
Consider an electric dipole, with $q$ as the magnitude of its charges and $p$ as its dipole moment, placed in a uniform electric field $E$. If its dipole moment is along the field direction then find the net force on it and its potential energy.
A) Force is $qE$ and potential energy is $p.E$ .
B) Force is zero and potential energy is minimum.
C) Force is $qE$ and potential energy is maximum.
D) Force is $2qE$ and potential energy is minimum.
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: An electric dipole constitutes a pair of equal and opposite charges separated by a distance of $2a$ . The dipole moment is said to be along the direction of the field. This makes the angle between the electric field and the dipole moment to be $\theta = 0^\circ $.
Formula used:
The force acting on a charge $q$ placed in a uniform electric field $E$ is given by, $F = qE$.
The potential energy $U$ of the electric dipole is given by, $U = - p.E$, where $p$ is its dipole moment and $E$ is the electric field.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Sketching a figure representing the electric dipole in a uniform electric field and find the net force acting on the electric dipole.
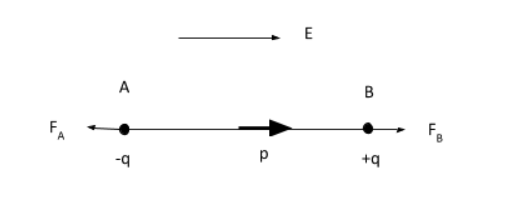
Two charges $ - q$and $q$ are placed at points A and B respectively in a uniform electric field $E$.
We know the force acting on a charge $q$ placed in a uniform electric field $E$ is given by, $F = qE$.
Then at A, the force acting on charge $ - q$ will be, ${F_A} = - qE$ .
At B, the force acting on charge $q$ will be, ${F_B} = qE$ .
Then the net force will be $F = \left( { - qE} \right) + qE = 0$ .
Therefore, the net force on the electric dipole will be zero.
Step 2: Expressing the relation for the potential energy of the dipole.
The potential energy $U$ of an electric dipole is defined as the dot product of its dipole moment $p$ and uniform electric field $E$ ie., $U = - p.E$ or, $U = - pE\cos \theta $ where $\theta $ is the angle between the dipole moment and the electric field.
Here, the dipole moment is along the direction of the electric field. So $\theta = 0^\circ $ and $\cos 0 = 1$.
Then the potential energy will be $U = - pE\cos \theta = - pE$ which is the minimum value of the potential energy.
Therefore, the potential energy of the electric dipole placed in a uniform electric field is minimum. Hence, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:
The value of the potential energy of an electric dipole placed in a uniform electric field ranges from $ - pE$ to $pE$ as the angle $\theta $ between the dipole moment and electric field varies from $0^\circ $ to $180^\circ $.
For $\theta = 0^\circ $ , we have $\cos \theta = 1$and $U = - pE$ as the minimum potential energy.
For $\theta = 180^\circ $, we have $\cos \theta = - 1$ and $U = pE$ as the maximum potential energy.
Formula used:
The force acting on a charge $q$ placed in a uniform electric field $E$ is given by, $F = qE$.
The potential energy $U$ of the electric dipole is given by, $U = - p.E$, where $p$ is its dipole moment and $E$ is the electric field.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Sketching a figure representing the electric dipole in a uniform electric field and find the net force acting on the electric dipole.

Two charges $ - q$and $q$ are placed at points A and B respectively in a uniform electric field $E$.
We know the force acting on a charge $q$ placed in a uniform electric field $E$ is given by, $F = qE$.
Then at A, the force acting on charge $ - q$ will be, ${F_A} = - qE$ .
At B, the force acting on charge $q$ will be, ${F_B} = qE$ .
Then the net force will be $F = \left( { - qE} \right) + qE = 0$ .
Therefore, the net force on the electric dipole will be zero.
Step 2: Expressing the relation for the potential energy of the dipole.
The potential energy $U$ of an electric dipole is defined as the dot product of its dipole moment $p$ and uniform electric field $E$ ie., $U = - p.E$ or, $U = - pE\cos \theta $ where $\theta $ is the angle between the dipole moment and the electric field.
Here, the dipole moment is along the direction of the electric field. So $\theta = 0^\circ $ and $\cos 0 = 1$.
Then the potential energy will be $U = - pE\cos \theta = - pE$ which is the minimum value of the potential energy.
Therefore, the potential energy of the electric dipole placed in a uniform electric field is minimum. Hence, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:
The value of the potential energy of an electric dipole placed in a uniform electric field ranges from $ - pE$ to $pE$ as the angle $\theta $ between the dipole moment and electric field varies from $0^\circ $ to $180^\circ $.
For $\theta = 0^\circ $ , we have $\cos \theta = 1$and $U = - pE$ as the minimum potential energy.
For $\theta = 180^\circ $, we have $\cos \theta = - 1$ and $U = pE$ as the maximum potential energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




