}$, ${\text{B}}{{\text{D}}_3}$is used. Hydrogen is substituted with deuterium. Generally they are Lewis acid since they are electron deficient. Borane is added to alkene to give organoborane. The reaction is given below:
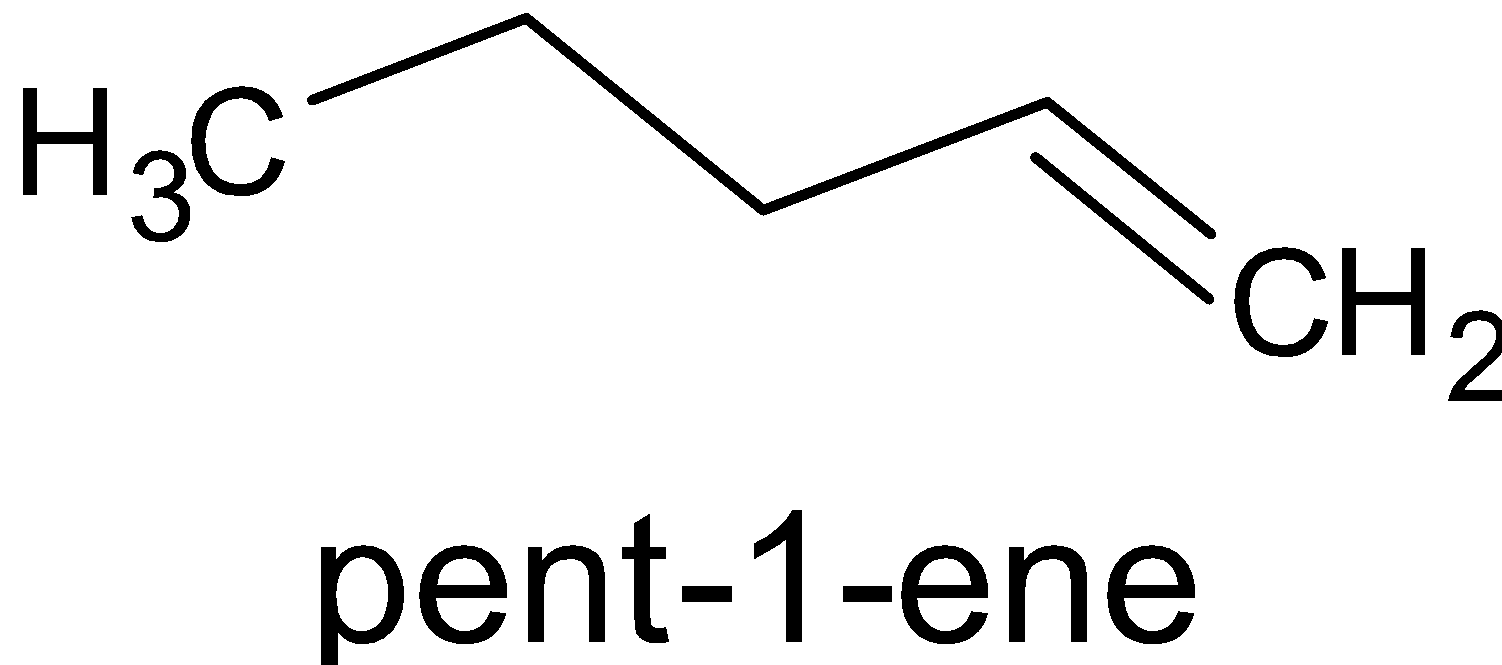 $\xrightarrow{{{\text{B}}{{\text{D}}_3}/{\text{THF}}}}$
