
Consider the following reactions:
‘A’ is:
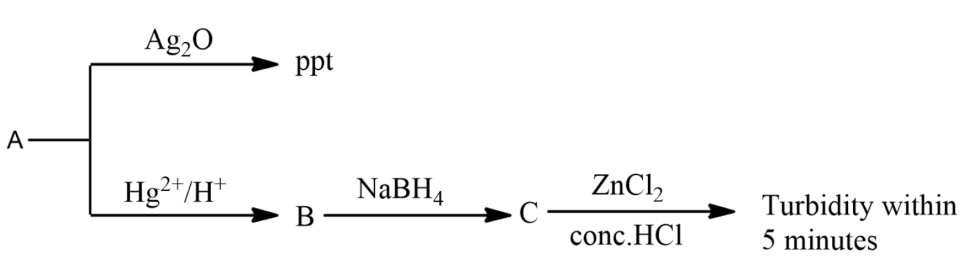
(A)- $CH\equiv CH$
(B)- $C{{H}_{2}}=C{{H}_{2}}$
(C)- $C{{H}_{3}}-C\equiv CH$
(D)- $C{{H}_{3}}-C\equiv C-C{{H}_{3}}$

Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint:. To give a positive test with tollen’s reagent, the compound must have terminal hydrogen which will react with tollen’s reagent forming a precipitate. Secondly, compound A must be a compound which on hydration gives compound B. The compound B on further reduction by sodium tetrahydridoborate or sodium borohydride gives secondary alcohol which will give turbidity within 5 min when reacted with $ZnC{{l}_{2}}+conc.HCl$.
Complete step by step answer:
-Tollen’s reagent is used basically for the presence of a carbonyl group, which can be of an aldehyde or ketone.
-Tollen’s reagent is also used to test for terminal alkynes $(R{{C}_{2}}H)$ . Compound with terminal alkynes confirms with tollen’s reagent by forming a white precipitate of acetylide $(Ag{{C}_{2}}R)$.
-So let us now consider the options given to us and the compound which fulfils all these conditions will be the compound A.
-Ethane in option B has terminal hydrogen but the hydration of alkyne gives alcohols and alcohols cannot be reduced by sodium borohydride.
-Ethyne in option A has terminal hydrogen to react with tollen’s reagent but on hydration, it gives aldehydes which on reduction gives primary alcohol. For turbidity to appear within 5 minutes, the compound must be a secondary carbon which will react with $ZnC{{l}_{2}}/conc.HCl$.
-Propyne in option C have terminal hydrogen to react with tollen’s reagent and on hydration is converted to alcohol, which is compound B. Compound B on reduction with sodium borohydride gives secondary alcohol, which is compound C. This compound C on further reaction with $ZnC{{l}_{2}}/conc.HCl$ gives turbidity.
-Butylene in option D does not have terminal hydrogen.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: A solution of zinc chloride in concentrated hydrochloric acid is known as Lucas reagent. This solution is used to distinguish alcohols of low molecular weight. This reaction is a substitution reaction in which chloride ion of zinc chloride replaces a hydroxyl group.
Complete step by step answer:
-Tollen’s reagent is used basically for the presence of a carbonyl group, which can be of an aldehyde or ketone.
-Tollen’s reagent is also used to test for terminal alkynes $(R{{C}_{2}}H)$ . Compound with terminal alkynes confirms with tollen’s reagent by forming a white precipitate of acetylide $(Ag{{C}_{2}}R)$.
-So let us now consider the options given to us and the compound which fulfils all these conditions will be the compound A.
-Ethane in option B has terminal hydrogen but the hydration of alkyne gives alcohols and alcohols cannot be reduced by sodium borohydride.
-Ethyne in option A has terminal hydrogen to react with tollen’s reagent but on hydration, it gives aldehydes which on reduction gives primary alcohol. For turbidity to appear within 5 minutes, the compound must be a secondary carbon which will react with $ZnC{{l}_{2}}/conc.HCl$.
-Propyne in option C have terminal hydrogen to react with tollen’s reagent and on hydration is converted to alcohol, which is compound B. Compound B on reduction with sodium borohydride gives secondary alcohol, which is compound C. This compound C on further reaction with $ZnC{{l}_{2}}/conc.HCl$ gives turbidity.
-Butylene in option D does not have terminal hydrogen.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: A solution of zinc chloride in concentrated hydrochloric acid is known as Lucas reagent. This solution is used to distinguish alcohols of low molecular weight. This reaction is a substitution reaction in which chloride ion of zinc chloride replaces a hydroxyl group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




