
What is the conjugate base of \[{{H}_{2}}P{{O}_{4}}^{-}\]?
$\begin{align}
& a){{H}_{{}}}P{{O}_{4}}^{2-} \\
& b){{P}_{2}}{{O}_{5}} \\
& c){{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{4}} \\
& d)P{{O}_{4}}^{3-} \\
\end{align}$
Answer
604.5k+ views
Hint: A more general definition is that a conjugate base is the base member, X-, of a pair of compounds that transform into each other by gaining or losing a proton. The conjugate base is able to gain or absorb a proton in a chemical reaction.
Step-by-Step Solution:
To answer this question properly, we need to be very thorough with the Brønsted-Lowry conjugate acid-base theory.
An acid, by the Brønsted-Lowry definition, is a species which acts as a proton donor (i.e., it gives away an H+), while a base is a proton (H+) acceptor. One of the most familiar examples of a Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reaction is between hydrochloric acid and hydroxide ion:
In this reaction, a proton is transferred from HCl (the acid, or proton donor) to hydroxide ion (the base, or proton acceptor). As we learned in the previous chapter, curved arrows depict the movement of electrons in this bond-breaking and bond-forming process.
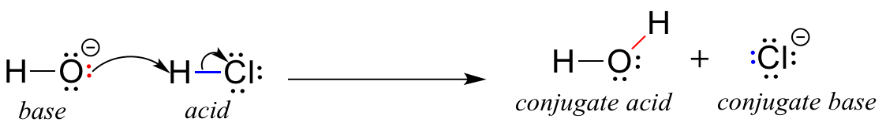
After a Brønsted-Lowry acid donates a proton, what remains is called the conjugate base. Chloride ion is thus the conjugate base of hydrochloric acid. Conversely, when a Brønsted-Lowry base accepts a proton it is converted into its conjugate acid form: water is thus the conjugate acid of hydroxide ion.
Therefore, by the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory, the answer to this question is a).
Note: While the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory is not as widely accepted as a valid acid-base theory as some of the others, it is the only one which deals with the ideas of conjugate acids and bases. This makes the study and thorough knowledge of the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory a necessity for any student of Chemistry.
Step-by-Step Solution:
To answer this question properly, we need to be very thorough with the Brønsted-Lowry conjugate acid-base theory.
An acid, by the Brønsted-Lowry definition, is a species which acts as a proton donor (i.e., it gives away an H+), while a base is a proton (H+) acceptor. One of the most familiar examples of a Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reaction is between hydrochloric acid and hydroxide ion:
In this reaction, a proton is transferred from HCl (the acid, or proton donor) to hydroxide ion (the base, or proton acceptor). As we learned in the previous chapter, curved arrows depict the movement of electrons in this bond-breaking and bond-forming process.

After a Brønsted-Lowry acid donates a proton, what remains is called the conjugate base. Chloride ion is thus the conjugate base of hydrochloric acid. Conversely, when a Brønsted-Lowry base accepts a proton it is converted into its conjugate acid form: water is thus the conjugate acid of hydroxide ion.
Therefore, by the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory, the answer to this question is a).
Note: While the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory is not as widely accepted as a valid acid-base theory as some of the others, it is the only one which deals with the ideas of conjugate acids and bases. This makes the study and thorough knowledge of the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory a necessity for any student of Chemistry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE

Calculate the equivalent resistance between a and b class 12 physics CBSE

How many states of matter are there in total class 12 chemistry CBSE

Which of the following is the best conductor of electricity class 12 physics CBSE