$\xrightarrow{{{\text{B}}{{\text{D}}_3}/{\text{THF}}}}$
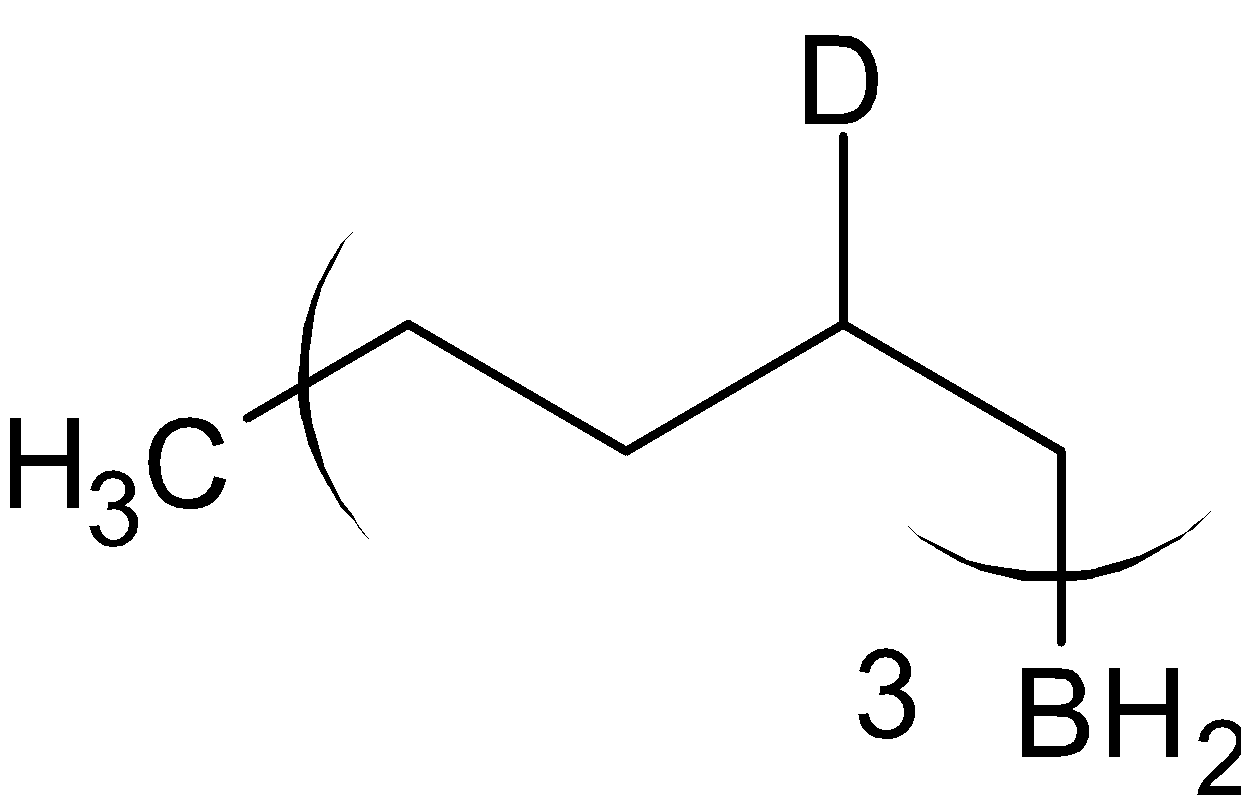
The product formed is called organoborane. This is now divided into two reactions, with acetic acid, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}}$ and with deuterated acetic acid, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOD}}$ .
