
Consider the reaction,\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Br + NaCN }} \to {\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CN + NaBr }}\].
This reaction will be the fastest in:
A. N,N’-dimethylformamide(DMF)
B. Water
C. ethanol
D. methanol
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint:The given reaction is a nucleophilic substitution \[{\text{(S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{)}}\] reaction. The rate of nucleophilic substitution reaction depends on the solvent. Nucleophilic substitution reactions are favourable in a polar aprotic solvent.
Complete answer:
The reaction given to us is:
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Br + NaCN }} \to {\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CN + NaBr }}\]
Here we can see that there is a substitution of the bromide group by the cyanide group. Since given alkyl halide is primary alkyl halide so we can say that it is \[{\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\] a reaction. The rate of nucleophilic substitution reaction depends on the solvent. As we know there are two types of solvents.
1. Polar protic solvent
2. Polar aprotic solvent.
Now, we will determine the type of solvent given to us as follows:
A. The structure of N,N-dimethylformamide(DMF) is :
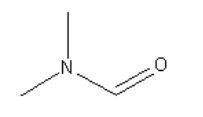
So, DMF is a polar aprotic solvent as the hydrogen atom is not bonded to electronegative nitrogen and oxygen atoms.
B. The structure of water is
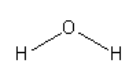
So, water is a polar protic solvent.
C. The structure of ethanol is

So, ethanol is a polar protic solvent.
D. The structure of methanol is
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ - OH}}\]
So, methanol is a polar protic solvent.
Polar protic solvent tends to form a hydrogen bond with a nucleophile and hinder the attack of the nucleophile. While the polar aprotic solvent does not form a hydrogen bond with a nucleophile. Thus, the polar aprotic solvent does not hinder the nucleophile so the rate of nucleophilic substitution is faster in the polar aprotic solvent.
Out of the given solvent to us only of N,N’-dimethylformamide(DMF) is polar aprotic solvent rest all (water, ethanol and methanol) are polar protic solvent. So, the given reaction is fastest in N,N’-dimethylformamide(DMF).
Thus, the correct option is (A) of N, N’-dimethylformamide (DMF).
Note:
In \[{\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\] reaction attack of nucleophiles is the rate-determining step. So the solvent that favours the attack of nucleophile is the favourable solvent. As polar aprotic solvent is a non-hindering solvent it speeds up the reaction.
Complete answer:
The reaction given to us is:
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Br + NaCN }} \to {\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CN + NaBr }}\]
Here we can see that there is a substitution of the bromide group by the cyanide group. Since given alkyl halide is primary alkyl halide so we can say that it is \[{\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\] a reaction. The rate of nucleophilic substitution reaction depends on the solvent. As we know there are two types of solvents.
1. Polar protic solvent
2. Polar aprotic solvent.
Now, we will determine the type of solvent given to us as follows:
A. The structure of N,N-dimethylformamide(DMF) is :

So, DMF is a polar aprotic solvent as the hydrogen atom is not bonded to electronegative nitrogen and oxygen atoms.
B. The structure of water is

So, water is a polar protic solvent.
C. The structure of ethanol is

So, ethanol is a polar protic solvent.
D. The structure of methanol is
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ - OH}}\]
So, methanol is a polar protic solvent.
Polar protic solvent tends to form a hydrogen bond with a nucleophile and hinder the attack of the nucleophile. While the polar aprotic solvent does not form a hydrogen bond with a nucleophile. Thus, the polar aprotic solvent does not hinder the nucleophile so the rate of nucleophilic substitution is faster in the polar aprotic solvent.
Out of the given solvent to us only of N,N’-dimethylformamide(DMF) is polar aprotic solvent rest all (water, ethanol and methanol) are polar protic solvent. So, the given reaction is fastest in N,N’-dimethylformamide(DMF).
Thus, the correct option is (A) of N, N’-dimethylformamide (DMF).
Note:
In \[{\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\] reaction attack of nucleophiles is the rate-determining step. So the solvent that favours the attack of nucleophile is the favourable solvent. As polar aprotic solvent is a non-hindering solvent it speeds up the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