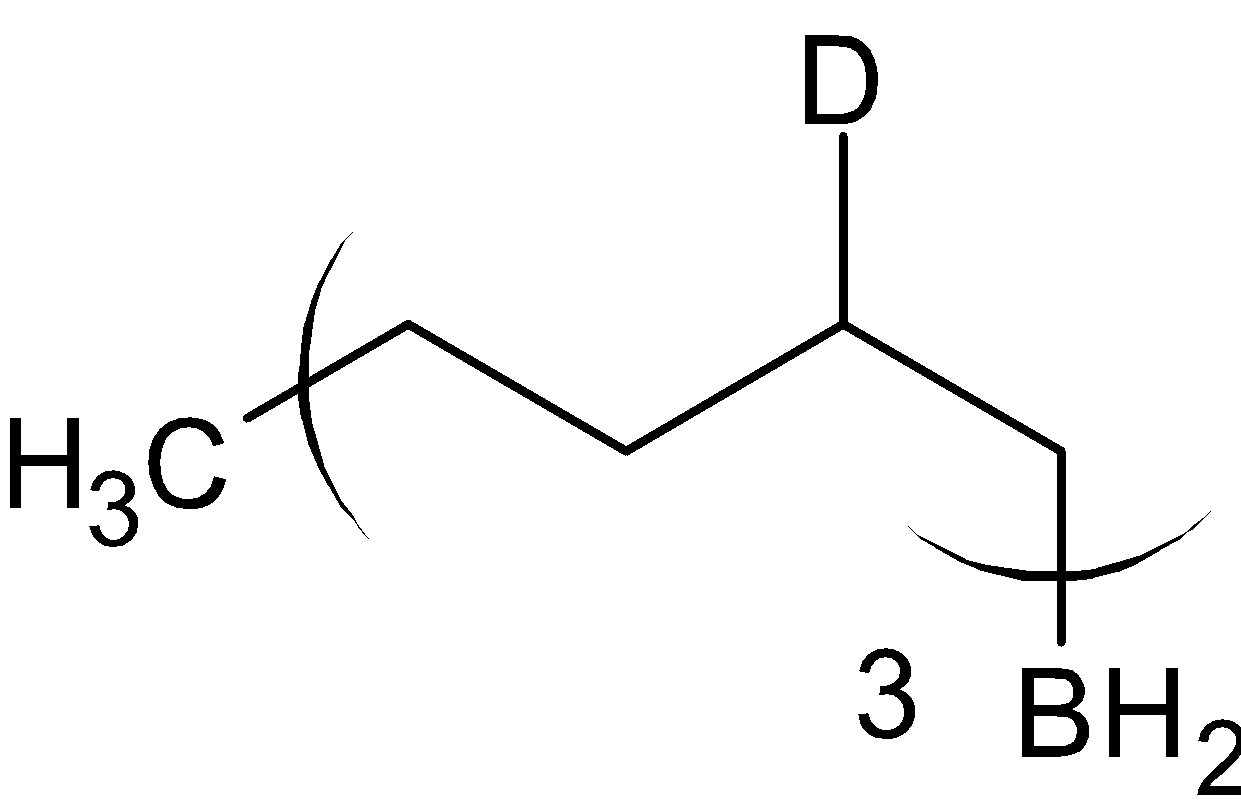
When organoborane is reacted with acetic acid, it substitutes borane with methyl group from acetic acid. When the organoboron is reacted with deuterated acetic acid, deuterium is substituted in the place of borane. The reaction is given below:
 $\xrightarrow{{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}}}}$
$\xrightarrow{{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}}}}$
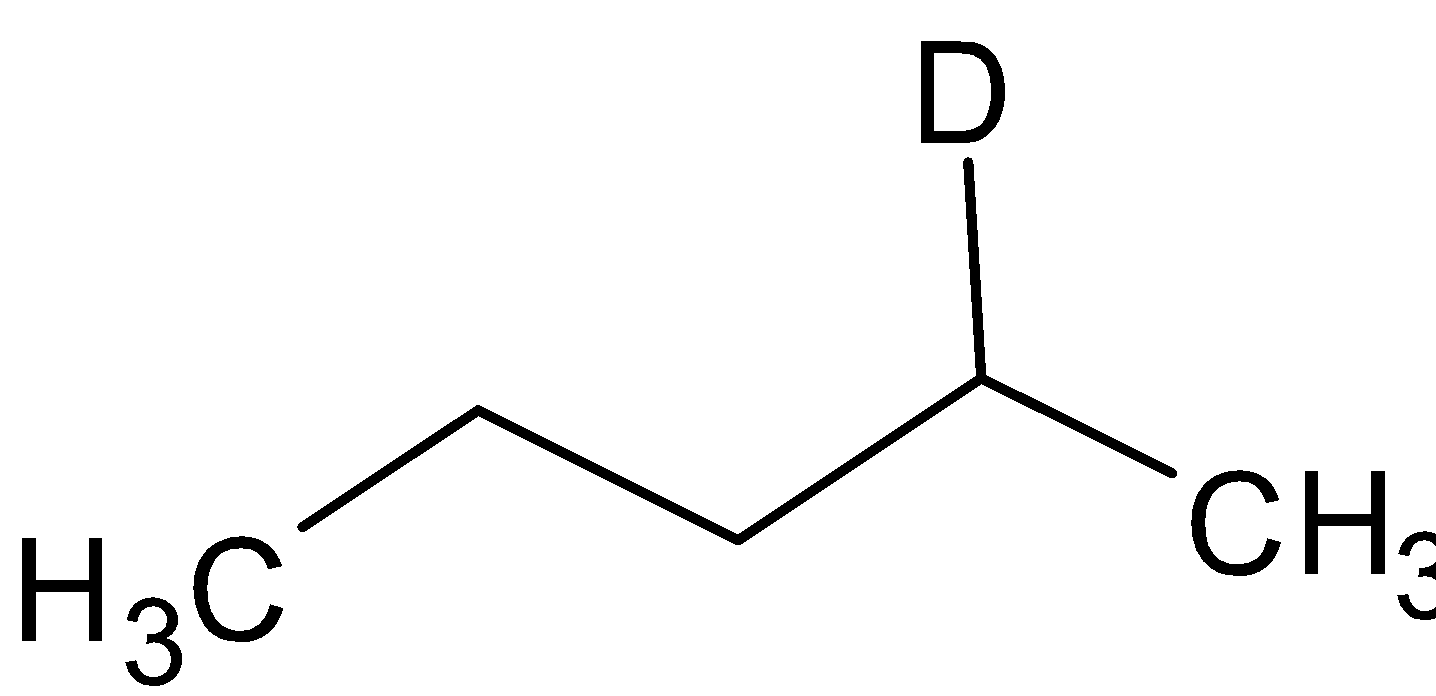
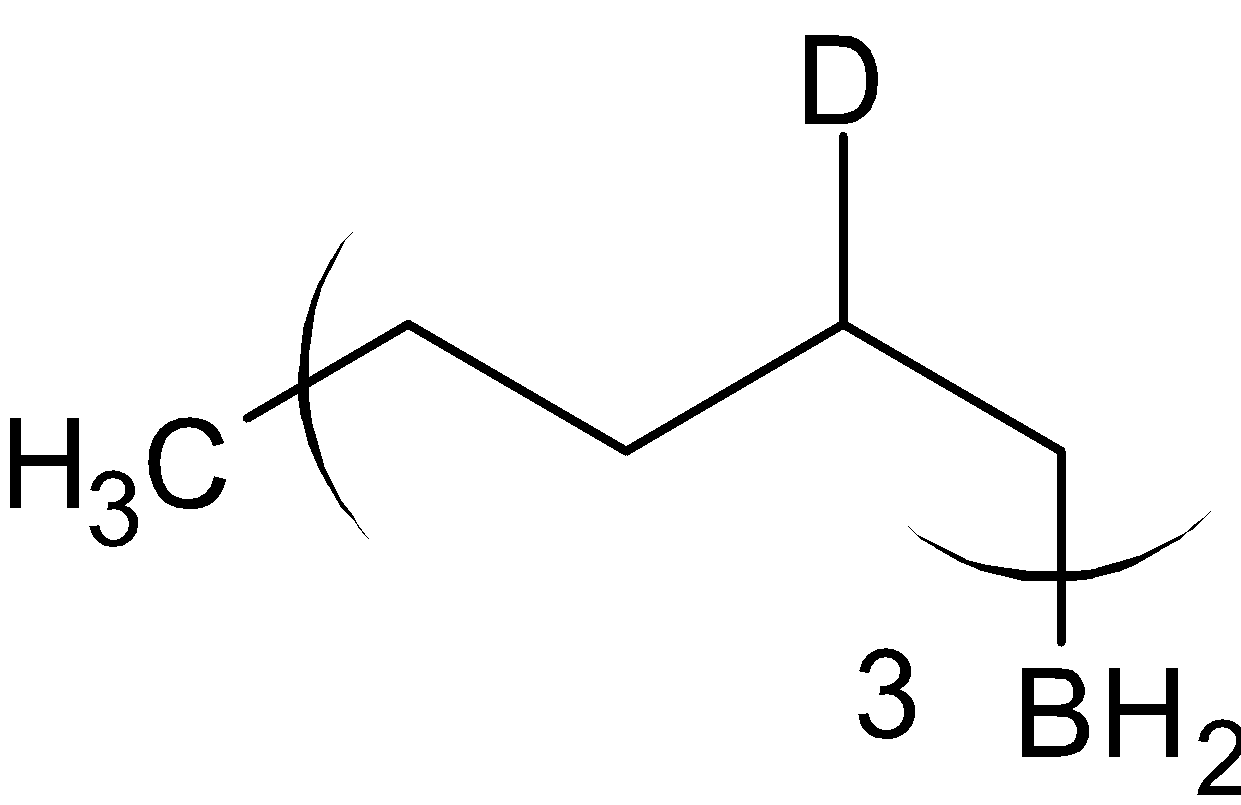 $\xrightarrow{{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOD}}}}$
$\xrightarrow{{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOD}}}}$
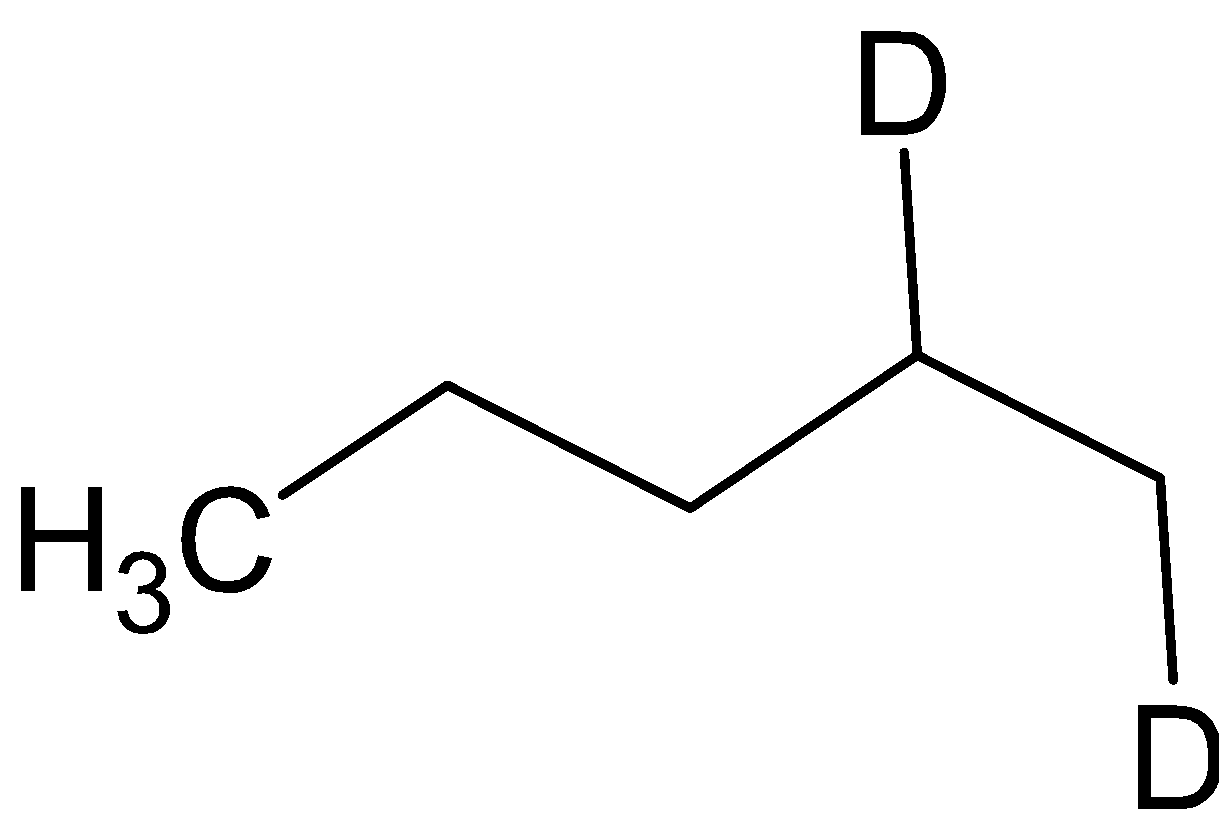
Thus the compound A is
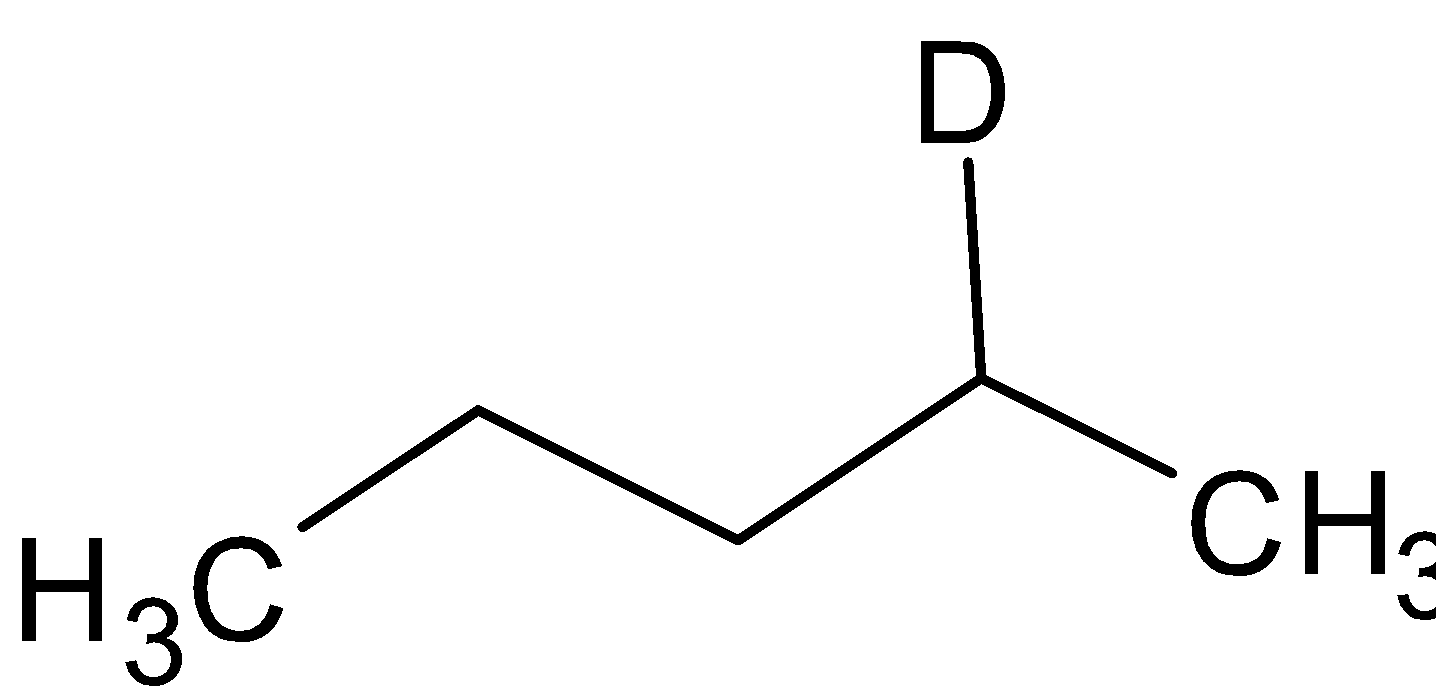 and the compound B is
and the compound B is
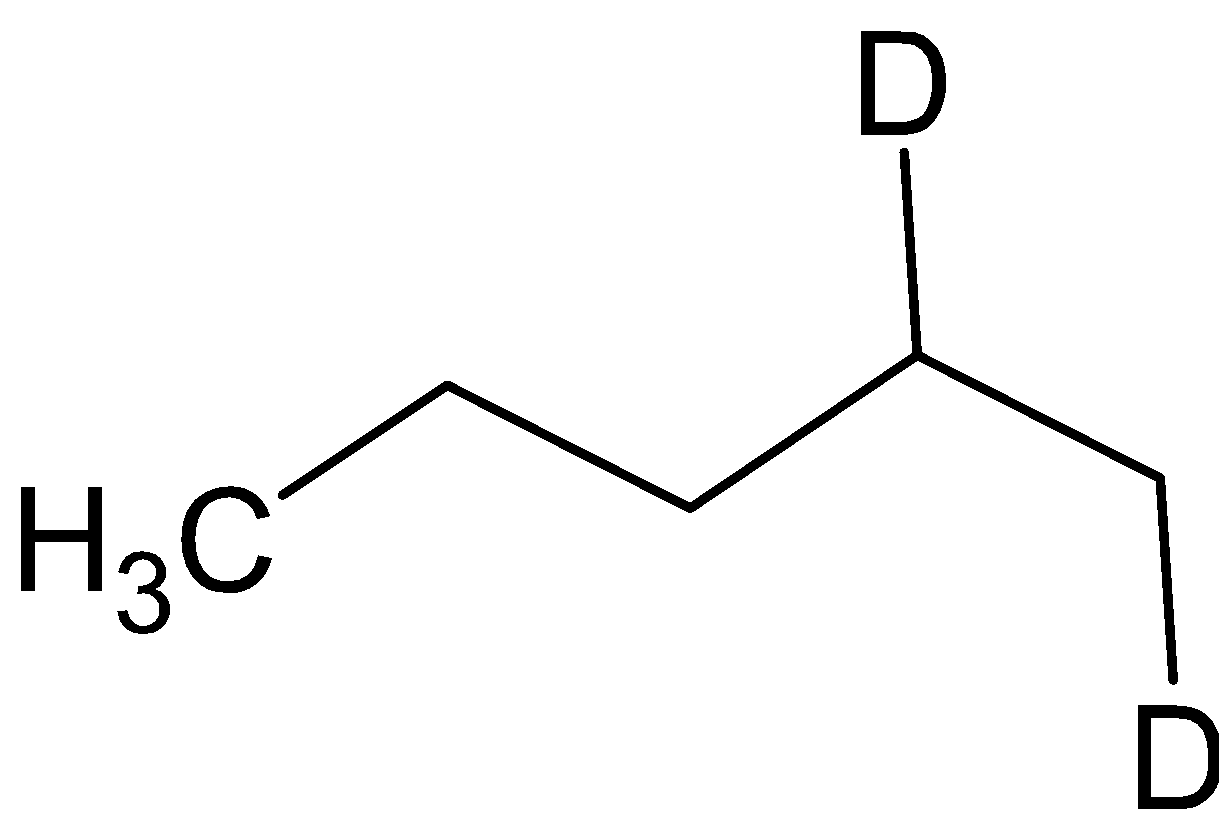
Hence option B is correct.
Additional information:
${\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_3}.{\text{THF}}$ is the most commonly used form of borane. Hydroboration steps add the hydrogen and the boron to the same side of the double bond.
Note:
Deuterated borane adds to the double bond in a single step, with boron adding to the less substituted carbon and hydrogen adding to the more highly substituted carbon. This orientation places the partial positive charge in the transition state on the more highly substituted carbon atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Alkenes are also called olefins. They contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. In such compounds, carbon is ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$ hybridized.
One of the major reactions of alkenes is hydroboration reaction. It is the addition of hydrogen-boron bonds to carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-oxygen double bonds, as well as triple bonds. This chemical reaction is used for organic synthesis of compounds.
Here, instead of ${\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_3}$, ${\text{B}}{{\text{D}}_3}$is used. Hydrogen is substituted with deuterium. Generally they are Lewis acid since they are electron deficient. Borane is added to alkene to give organoborane. The reaction is given below:


The product formed is called organoborane. This is now divided into two reactions, with acetic acid, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}}$ and with deuterated acetic acid, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOD}}$ .
When organoborane is reacted with acetic acid, it substitutes borane with methyl group from acetic acid. When the organoboron is reacted with deuterated acetic acid, deuterium is substituted in the place of borane. The reaction is given below:




Thus the compound A is


Hence option B is correct.
Additional information:
${\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_3}.{\text{THF}}$ is the most commonly used form of borane. Hydroboration steps add the hydrogen and the boron to the same side of the double bond.
Note:
Deuterated borane adds to the double bond in a single step, with boron adding to the less substituted carbon and hydrogen adding to the more highly substituted carbon. This orientation places the partial positive charge in the transition state on the more highly substituted carbon atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




